Sensata MS4024PAE User manual

MS-PAE Series
Pure Sine Wave Inverter/Charger
Owner’s Manual
© 2017 Sensata Technologies Page i
Record the MS-PAE’s model and serial number in case you need to provide this
information in the future.
Model: Serial Number:
MS4024PAE WAA or AA
MS4448PAE WAB or AB
Disclaimer of Liability
The use of this manual and the conditions or methods of installation, operation, use, and
maintenance of the MS-PAE Series inverter/charger is beyond the control of Sensata Technologies.
Therefore, this company assumes no responsibility and expressly disclaims any liability for loss,
damage, or expense whether direct, indirect, consequential, or incidental that may arise out of or
be in anyway connected with such installation, operation, use, or maintenance.
Due to continuous improvements and product updates, the images shown in this manual may not
exactly match the unit purchased.
Restrictions on Use
The MS-PAE Series inverter/charger may only be used in life support devices and systems with
the express written approval of Sensata Technologies. Failure of this inverter can reasonably be
expected to cause failure of that life support device or system, or to affect the safety or effectiveness
of that device or system. If the MS-PAE inverter fails, it is reasonable to assume the health of the
user or other persons may be endangered.
Copyright Notice
Copyright © 2017 by Sensata Technologies. All rights reserved. Permission to copy, distribute, and/
or modify this document is prohibited without express written permission from Sensata Technologies.
Document Information
Description – MS-PAE Owner’s Manual
Part Number and Revision – 64-0032 Rev C
Date Published – April 2017
This manual is printed without color for cost savings. The entire manual is available for download—
with many of the diagrams available in color—from our website at: www.SensataPower.com.
Contact Information
For Magnum Energy Products:
Sensata Technologies
Phone: 425-353-8833
Fax: 425-353-8390
Web: www.SensataPower.com
Statement of Appreciation
Thank you from all of us at Sensata Technologies for purchasing this MS-PAE inverter/charger. The
MS-PAE is a product under the Magnum Energy brand from Sensata Technologies. We understand
that you have many purchasing options in the marketplace, and we are pleased that you have
decided on this product. This MS-PAE inverter/charger was proudly assembled and tested in the
United States.
At Sensata, we are committed to providing you with quality products and services, and hope that
your experience with us is pleasant and professional.

Page ii © 2017 Sensata Technologies
Product Safety Information
IMPORTANT PRODUCT SAFETY INFORMATION
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
THIS MANUAL CONTAINS IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE MS-PAE SERIES INVERTER/
CHARGER THAT MUST BE FOLLOWED DURING THE INSTALLATION AND OPERATION OF THIS
PRODUCT. Before using the MS-PAE Series inverter/charger, read all instructions and cautionary
markings. Also, be sure to review the individual manuals provided for each component of your
system. The installation instructions are for use by qualified personnel only. Do not perform any
installation or servicing other than that specified in this owner’s manual unless you are qualified
to do so. Incorrect installation or servicing may result in a risk of electric shock, fire, or other
safety hazard.
Safety Precautions
• All electrical work must be performed in accordance with local and national electrical codes.
• This product is designed for indoor/compartment installation. It must not be exposed to rain,
snow, moisture, or liquids of any type.
• Use insulated tools to reduce the chance of electrical shock or accidental short circuits.
• There are no user-serviceable parts contained in this product.
• This unit is provided with integral protection against overloads.
• Live power may be present at more than one point since an inverter utilizes both DC (batteries,
PV, etc.,) and AC (utility or generator) power. To reduce risk of electric shock, ensure all DC
and AC wiring is disconnected prior to installing or performing maintenance on the inverter.
Turning off the inverter will not reduce this risk, the inverter must be totally disconnected from
all sources.
• Use Class 1 wiring methods for field wiring connections to terminals of a Class 2 circuit.
• Listed or labeled equipment shall be installed and used in accordance with any instructions
included in the listing or labeling.
• Always verify proper wiring prior to starting the inverter.
• Use only copper wires with a minimum temperature rating of 90°C (194°F).
• AC wiring must be no less than 10 AWG (5.3 mm²) gauge copper wire.
• Battery cables should be no less than #4/0 AWG (107.2 mm²) for 24-volt systems and no less
than #2/0 AWG (67.4 mm²) for 48-volt systems. Crimped and sealed copper ring terminal
lugs with a 5/16 hole should be used to connect to the DC terminals on the inverter.
• Torque all AC wiring connections and DC cable connections to the required torque values.
• The inverter must be properly mounted, see Section 2.1.4 “Mounting the Inverter” in this
manual.
• Overcurrent protection for the battery supply is not provided as an integral part of this
inverter. Overcurrent protection of the battery cables must be provided as part of the system
installation. Refer to Section 2.2 “DC Wiring” for more information.
• Overcurrent protection for the AC output wiring is not provided as an integral part of this
inverter. Overcurrent protection of the AC output wiring must be provided as part of the
system installation. Refer to Section 2.3 “AC Wiring” for more information.
• The AC output neutral conductor and the DC negative conductors are not connected (bonded)
to the inverter chassis. Both the input and output conductors are isolated from the enclosure
and each other. System grounding, if required, is the responsibility of the system installer and
must comply with local and national electrical codes and standards. Refer to the Section 2.4
“Grounding Inverters” for more information.

© 2017 Sensata Technologies Page iii
Product Safety Information
Battery Safety
• Use insulated tools and be very careful when working around batteries, they can produce
extremely high currents if short-circuited (e.g., dropping a metal tool across the battery
terminal), which could cause a fire or explosion.
• Read and follow the battery manufacturer’s safety precautions before installing the inverter
and batteries. Always verify proper polarity and voltage before connecting the batteries
to the inverter. Once the batteries are connected to the inverter, ensure the maintenance
and charging requirements (i.e., charge voltage and charge rate) provided by the battery
manufacturer are followed to extend the life of the batteries and to prevent damage to the
batteries while charging.
• Wear eye protection such as safety glasses, and avoid touching your eyes and face when
working with batteries to keep any fluid/corrosion on the battery from coming in contact
with eyes and skin. Have plenty of fresh water and soap nearby and thoroughly wash in case
battery acid contacts skin, clothing, or eyes. In the event of exposure to the eyes, flood them
for at least 15 minutes with running water and seek immediate medical attention. Baking soda
neutralizes lead acid battery electrolyte and vinegar neutralizes spilled NiCad and NiFe battery
electrolyte; depending on your battery type, keep a supply on hand near the batteries.
• Remove all jewelry such as rings, watches, bracelets, etc., when installing or performing
maintenance on the batteries and inverter. A battery can produce a short-circuit current high
enough to weld metal jewelry, causing severe burns.
• Never work alone. Always have someone within the range of your voice or close enough to
come to your aid when working around batteries.
• Use proper lifting techniques when working with batteries.
• Never use old or untested batteries. Check each battery’s label for age, type, and date code
to ensure all batteries are identical.
• Batteries are sensitive to changes in temperature. Install batteries in a stable environment.
• Batteries can produce explosive gasses, so install batteries in a well-ventilated area. For
compartment or enclosure installations, always vent batteries from the highest point to the
outside. Design the battery enclosure to prevent accumulation and concentration of hydrogen
gas in “pockets” at the top of the compartment.
• Provide at least one inch of air space between batteries to provide optimum cooling.
• Never smoke or allow a spark near batteries.
• To prevent a spark at the battery and reduce the chance of explosion, always connect the
cables to the batteries first. Then connect the cables to the inverter.
• Never charge a frozen battery.
• The battery bank should be installed in a clean, dry, ventilated environment where they are
protected from high and low temperatures. If installed in a vehicle/boat, the batteries must be
mounted upright (if using liquid batteries) and securely fastened. The location must be fully
accessible and protected from exposure to heat producing devices, and away from any fuel tanks.
Safety Symbols
To reduce the risk of electrical shock, fire, or other safety hazard, the following safety symbols
have been placed throughout this manual to indicate dangerous and important safety instructions.
WARNING: This symbol indicates that failure to take a specified action could result in
physical harm to the user.
CAUTION: This symbol indicates that failure to take a specified action could result in
damage to the equipment.
Info: This symbol indicates information that emphasizes or supplements important
points of the main text.

