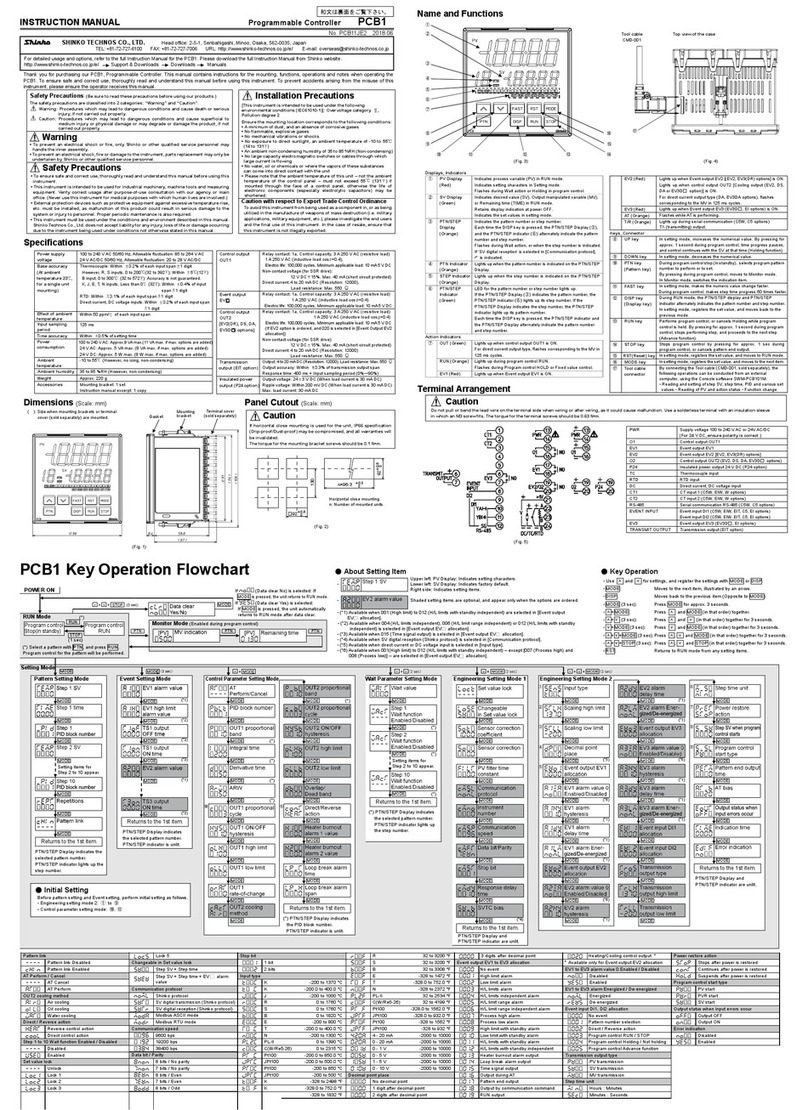
9
• Response message from the slave in exception (error) status (When a value out of the setting range is set)
The function code MSB is set to 1 for the response message in exception (error) status [86H (38H 36H)].
The exception code 03H (30H 33H: Value out of the setting range) is returned (error).
Header
(3AH)
Slave
address
(30H 31H)
Function
code
(38H 36H)
Exception code
[03H]
(30H 33H)
Error check
LRC
(37H 36H)
Delimiter
CR+LF
(0DH 0AH)
1 2 2 2 2 2
6.3 RTU mode
8-bit binary data in command is transmitted as it is.
Data format Start bit : 1 bit
Data bit : 8 bits
Parity : No parity (Even, Odd) Selectable
Stop bit : 1 bit (2 bits) Selectable
Error detection : CRC-16 (Cyclic Redundancy Check)
Data interval : 3.5 character transmission times or less
To transmit continuously, an interval between characters which consist of one message, must
be within 3.5 character transmission times.
(1) Message configuration
RTU mode is configured to start after idle time is processed for more than 3.5 character transmissions
and end after idle time is processed for more than 3.5 character transmissions.
3.5 idle
characters
Slave
address
Function
Code Data Error check
CRC-16
3.5 idle
characters
Slave address
Slave address is an individual instrument number on the slave side, and is set within the range 0 to 95
(00H to 5FH).
The master identifies slaves by the slave address of the requested message.
The slave informs the master which slave is responding to the master by placing its own address
in the response message.
Slave address 0 (00H, broadcast address) can identify all the slaves connected. However slaves do not respond.
Function code
The function code is the command code for the slave to undertake the following action types.
Function code Contents
03 (03H) Reading the set value and information from slaves
06 (06H) Setting to slaves
Function code is used to discern whether the response is normal (acknowledgement) or if any error
(negative acknowledgement) has occurred when the slave returns the response message to the master.
When acknowledgement is returned, the slave simply returns the original function code.
When negative acknowledgement is returned, the MSB of the original function code is set as 1 for the response.
For example, when the master sends request message setting 10H to the function code by mistake, slave
returns 90H by setting the MSB to 1, because the former is an illegal function.
For negative acknowledgement, the exception codes below are set to the data of the response messages
and returned to the master in order to inform it of what kind of error has occurred.
Exception code Contents
1 (01H) Illegal function (Non-existent function)
2 (02H) Illegal data address (Non-existent data address)
3 (03H) Illegal data value (Value out of the setting range)
17 (11H) Shinko error code 4 (Unsettable status, e.g. AT is performing)
18 (12H) Shinko error code 5 (During setting mode by keypad operation)
Data
Data differs depending on the function code.
A request message from the master side is composed of data item, number of data and setting data.
A response message from the slave side is composed of a number of byte, data and exception codes
in negative acknowledgements.
The number of data to be dealt with in one message is “1”. Therefore the number of data is fixed as (0001H).
The number of response byte is (02H).
Effective range of data is –32768 to 32767 (8000H to 7FFFH).
Error check: 16 bit data to detect communication errors. Refer to “(2) Error check of RTU mode”. (p.10)