© Sealevel Systems, Inc. 3420 Manual | SL9145 9/2022
“PAL” Addressing
If header E11 is set to the “PAL” position, the board can be addressed at a customized location. Using the
“PAL” option will allow you to obtain COM1: - COM4: addresses, XENIX COM: addresses, or any other
standard or nonstandard address configuration. Using the “PAL” feature is a very cost-effective means of
solving complex addressing problems. For more information on implementing the “PAL” option, please
contact Sealevel Systems Technical Support.
IRQ Selection
Each port on the COMM+8 has an interrupt jumper that may have to be set prior to use. The software you
are using with the board will determine which interrupts, if any are to be used. The DOS serial port interface
software does not use interrupts, while interrupt buffer programs do. DOS does not require the interrupt to
be set, while most Multi - User Operating Systems will. Consult the particular manual for the software that
you are using to determine the proper setting.
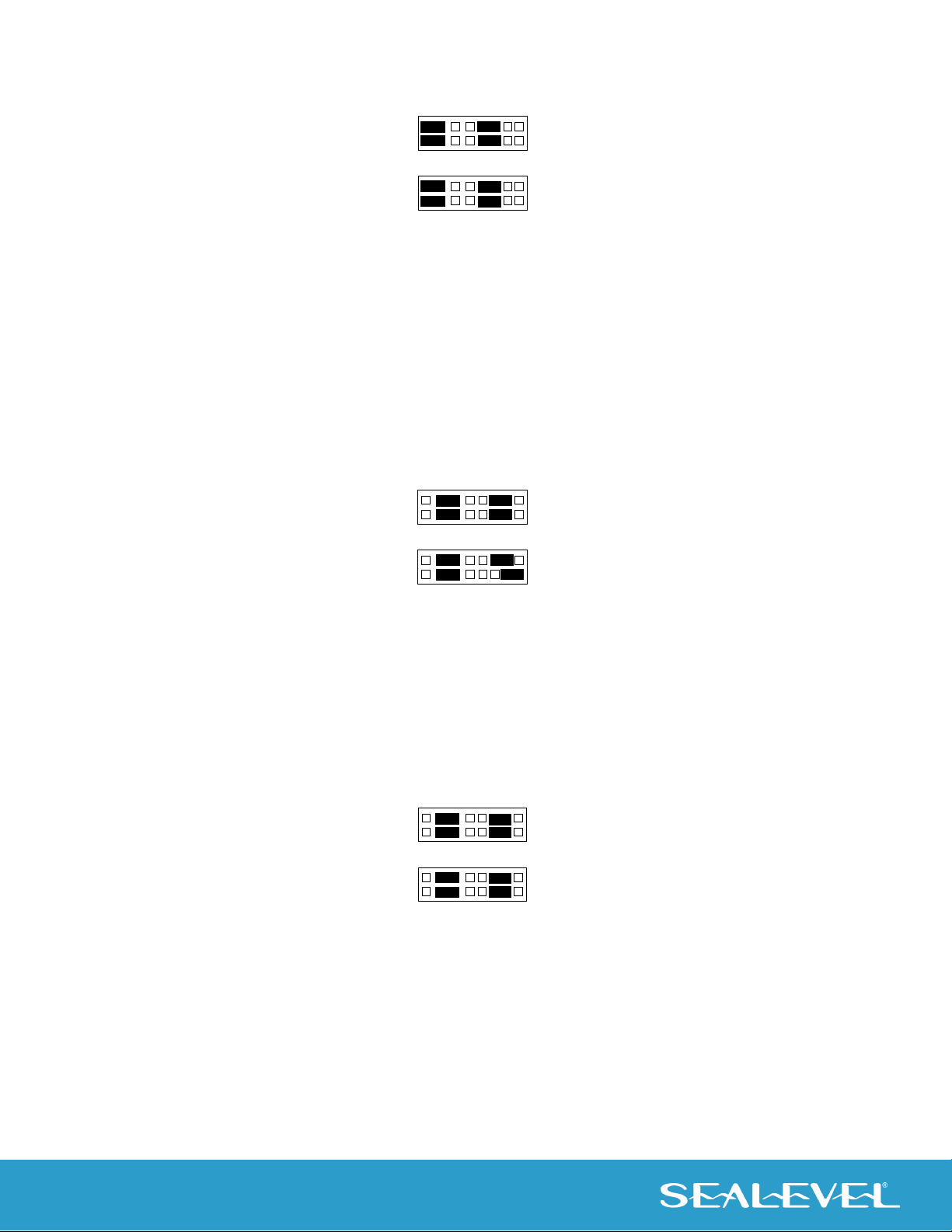
To set the interrupt for a particular port, first select the header for the port desired. Headers E1-E8
correspond to Ports 1-8. Next select an IRQ by placing one of the jumpers on the header location that
corresponds to the IRQ number that you wish to use. Below is an example of a selected IRQ.
Figure 3 - Headers E1 to E8 (IRQ15 selected)
Interrupt Mode Options
The COMM+8 will allow each port to have an independent interrupt level or share an interrupt with another
port on the adapter. The COMM+8 will even share interrupts with a compatible port that is located on
another adapter. The COMM+8 can operate in three interrupt modes. Header E9 determines the interrupt
mode for Ports 1-4 and header E10 determines the interrupt mode for ports 5-8.
“N” indicates the (N)ormal, single interrupt per port mode. “S” Indicates the (S)hared interrupt mode, which
allows more than one port to access a single IRQ. Any two or more ports can share a common IRQ by
placing the jumpers on the same IRQ setting and setting the appropriate selections at E1-E8. Consult your
particular software for IRQ selection. If no interrupt is desired, remove the jumper. “M” indicates the
inclusion of a 1K ohm pull-down resistor required on one port when sharing interrupts.