Page iv © 2017 Sensata Technologies
Product Safety Information
CONSIGNES DE SÉCURITÉ IMPORTANTES
CONSERVER CES INSTRUCTIONS
CE MANUEL CONTIENT DE IMPORTANTES POUR LA SÉRIE MS ONDULEUR/CHARGEUR QUI DOIVENT
ETRE SUIVIES PENDANT L’INSTALLATION ET FONCTIONNEMENT DE CE PRODUIT. Avant d’utiliser
la série MS, lire toutes les instructions etles mises en garde. Aussi, n’oubliez pas depasser en revue
les différents manuels fournispour chaque composant du système. Lesinstructions d’installation
sont pour une utilisationpar du personnel qualifié. Ne pas effectuer une installation ou d’entretien
autres que ceux spécifiés dans ce manuel, sauf si vous êtes qualifié pour le faire. Une mauvaise
installation ou d’entretien peut entraîner un risque de choc électrique, un incendie ou autre danger
pour la sécurité.
Consignes de Sécurité
• Tous les travaux électriques doivent être effectués en conformité avec les codes locaux et
nationaux électriques.
• Ce produit est conçu pour l’installation / du compartiment intérieur. Il ne doit pas être exposé
à la pluie, la neige, l’humidité ou des liquides de tout type.
• Utiliser des outils isolés pour réduire le risque de choc électrique ou courts-circuits accidentels.
• Il n’y a pas réparable par l’utilisateur contenues dans ce produit.
• Cet appareil est fourni avec une protection intégrale contre les surcharges.
• Puissance en direct peuvent être présents à plus d’un point depuis un onduleur utilise à la fois
DC (piles, PV, etc) et AC (utilitaire ou générateur) d’alimentation. Pour réduire le risque de
choc électrique, assurez-vous que tout le câblage DC et AC est débranchée avant l’installation
ou la maintenance sur le variateur. Mise hors tension de l’onduleur ne réduira pas ce risque,
l’onduleur doit être totalement déconnectée de toutes les sources.
• Utiliser des méthodes de câblage classe 1 pour les connexions de câblage sur le terrain aux
bornes d’un circuit de Classe 2.
• Coté ou étiquetés équipement doit être installé et utilisé conformément aux instructions
figurant dans la liste ou l’étiquetage.
• Toujours vérifier le câblage avant de commencer l’onduleur.
• Utilisez des fils de cuivre seulement avec une cote de température minimale de 90°C (194°F).
• AC câblage ne doit pas être inférieure à 10 AWG (5.3 mm²) de cuivre de calibre.
• Les câbles de batterie ne doit pas moins de 107.2 mm² (#4/0 AWG) pour 24 volts systèmes
et pas moins de 67.4 mm² (#2/0 AWG) pour 48 volts systèmes. Frisées et scellé cosses
en cuivre anneau des bornes avec un trou de 5/16 doit être utilisé pour se connecter à des
bornes de courant continu sur l’onduleur.
• Couple toutes les connexions de câblage ca et les connexions de câbles à courant continu à
des valeurs de couple nécessaires.
• L’onduleur doit être monté correctement, voir la section 2.1.4 “Montage de l’onduleur” dans
ce manuel.
• Protection contre les surintensités pour l’alimentation de la batterie ne est pas fourni en tant
que partie intégrante de cet onduleur. La protection contre les surintensités des câbles de
batterie doit être fournie dans le cadre de l’installation du système. Reportez-vous à la section
2.2 “Câblage DC” pour plus d’informations.
• Protection contre les surintensités pour le câblage de sortie AC n’est pas fourni en tant que
partie intégrante de cet onduleur. Protection contre les surintensités du câblage de sortie CA
doit être fournie dans le cadre de l’installation du système. Reportez-vous à la Section 2.3
“Câblage CA” dans le chapitre d’installation pour plus d’informations.
• Le conducteur de sortie CA conducteurs neutre et continue négative ne sont pas connectés
(servitude) au châssis inverseur. La fois l’entrée et des conducteurs de sortie sont isolés de
l’enceinte et l’autre. La terre du système, si nécessaire, est de la responsabilité de l’installateur
du système et doit se conformer à des codes locaux et nationaux et les normes électriques.
Reportez-vous à la Section 2.4 Mise à la terre Onduleurs dans le chapitre d’installation pour
plus d’informations.

© 2017 Sensata Technologies Page v
Product Safety Information
Sécurité de la Batterie
• Utiliser des outils isolés et être très prudent lorsque vous travaillez près des batteries, elles peuvent
produire des courants extrêmement élevés si en court-circuit (par exemple, échapper un outil métallique
à travers la borne de la batterie), ce qui pourrait provoquer un incendie ou une explosion.
• Lisez et suivez les consignes de sécurité du fabricant de la batterie avant d’installer l’onduleur
et des batteries. Toujours vérifier la polarité et la tension avant de brancher les batteries à
l’onduleur. Une fois que les batteries sont connectées à l’onduleur, assurer la maintenance et
les exigences de charge (c.-à-tension de charge et taux de charge) fournis par le fabricant de
la batterie sont suivies pour prolonger la vie des batteries et pour éviter d’endommager les
batteries pendant la charge.
• Porter des lunettes de protection tels que des lunettes de sécurité, et évitez de toucher vos yeux et
le visage lorsque l’on travaille avec des piles de garder tout fluide / corrosion sur la batterie d’entrer
en contact avec les yeux et la peau. Ayez suffisamment d’eau fraîche et de savon à proximité et se
laver dans le cas d’acide contact avec la peau de la batterie, les vêtements ou les yeux. Dans le cas
d’exposition pour les yeux, les inonder pendant au moins 15 minutes à l’eau courante et consulter
immédiatement un médecin.Le bicarbonate de soude neutralise l’acide de plomb électrolyte de la
batterie et le vinaigre neutralise renversé NiCad et NiFe batterie à électrolyte; en fonction de votre
type de batterie, gardez sous la main près des batteries.
• Enlevez tous les bijoux tels que bagues, montres, bracelets, etc, lors de l’installation ou la
maintenance sur les batteries et l’onduleur. Une batterie peut produire un court-circuit assez
de courant élevé pour souder les bijoux en métal, provoquant de graves brûlures.
• Ne jamais travailler seul. Toujours avoir quelqu’un au sein de la gamme de votre voix ou
suffisamment près pour vous venir en aide lorsque vous travaillez près des batteries.
• Utiliser des techniques de levage appropriées lorsque vous travaillez avec des piles.
• Ne jamais utiliser de piles usagées ou non testés. Vérifiez l’étiquette de chaque batterie à
l’âge, le type et le code de date afin d’assurer toutes les batteries sont identiques.
• Piles sensibles aux changements temporaires, installer dans un environnement stable.
• Les batteries peuvent produire des gaz explosifs, etc installer les piles dans un endroit bien
ventilé. Pour les installations compartiment ou une enceinte, toujours évacuer les piles du
plus haut point à l’extérieur. Concevoir le boîtier de piles pour éviter l’accumulation et la
concentration de gaz d’hydrogène dans “poches” en haut du compartiment.
• Fournir au moins un pouce de l’espace aérien entre les batteries pour fournir un refroidissement optimal.
• Ne jamais fumer ou laisser une étincelle près des batteries.
• Pour éviter une étincelle à la batterie et de réduire le risque d’explosion, toujours connecter
les câbles aux batteries en premier. Ensuite, connectez les câbles à l’onduleur.
• Ne jamais charger une batterie gelée.
• La banque de la batterie doit être installé dans un endroit propre, sec, aéré et où ils sont
protégés contre les températures élevées et basses. S’il est installé dans un véhicule / bateau,
les batteries doivent être monté en position verticale (si vous utilisez des piles liquides) et
solidement fixés. L’emplacement doit être pleinement accessible et protégé contre l’exposition
à la chaleur la fabrication de dispositifs, et loin de toute réservoirs de carburant.
Symboles de Sécurité
Les symboles de sécurité suivants ont été placéstout au long de ce manuel pour indiquer des
conditions dangereuses et les consignes de sécurité importantes.
AVERTISSEMENT: Ce symbole indique que le défaut de prendre une action spécifiée
pourraitcauser des dommages physiques à l’utilisateur.
ATTENTION: Ce symbole indique que le défaut de prendre une action spécifiée peut
entraîner des dommages à l’équipement.
Info: Ce symbole indique une information qui met l’accent ou des suppléments points
importants du texte principal.

Page vi © 2017 Sensata Technologies
Table of Contents
1.0 Introduction...................................................................................................... 1
1.0.1 Regulatory Compliance ................................................................................. 1
1.1 How the MS-PAE Series Inverter/Charger Works ................................................. 2
1.1.1 Inverter Applications for Permanent Installations.............................................. 2
1.1.2 Advantages of a Pure Sine Wave Inverter........................................................ 2
1.2 Features and Benefits...................................................................................... 3
2.0 Installation........................................................................................................ 6
2.1 Pre-Installation .............................................................................................. 6
2.1.1 Unpacking and Inspection ............................................................................. 6
2.1.2 Required Components and Materials ............................................................... 6
2.1.3 Locating the Inverter .................................................................................... 8
2.1.4 Mounting the Inverter................................................................................... 9
2.1.5 Wiring the Inverter......................................................................................11
2.1.6 Protecting Wire – Conduit Box or Inverter Enclosure ........................................11
2.1.7 Wiring Requirements ...................................................................................11
2.1.8 Wire Routing ..............................................................................................11
2.1.9 Torque Requirements ..................................................................................11
2.2 DC Wiring.....................................................................................................12
2.2.1 DC Wire Sizing............................................................................................14
2.2.2 DC Overcurrent Protection............................................................................14
2.2.3 DC Cable Connections..................................................................................15
2.2.4 Wiring the Battery Bank ...............................................................................16
2.2.5 Battery Temperature Sensor Installation and Wiring ........................................16
2.2.6 Wiring the Inverter to the Battery Bank..........................................................17
2.3 AC Wiring .....................................................................................................18
2.3.1 Pre-AC Wiring Requirements.........................................................................18
2.3.2 AC Wire Size and Overcurrent Protection ........................................................18
2.3.3 Recommended Ground Fault Circuit Interruption (GFCI) Breakers ......................19
2.3.4 AC Input and Output Wiring Connections........................................................19
2.3.5 Wiring the AC Input and Output ....................................................................20
2.3.6 Using the MS-PAE with Three-Phase Power .....................................................22
2.4 Grounding Inverters.......................................................................................24
2.4.1 Sizing the Grounding Electrode Conductors (GEC)............................................25
2.4.2 System Bonding Jumper...............................................................................27
2.4.3 Equipment Grounding Conductor ...................................................................27
2.5 Installing Lightning Arrestors...........................................................................28
2.6 Inverter Warning Label...................................................................................28
2.6.1 Inverter Power Identification and Disconnect Location ......................................29
2.7 Final Inspection.............................................................................................29
2.8 Functional Test for a Single MS-PAE Inverter .....................................................30
3.0 Operation ........................................................................................................ 31
3.1 Inverter Mode ...............................................................................................31
3.2 Standby Mode ...............................................................................................32
3.2.1 Battery Charging.........................................................................................32
3.2.2 Transfer Time .............................................................................................34
3.3 Battery Temperature Sensor Operation.............................................................34
3.4 Protection Circuitry Operation..........................................................................35
3.5 Inverter Start-Up...........................................................................................36
3.6 Factory Default Values ...................................................................................37

© 2017 Sensata Technologies Page vii
Table of Contents (Cont.)
3.7 Inverter Fan Operation ...................................................................................38
3.8 Using a Remote with the MS-PAE Series Inverter ...............................................38
4.0 Parallel Operation ........................................................................................... 39
4.1 Overview......................................................................................................39
4.2 Parallel System Requirements .........................................................................39
4.3 Parallel System Connections and Components ...................................................41
4.3.1 AC and DC Connections Simplified using Magnum Panels ..................................41
4.3.2 AC Connections Required in Parallel System ...................................................41
4.3.3 DC Connections Required in Parallel System ...................................................41
4.4 Functional Test for Parallel-stacked MS-PAE Inverters.........................................43
4.4.1 Power-up Procedure (Stacked System)...........................................................43
4.4.2 Verifying Parallel-stacked Communication.......................................................43
4.4.3 Performing the Functional Test......................................................................45
4.5 Parallel Threshold Feature for MS-PAE Inverters.................................................45
5.0 Using the MS-PAE Series in an AC Coupled Application.................................... 46
5.1 What is an AC Coupled System........................................................................46
5.2 Frequency Shift Feature..................................................................................46
5.3 Configuring a Remote to work in an AC Coupled System .....................................46
6.0 Troubleshooting .............................................................................................. 47
6.1 Resetting the Inverter ....................................................................................48
6.1.1 Performing an Inverter Reset (i.e., soft reset).................................................48
6.1.2 Performing a Power Reset (i.e., hard reset).....................................................48
Appendix A – Specifications and Optional Equipment ................................................ 49
A-1 Efficiency Graphs...........................................................................................50
A-2 Optional Equipment/Accessories ......................................................................51
Appendix B – Battery Information ............................................................................ 52
B-1 Battery Location ............................................................................................52
B-2 Battery Types ...............................................................................................52
B-3 Battery Temperature......................................................................................52
B-4 Battery Bank Sizing .......................................................................................52
B-5 Battery Bank Sizing Worksheet........................................................................53
B-6 Battery Wiring...............................................................................................54
Appendix C – Power Consumption and Output Waveforms ........................................ 57
C-1 Appliance Power Consumption .........................................................................57
C-2 Inverter Output Waveforms............................................................................... 57
Appendix D – Inverter/Charger Terminology ............................................................ 58
Appendix E – Warranty and Service .......................................................................... 60
E-1 Limited Warranty...........................................................................................60
E-2 How to Receive Repair Service ........................................................................60

Page viii © 2017 Sensata Technologies
List of Tables
Table 2-1, Recommended DC Wire/Overcurrent Device ......................................................14
Table 2-2, DC Wire Size For Increased Distance ................................................................15
Table 2-3, AC Grounding Electrode Conductor (GEC–AC) Sizing...........................................25
Table 2-4, Equipment Grounding Conductor (EGC) Sizing...................................................27
Table 3-1, Inverter Battery Turn On/Off Levels..................................................................35
Table 3-2, Inverter/Charger Default Values*.....................................................................37
Table 3-3, Inverter Compatibility Level ............................................................................38
Table 6-1, Troubleshooting Guide....................................................................................47
Table A-1, MS-PAE Specifications (at 25°C) ......................................................................49
Table C-1, Typical Appliance Power Consumption...............................................................57
List of Figures
Figure 1-1, Power Switch, Status LED, and Accessory Connection Ports................................. 3
Figure 1-2, Electrical Connection Points ............................................................................ 4
Figure 1-3, Left Side Features ......................................................................................... 5
Figure 2-1, Simplified Installation Diagram – Single Inverter ............................................... 7
Figure 2-2, Approved Mounting Positions .......................................................................... 9
Figure 2-3, MS-PAE Series Dimensions ............................................................................10
Figure 2-4, DC and Battery Temperature Sensor Wiring .....................................................13
Figure 2-5, Battery Hardware Installation ........................................................................15
Figure 2-6, Inverter DC Hardware Installation ..................................................................15
Figure 2-7, Battery Temperature Sensor ..........................................................................16
Figure 2-8, AC Terminal Block ........................................................................................19
Figure 2-9, AC Wiring (Single unit on a MMP enclosure) .....................................................21
Figure 2-10, Connecting the MS-PAE to Three-Phase Power using a Buck-Boost Transformer...23
Figure 2-11, Connecting the MS-PAE Directly to Three-Phase Power ....................................23
Figure 2-12, Grounding System for MS-PAE Series ............................................................24
Figure 2-13, Method 1 – DC Ground Rod with Multiple Connections .....................................25
Figure 2-14, Method 2 – DC Ground Rod with Multiple Connections .....................................26
Figure 2-15, Method 3 – DC Ground Rod with Single Connection.........................................26
Figure 2-16, Warning Label............................................................................................28
Figure 2-17, AC Voltage Checks......................................................................................30
Figure 3-1, Power Flow – Inverter Mode...........................................................................31
Figure 3-2, Power Flow – Standby Mode ..........................................................................32
Figure 3-3, Automatic 4-Stage Charging Graph.................................................................33
Figure 3-4, BTS Temperature to Charge Voltage Change ....................................................34
Figure 3-5, Power Switch and Status Indicator..................................................................36
Figure 4-1, Simplified Installation Diagram – Multiple Parallel-stacked Inverters....................40
Figure 4-2, Simplified Panel (AC Panel)............................................................................41
Figure 4-3, Simplified Panel (DC Panel) ...........................................................................41
Figure 4-4, Battery Connections in a Parallel System .........................................................42
Figure 4-5, ME-RTR (Port) Master/Slave Displays ..............................................................44
Figure 6-1, Performing an Inverter Reset .........................................................................48
Figure A-1, MS4024PAE Efficiency Chart ..........................................................................50
Figure A-2, MS4448PAE Efficiency Chart ..........................................................................50
Figure B-1, Series Battery Wiring....................................................................................54
Figure B-2, Parallel Battery Wiring ..................................................................................54
Figure B-3, Series-Parallel Battery Wiring ........................................................................54
Figure B-4, Battery Bank Wiring Examples (24-volt)..........................................................55
Figure B-5, Battery Bank Wiring Examples (48-volt)..........................................................56
Figure C-1, AC Waveforms .............................................................................................57

© 2017 Sensata Technologies Page 1
Introduction
1.0 Introduction
Congratulations on your purchase of the MS-PAE Series inverter/charger from Sensata. The MS-
PAE Series is a “pure” sine wave, standalone, non-grid interactive inverter designed to provide
120 and 240 VAC in a single unit to power loads when inverting/charging. It has two 120 VAC
lines (L1 and L2), a neutral and a ground. The two 120 VAC output lines are 180° out-of-phase
with each other so that the combination of the L1 and L2 lines total 240 VAC, and the voltage
between either L1 or L2 and neutral is 120 VAC. The MS-PAE Series charger can accept 120 VAC
input (to L1 or L2) or 120/240 VAC split-phase input power (to L1 and L2). The incoming AC
power is shared with the charger and the output continues to be 120/240 VAC with either a 120
VAC or a 120/240 VAC input.
When the power requirements of the system are beyond the capacity of a single MS-PAE Series
inverter—or the system is expanded as more loads are added—up to four MS-PAE Series inverters
can be connected together in a parallel configuration. Connecting inverters in parallel increases the
overall inverter power and surge capacity to power a large single load, or several smaller loads.
Simply connect the inverter’s output to your distribution circuits or electrical panel, connect your
utility or generator power (AC) to the inverter’s easy-to-reach terminal block, connect the batteries,
and then switch on the power. Using optional remote controls (ME-RTR, ME-ARC, or ME-RC), you
can easily operate and monitor your inverter from a remote location.
Info: This is a sizable manual and much of it is fairly technical. Terms may be used
throughout the manual that are unfamiliar to you. Refer to the Inverter/Charger
Terminology glossary in Appendix D for clarification.
The MS-PAE Series inverter/charger includes the following:
• 4000 watt model in a small footprint—less area needed for installation
• Ability to parallel up to four identical MS-PAE inverters to increase output power capability
(requires ME-RTR)
• Pure sine wave output
• 120/240 VAC split-phase output in a single inverter
• Automatic PFC (Power Factor Corrected) multi-stage battery charging
• RS485 standard communication protocol
• Remote and Network ports (easy connection for optional accessories)
• Inverter-mounted ON/OFF switch with LED indicator
• 30-amp per leg AC pass-thru capability
• Field serviceable for qualified personnel—tested repair kits available
• Automatic battery temperature compensation (when using the Battery Temperature Sensor)
for optimum charging even during extreme temperature changes
• Overcurrent, over-temperature, and high/low battery voltage protection
1.0.1 Regulatory Compliance
The MS-PAE Series inverter/charger is designated as a Standalone (non grid-interactive) power
inverter with an internal battery charger. It can be connected to the utility grid (or to a generator)
to allow the inverter batteries to be charged, and to power inverter loads while connected. The
MS-PAE Series is not a grid-interactive (also known as utility-interactive) inverter and does not
have the capability to export (or sell) power back into the utility grid.
The MS-PAE Series has been tested and listed to UL1741, 1st Edition (Inverters, Converters and
Controllers for Use in Independent Power Systems) for use in the US; and is also certified to CSA
C22.2 No. 107.1-01 (General Use Power Supplies) for use in Canada. It has been tested and
certified to these product safety standards by Intertek Testing Services (known as ETL), which is
a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL). NRTL’s are qualified organizations that meet
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations to perform independent safety
testing and product certification.

Page 2 © 2017 Sensata Technologies
Introduction
1.1 How the MS-PAE Series Inverter/Charger Works
There are two main modes of operation associated with the MS-PAE inverter/charger:
Inverter Mode
When the inverter is properly connected to batteries and turned on, the direct current (DC) from
the batteries is transformed into a pure sine wave alternating current (AC). This AC is similar to
the voltage provided by your utility, and is used to power the electrical appliances (i.e., AC loads)
connected to the inverter’s output.
Standby Mode
When an external source of AC power (e.g., utility power or generator) is connected and qualified
on the inverter’s AC input, it operates in Standby mode. In Standby mode, the unit operates as a
battery charger to convert the incoming AC power into DC power to recharge the batteries; while
at the same time, an internal AC transfer relay is automatically closed and passes the incoming AC
power directly to the inverter’s output to continue powering the connected electrical appliances.
1.1.1 Inverter Applications for Permanent Installations
An inverter can be used for backup power in a permanent location that normally uses utility power,
such as a home or office. When utility power is available, the inverter keeps the batteries charged.
When the utility power fails, the inverter comes on automatically to supply AC power to your home
or office during the power failure. For a home or business, reliable backup power is needed to
prevent lost computer data, or to maintain lights and keep food fresh in the refrigerator/freezer.
In some areas, where utility power is not available, the inverter can be used in a standalone
renewable power system. The inverter enables AC electrical appliances to be run from the storage
battery bank. When the battery bank becomes discharged, either renewable DC sources (solar,
wind, or hydropower) can be used to recharge the batteries, or a generator can be connected to
the inverter to power the system while the batteries recharge.
1.1.2 Advantages of a Pure Sine Wave Inverter
Today’s inverters come in three basic output waveforms: square wave, modified sine wave (which
is actually a modified square wave), and pure sine wave (see Figure C-1 in Appendix C). Modified
sine wave inverters approximate a pure sine wave form and will run most appliances (see also
Section C-1 “Appliance Power Consumption” in Appendix C) and electronics without any problems.
These inverters are less expensive, and therefore, offer a viable alternative to more expensive
pure sine inverters.
The output of the MS-PAE Series, which is a pure sine wave inverter, is equal to or in many cases,
better than the utility power used in your home. Virtually any electronic device will operate from
a pure sine wave inverter. Motors run cooler, microwaves usually cook faster, and clocks keep
better time just to name a few examples. Without compromising quality or performance, the MS-
PAE Series provides you with all the advantages of a pure sine wave inverter at a much lower
cost than many on the market.
The MS-PAE Series is built on the same platform as our popular MS Series which helps reduce
cost by using standard parts/accessories across many models. Magnum accessories such as the
Advanced Remote Control (ME-ARC), Router (ME-RTR), Automatic Generator Start-Networked
(ME-AGS-N), and Battery Monitor Kit (ME-BMK) can be used. See Section A-2 “Optional Equipment
and Accessories” for more information on these products.
Info: For the MS-PAE Series inverter/charger to perform optimally, a minimum battery
bank of 200 AH is recommended for moderate loads (<1000W), and greater than 400
AH for heavy loads (≥1000W).

© 2017 Sensata Technologies Page 3
Introduction
1.2 Features and Benefits
The MS-PAE Series inverter/charger is designed to allow quick access to wiring, circuit breakers
and controls, and easy viewing of the LED (Light Emitting Diode) status indicator. Its die cast
base plate with one-piece aluminum cover ensures maximum durability with minimum weight,
as well as cooler more efficient operation. The MS-PAE Series has the following external features
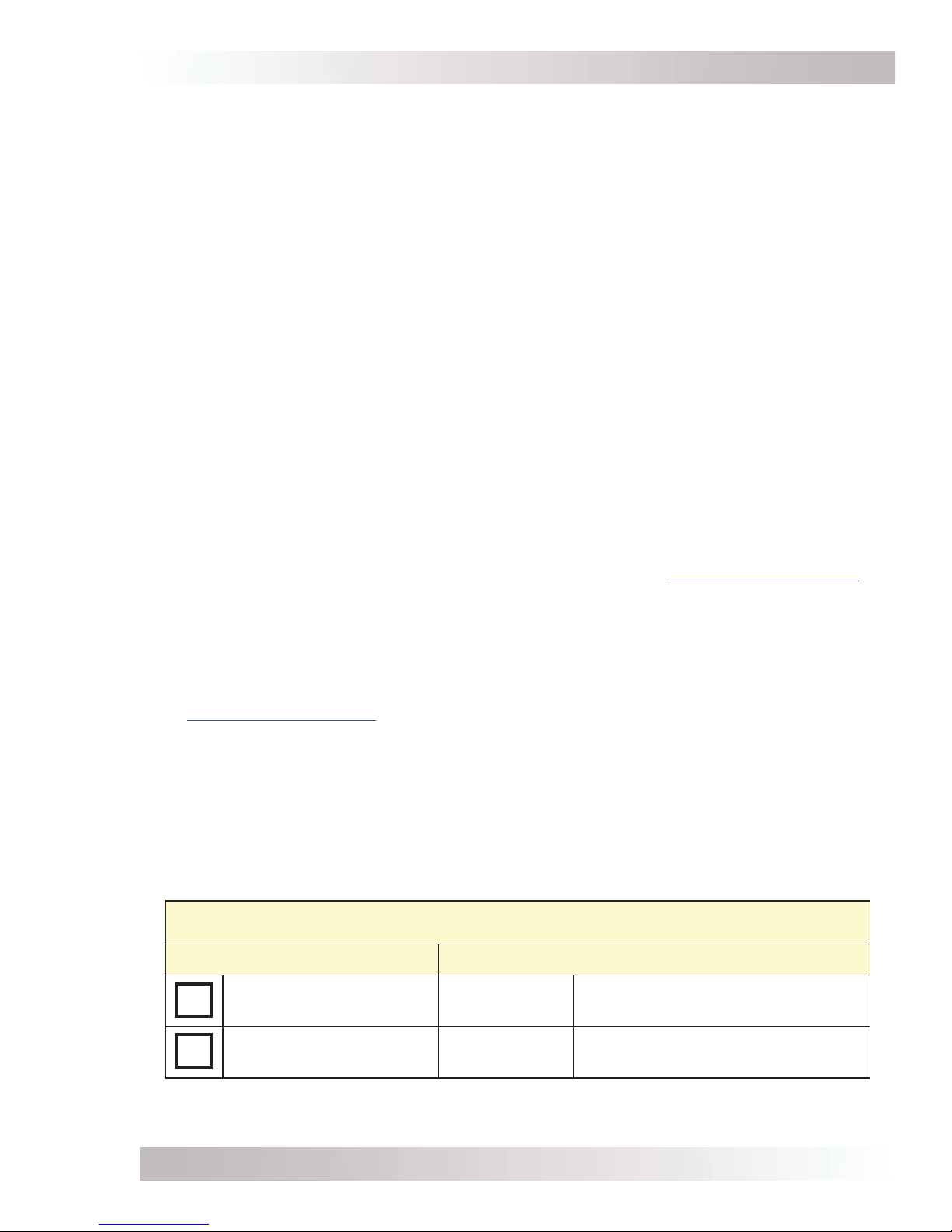
(see Figures 1-1, 1-2, and 1-3):
1Power ON/OFF Switch – a momentary pushbutton switch that alternately turns the
inverter on or off.
2Charging/Inverting LED Indicator – a green LED that illuminates to provide information
on inverter or charger operation.
3Stack/Accessories Port (red label) – a RJ45 port that connects to the ME-RTR router,
which is used to configure and synchronize multiple MS-PAE units to operate in parallel
for increased power capacity.
CAUTION: Only connect this parallel Stack port to a ME-RTR router. Although the cabling
and connectors used in this network system are the same as ethernet connectors, this
network is not an ethernet system. Attempting to connect these two different systems
may cause damage and is not covered under warranty.
Info: MS-PAE Series inverters cannot be connected in parallel without networking them
to the optional ME-RTR (AKA router).
4Network Port (green label) – a RJ11 port that accepts optional network-capable
accessories [i.e., Auto Gen Start (AGS) or Battery Monitor (BMK)].
5Remote Port (blue label) – a RJ11 port that allows optional remote control displays
(i.e., ME-RC, ME-ARC, or ME-RTR) to be connected.
6Battery Temp Sensor Port (yellow label) – a RJ11 port that accepts the remote Battery
Temperature Sensor (BTS) accessory.
Figure 1-1, Power Switch, Status LED, and Accessory Connection Ports
1
2
3
4
5
6
Power ON/OFF Switch
Charging/Inverting LED Indicator
Stack/Accessories Port
(red label – RJ45 connection)
Network Port
(green label – RJ11 connection)
Remote Port
(blue label – RJ11 connection)
Battery Temp Sensor Port
(yellow label – RJ11 connection)

Page 4 © 2017 Sensata Technologies
Introduction
Figure 1-2, Electrical Connection Points
9
10
8
712
11
Positive (+)
DC Terminal
Negative (–)
DC Terminal
Mounting
Flange
DC
Equipment
Ground
Terminal
AC Entry/Exit
Connections
Intake Air Vents
(and on right side)
7DC Equipment Ground Terminal – ties the exposed chassis of the inverter to the DC
grounding system. Accepts CU/AL conductors from #14 to #2 AWG (2.1 to 33.6 mm2).
8AC Entry/Exit Connections – two 3/4” knockouts with cable-clamp strain reliefs to
accommodate and hold the AC input and output field wiring.
9Intake Air Vents –ventilation openings that pull in air to keep the inverter cool for peak
performance.
10 Positive DC Terminal – a 360 degree connection point for the positive (+) cable from
the battery bank. Includes a 5/16-18 stainless Kep or Flange nut on a 5/16-18 bolt
(5/8” usable length) that holds the battery cable to the positive DC terminal.
11 Negative DC Terminal – a 360 degree connection point for the negative (–) cable
from the battery bank. Includes a 5/16-18 stainless Kep or Flange nut on a 5/16-18 bolt
(5/8” usable length) that holds the battery cable to the negative DC terminal.
12 Mounting Flange – secures the inverter to a shelf or wall.
© 2017 Sensata Technologies Page 5
Introduction
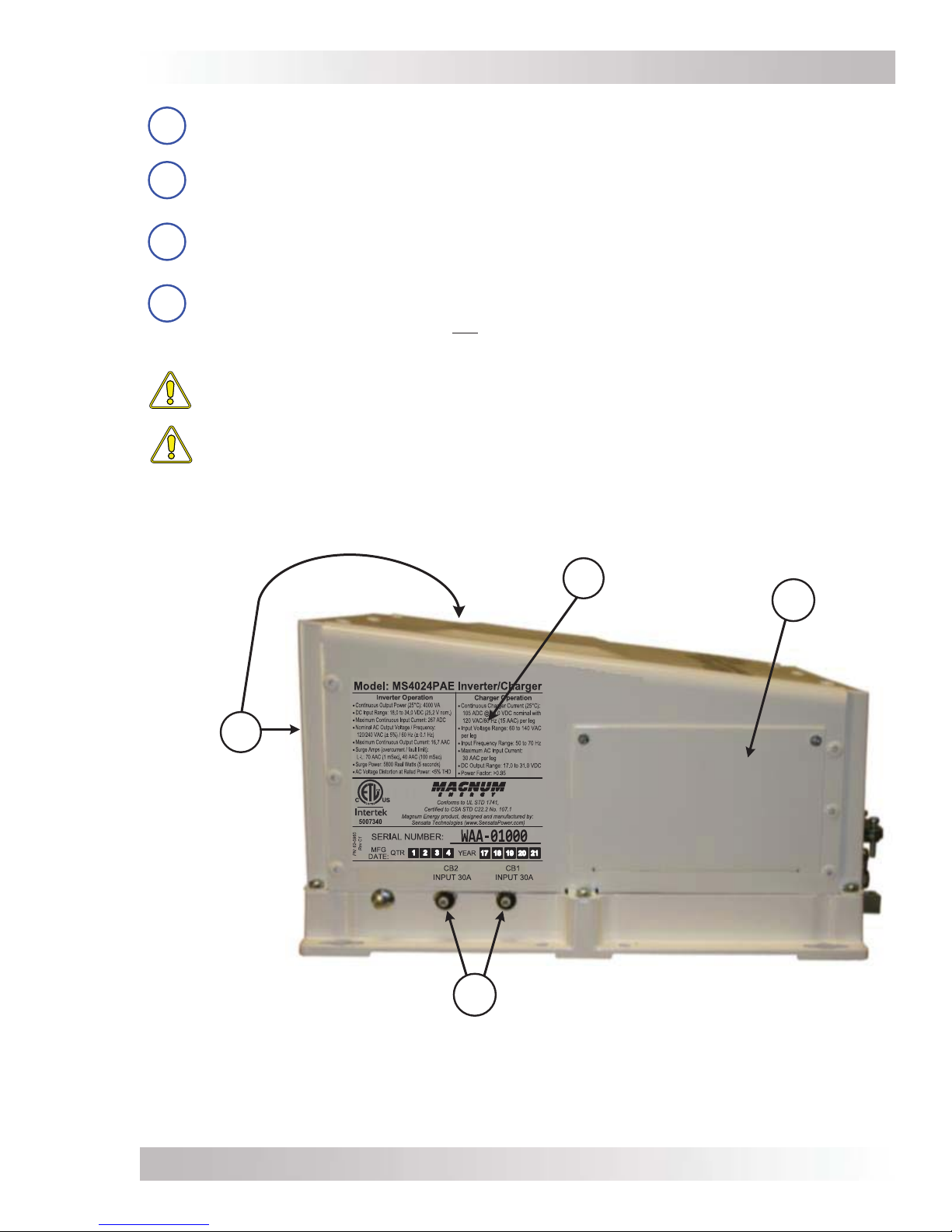
16
15
13
14
Figure 1-3, Left Side Features
13 Exhaust Air Vents – ventilation openings that allows heated air to be removed by the
internal cooling fan.
14 Model/Serial Number Label –includes model/serial number information, date of
manufacture, and inverter and charger specifications. See the MS-PAE Specifications
in Appendix A for more information and the different models available.
15 AC Access Cover – provides access to the internal AC wiring terminal block. This terminal
block is used to hardwire all inverter AC input and output wiring connections. Remove the
two screws to access the AC wiring terminal block.
16 Input Circuit Breakers (CB1 and CB2) – these circuit breakers protect the unit’s
internal wiring and pass-thru relay on each input (L1 and L2)—while in the standby mode.
These input circuit breakers are not branch-circuit rated. These circuit breakers pop out
when they open. Press in to reset power capacity.
CAUTION: Circuit breakers that are branch-circuit rated must be installed in the
inverter’s input and output wiring.
CAUTION: The inverter’s internal AC transfer relay is rated for 30 amps per leg. The
pass-thru current must be no greater than 30 amps per leg, or damage to the relays
may occur.
AC Access
Cover
Model/Serial
Number Label
Exhaust
Air Vents
(back side and
on right side)
Input Circuit
Breakers

Page 6 © 2017 Sensata Technologies
Installation
2.0 Installation
Before proceeding, read the entire installation section to determine how you are going to install
your MS-PAE inverter/charger. The more thorough you plan in the beginning, the better your
inverter needs will be met.
Info: Installations should be performed by qualified personnel, such as a licensed
or certified electrician. It is the installer’s responsibility to determine which safety
codes apply and to ensure that all applicable installation requirements are followed.
Applicable installation codes vary depending on the specific location and application of
the installation.
CAUTION: Review the “Important Product Safety Information” on pages ii-v before
proceeding with the installation.
CAUTION: The inverter is heavy (55 lb/24.9 kg). Use proper lifting techniques during
installation to prevent personal injury.
The simplified system diagrams shown in this manual are provided to assist you in planning and
designing your installation. They are not intended to override or restrict any national or local
electrical codes. These diagrams should not be the determining factor as to whether the installation
is compliant, that is the responsibility of the electrician and the on-site inspector.
Info: If you are installing multiple MS-PAE inverters in a parallel configuration, follow the
information in this section and refer also to Section 4.0 for specific parallel instructions.
2.1 Pre-Installation
2.1.1 Unpacking and Inspection
Carefully remove the MS-PAE Series inverter/charger from its shipping container and inspect all
contents. Verify the following items are included:
• The MS-PAE inverter/charger
• Red and black DC terminal covers with Phillips screws
• AC access cover with two Phillips screws
• Two 5/16” Kep or Flange nuts (installed on the DC terminals)
• Battery Temperature Sensor with 15-foot cable
• Warning label
• MS-PAE Series Owner’s Manual
If items appear to be missing or damaged, contact your authorized Magnum product dealer or
Sensata. If at all possible, keep your shipping box. It will help protect your inverter from damage if
it ever needs to be returned for service. Save your proof-of-purchase as a record of your ownership;
it will also be needed if the unit should require in-warranty service.
Record the unit’s model and serial number in the front of this manual in case you need to provide
this information in the future. It is much easier to record this information now, instead of trying
to gather it after the unit has been installed.
2.1.2 Required Components and Materials
Tools:
• Misc. screw drivers • 1/2” wrench • Wire strippers
• Drill and drill bits • Pliers • Pencil or marker
• Multimeter • Level
Hardware/Materials:
• Conduit, strain-reliefs and appropriate fittings • Wire ties
• 1/4” mounting bolts and lock washers (x4 minimum) • Electrical tape

© 2017 Sensata Technologies Page 7
Installation
Figure 2-1, Simplified Installation Diagram – Single Inverter
Battery
Bank
120/240VAC
power to
inverter
DC
Disconnect
Breaker
MS-PAE
Series
Inverter/
Charger
Main Panel
120/240VAC Inverter power
(or pass-thru power) to Sub-panel
ME-BMK
Battery Monitor
with shunt
(Magnum Accessory)
DC
Shunt
AC
Transfer
Switch
Generator Power
(120/240VAC Output)
Utility Power
(120/240VAC Output)
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
BTS
ME-SBC
Smart Battery
Combiner
(Magnum Accessory)
ME-AGS-N
Auto Gen Start
Controller
(Magnum Accessory)
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
240
VAC 120
VAC
120
VAC
Sub-Panel
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
30A
30A
SELECT
TECH
AGS METER SETU PSH ORE
INVERTE
R
CH ARGER
INV
CHG
FAU LT
PWR
ON/OFF
ON/
OFF
Remote Controls (Magnum Accessories)
ME-RC ME-ARC
Note: See Figure 4-1 for a
simplified diagram showing
multiple inverters in a stacked
configuration.

Page 8 © 2017 Sensata Technologies
Installation
2.1.3 Locating the Inverter
Only install the inverter in a location that meets the following requirements:
Clean and Dry – The inverter should not be installed in an area that allows dust, fumes, insects or
rodents to enter or block the inverter’s ventilation openings. This area also must be free from any
risk of condensation, water, or any other liquid that can enter or fall on the inverter. The inverter
uses stainless steel fasteners, plated copper busbars, a power-coated aluminum base, and the
internal circuit boards are conformal coated—all done to help fight the harmful effects of corrosive
environments. However, the life of the inverter is uncertain if used in these type of environments,
and inverter failure under these conditions is not covered under warranty.
Info: If the inverter is installed in an area where moisture may occur, we recommend
putting silicone dielectric grease compound into the RJ45/RJ11 electrical ports (Figure
1-1, Items 3-6). Before installing the accessory cables or if leaving any ports open,
squirt a liberal amount into each port. Silicone dielectric compound makes an effective
moisture barrier to help prevent corrosion.
Cool – The inverter should be protected from direct sun exposure or equipment that produces
extreme heat.
Info: The ambient temperature around the inverter must not exceed 77°F (25°C) to
meet power specifications.
Ventilation – In order for the inverter to provide full output power and avoid over-temperature
fault conditions, do not cover or block the inverter’s ventilation openings or install this inverter
in an area with limited airflow. The inverter uses two internal fans to provide forced air cooling,
these fans pull in air through the intake vents (Figure 1-2, Item 9) and blow out air through the
exhaust vents (Figure 1-3, Item 13). Allow at the minimum an airspace clearance of 6” (15.2 cm)
at the intake and exhaust vents, and 3” (7.6 cm) everywhere else to provide adequate ventilation.
If the inverter is installed in an enclosure, a fresh air intake opening must be provided directly to the
front side (intake vents) of the inverter and an exhaust opening on the back side (exhaust vents)
of the inverter. This will allow cool air from the outside to flow into the inverter and heated air to
exit from the inverter and out of the enclosure. When mounted in an enclosed compartment, airflow
must be at least 100 cfm in order to maintain no more than a 68°F (20°C) rise in compartment
temperature.
CAUTION: Do not install this inverter in a zero clearance compartment. Do not cover
or obstruct the ventilation openings—overheating may result.
Safe – Keep any flammable/combustible material (i.e., paper, cloth, plastic, etc.) that may be
ignited by heat, sparks, or flames at a minimum distance of 2 feet (61 cm) away from the inverter.
Do not install this inverter in any area that contains extremely flammable liquids like gasoline or
propane, or in locations that require ignition-protected devices.
Close to the battery bank – As with any inverter, it should be located as close to the batteries
as possible. Long DC wires tend to lose efficiency and reduce the overall performance of an
inverter. However, the unit should not be installed in the same compartment as the batteries or
mounted where it will be exposed to gases produced by the batteries. These gases are corrosive
and will damage the inverter; also, if these gases are not ventilated and allowed to collect, they
could ignite and cause an explosion. The absolute maximum recommended battery cable length is
15 feet (4.6 m).
Accessible –Do not block access to the inverter’s RJ45/RJ11 electrical ports, ON/OFF switch, and
status indicator. Also, allow enough room to access the AC and DC wiring terminals and connections,
as they will need to be checked and tightened periodically. See Figure 2-3 for the MS-PAE Series
inverter/charger’s dimensions.
Away from sensitive electronic equipment – High powered inverters can generate levels of RFI
(Radio Frequency Interference). Locate any electronic equipment susceptible to radio frequency
and electromagnetic interference as far away from the inverter as possible.
© 2017 Sensata Technologies Page 9
Installation
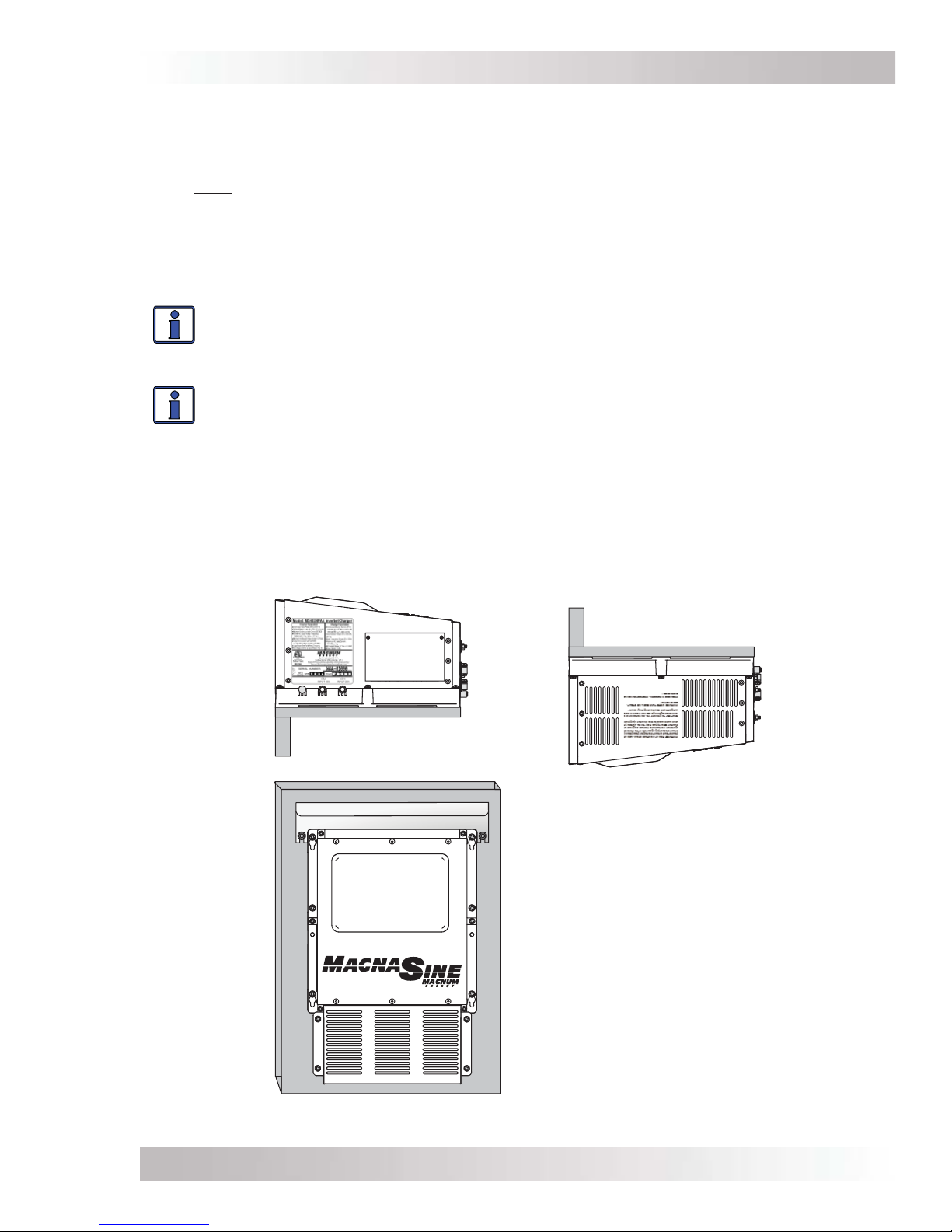
2.1.4 Mounting the Inverter
The inverter base can reach a temperature up to 194°F (90°C), and should be mounted on a
noncombustible surface*. This surface and the mounting hardware must also be capable of
supporting at least twice the weight of the inverter. To meet regulatory requirements, the MS-PAE
Series must be mounted in one of the following positions—as shown in Figure 2-2:
• above or under a horizontal surface (shelf or table),
• or, on a vertical surface (wall) with the DC terminals toward the bottom, the MP-HOOD
(inverter hood) installed over the exhaust vents (top), and either the ME-CB or MPX-CB
(Conduit box), the MMP Series (single inverter enclosure), or the MP Series (multiple inverter
enclosure) attached to the inverter’s DC end (bottom).
Info: ME-CB, MPX-CB, MMP/MP Series enclosures prevent material from falling out the
bottom in the event of an internal fire, and also allow sufficient ventilation to prevent the
inverter from overheating under normal operating conditions. The MP-HOOD inverter
hood helps prevent items from falling inside causing damage to the inverter.
Info: Sensata provides a back plate with a suitable surface for mounting the inverter.
These back plates also provide the ability to mount either the MMP Series enclosure
(PN: BP-MMP) or the MP Series Enclosure (PN: BP-S, Single Plate or BP-D, Dual Plate).
After determining the mounting position, refer to the physical dimensions as shown in Figure 2-3
or use the base of the inverter as a template to mark your mounting screw locations. After marking
the mounting screw locations, mount the unit with appropriate mounting hardware.
*Noncombustible surface – Material that will not ignite, burn, support combustion, or release flammable
vapors when subjected to fire or heat as per the ASTM E136 standard (such as fiber cement board,
stone, steel, iron, brick, tile and concrete). Common building materials such as gypsum board as well
as any paint, wall coverings, and certainly wood will not suffice.
Figure 2-2, Approved Mounting Positions
30
3030
SHELF OR TABLE MOUNTED
(RIGHT SIDE UP)
SHELF OR TABLE MOUNTED
(UPSIDE DOWN)
WALL MOUNTED
(DC TERMINALS ON THE BOTTOM*)
*When the inverter is mounted
on the wall in this position, the
inverter hood (MP-HOOD) must
be mounted over the exhaust
vents (top); and either a conduit
box (ME-CB or MPX-CB) or MMP/
MP Series enclosure must be
attached to the inverter’s DC
end (bottom).

Page 10 © 2017 Sensata Technologies
Installation
Bottom
Left
Side
Right
Side
Front 2"
(5.1 cm)
4 ⅞"
(12.4 cm)
4 ⅞"
(12.4 cm)
13 ¾"
(34.9 cm)
12 ⅝"
(32.1 cm)
12"
(30.5 cm)
6 ⅝"
(16.8 cm)
8"
(20.3 cm)
Exhaust Air Vents
Exhaust Air Vents
Air Intake
Vents
Air Intake Vents
Top
30
30
30
Mounting Holes
Keyhole slots
(x4)
Mounting Holes
(x4)
Use up to
9/32"
(7 mm)
screw/bolt
Figure 2-3, MS-PAE Series Dimensions

© 2017 Sensata Technologies Page 11
Installation
2.1.5 Wiring the Inverter
This section also describes the requirements and recommendations for wiring the MS-PAE Series
inverter/charger. Before wiring the MS-PAE Series inverter/charger, read all instructions.
All wiring should meet all local codes and standards and be performed by qualified
personnel such as a licensed electrician.
The NEC (National Electric Code, ANSI/NFPA 70) for the United States and the CEC (Canadian
Electrical Code) for Canada provide the standards for safely wiring residential and commercial
installations. The NEC/CEC lists the requirement for wire sizes, overcurrent protection, and
installation methods and requirements.
Inverter/charger systems involve power from multiple sources (inverter, generator, utility, batteries,
solar arrays, etc.) which make the wiring more hazardous and challenging.
The input and output AC and DC circuits are isolated from the inverter chassis. The inverter system
grounding is the responsibility of the installer in accordance with the NEC.
WARNING: To prevent accidental shock, ensure all sources of DC power (i.e., batteries,
solar, wind, or hydro) and AC power (utility power or AC generator) are de-energized
(i.e., breakers opened, fuses removed) before proceeding.
2.1.6 Protecting Wire – Conduit Box or Inverter Enclosure
The AC and DC wires into and out of the inverter must be protected by rigid tubing, as required
by code to comply with residential and commercial installations. This is normally done by feeding
the wires through conduit. Sensata provides a conduit box (ME-CB or MPX-CB), a single inverter
enclosure (MMP Series), and a multiple inverter enclosure (MP Series) that include knockouts
to conveniently accommodate AC/DC wiring enclosed and protected by conduit. The MP/MMP
enclosures also include the necessary AC and DC inverter breakers that allow both the AC and DC
conduit to be connected to the inverter.
2.1.7 Wiring Requirements
• All conductors that are at risk to physical damage must be protected by conduit, tape, or
placed in a raceway.
• Always check for existing electrical, plumbing, or other areas of potential damage prior to
making cuts in structural surfaces or walls.
• Both AC and DC overcurrent protection must be provided as part of the installation.
• The inverter requires a reliable negative and ground return path directly to the battery.
• Use only copper wires with a minimum temperature rating of 194°F (90°C).
2.1.8 Wire Routing
Before connecting any wires, determine all wire routes throughout the home to and from the
inverter. Typical routing scenarios are:
• AC input wiring from the main AC panel to the inverter
• AC input wiring from a generator (optional) to the inverter
• DC input wiring from the batteries to the inverter
• AC output wiring from the inverter to an AC sub-panel or to dedicated circuits
• Battery Temperature Sensor cable from the inverter to the batteries
• Remote control cable (optional) to the inverter
• Ground wiring from the inverter to an external ground
2.1.9 Torque Requirements
Torque all AC wiring connections to 16 in lbf (1.8 Nm) and AC/DC ground connections to 45 in lbf
(5.1 Nm). Torque DC cable connections from 10 to 12 ft lbf (13.6 to 16.3 Nm).
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents