wiring or it own cord. Contact with a "live" wire
will also make exposed metal parts of the tool
“live” and shock the operator.
When ripping always use a rip fence or
straight edge guide. This improves accuracy
of cut and reduces the chance for blade
binding.
Always use blades with correct size and
shape (diamond vs. round) of arbor holes.
Blades that do not match the mounting
hardware of the saw will run eccentrically,
causing loss of control.
Never use damaged or incorrect blade
washers or bolts. The blade washers and bolt
were specially designed for your saw, for
optimum performance and safety of operation.
Inspect the condition and quality of the
wood and remove all nails from lumber
before cutting. Wet lumber, green lumber or
pressure treated lumber require special
attention during cutting operation to prevent
kickback.
Hold the saw firmly to prevent loss of
control. Figures in this manual illustrate
typical hand support of the saw.
Depending upon use, the switch may not
last the life of the saw. If the switch should
fail in the “OFF” position, the saw may not
start. If it should fail while the saw is
running, the saw may not shut off. If either
occurs, unplug the saw immediately and do not
use until repaired.
This circular saw should not be mounted to
atable and converted to a table saw.
Circular saws are not designed or intended to
be used as table saws.
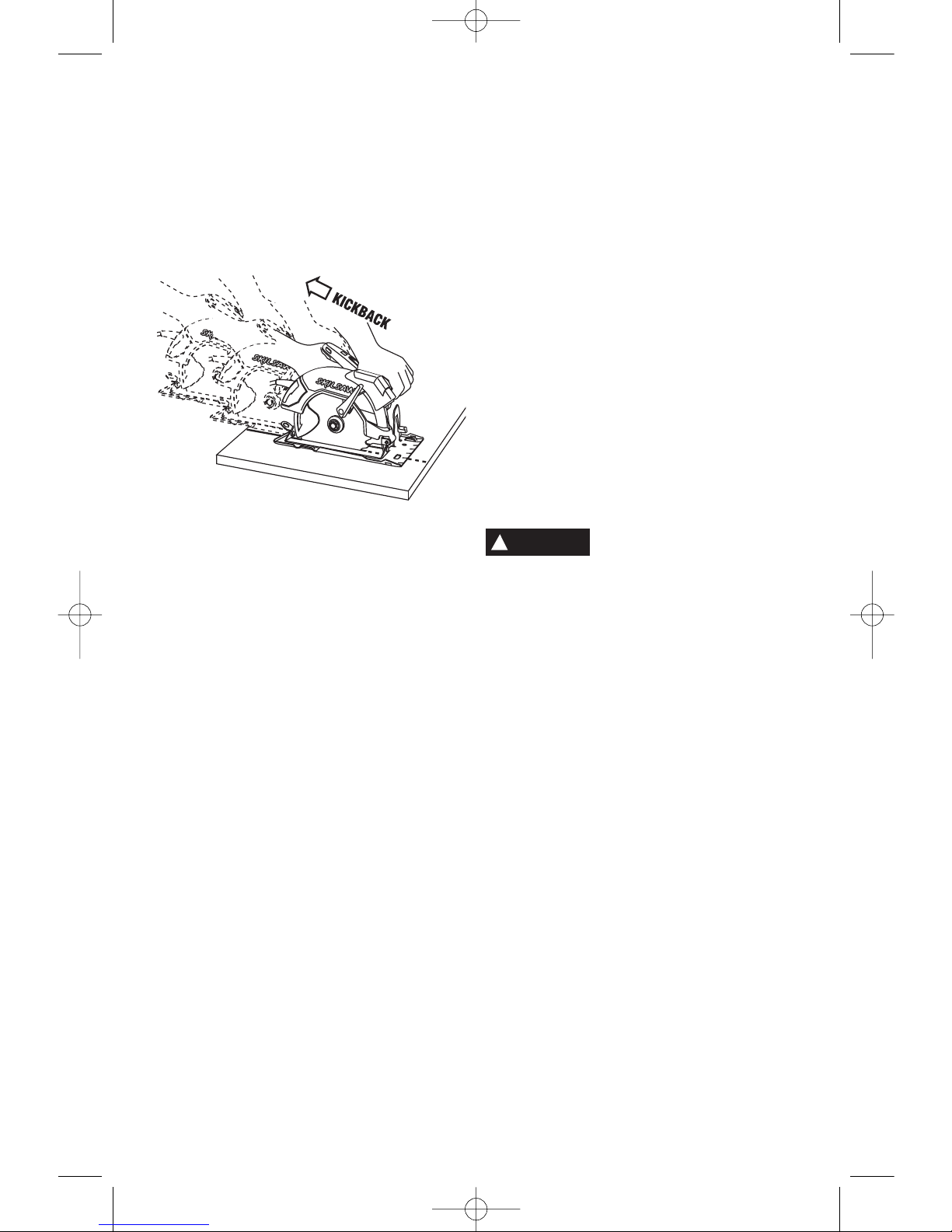
Kickback and related warnings
Causes and operator prevention of
kickback:
Kickback is a sudden reaction to a pinched,
bound or misaligned saw blade, causing an
uncontrolled saw to lift up and out of the
workpiece toward the operator.
When the blade is pinched or bound tightly by
the kerf closing down, the blade stalls and the
motor reaction drives the unit rapidly back
toward the operator.
If the blade becomes twisted or misaligned in
the cut, the teeth at the back edge of the blade
can dig into the top surface of the wood
causing the blade to climb out of the kerf and
jump back toward the operator.
Kickback is the result of tool misuse and/or
incorrect operating procedures or conditions
and can be avoided by taking proper
precautions as given below:
Maintain a firm grip with both hands on the
saw and position your body and arm to
allow you to resist kickback forces.
Position your body to either side of the
blade, but not in line with the blade.
Kickback could cause the saw to jump
backwards, but kickback forces can be
controlled by the operator, if proper
precautions are taken.
When blade is binding, or when interrupting
acut for any reason, release the trigger and
hold the saw motionless in the material
until the blade comes to a complete stop.
Never attempt to remove the saw from the
work or pull the saw backward while the
blade is in motion or kickback may occur.
Investigate and take corrective action to
eliminate the cause of blade binding.
When restarting a saw in a workpiece,
center the saw blade in the kerf and check
that saw teeth are not engaged into the
material. If saw blade is binding, it may walk
up or kickback from the workpiece as the saw
is restarted.
Support large panels to minimize the risk of
blade pinching and kickback. Large panels
tend to sag under their own weight. Supports
must be placed under the panel on both sides,
near the line of cut and near the edge of the
panel.
Do not use dull or damaged blade.
Unsharpened or improperly set blades
produce narrow kerf causing excessive friction,
blade binding and kickback.
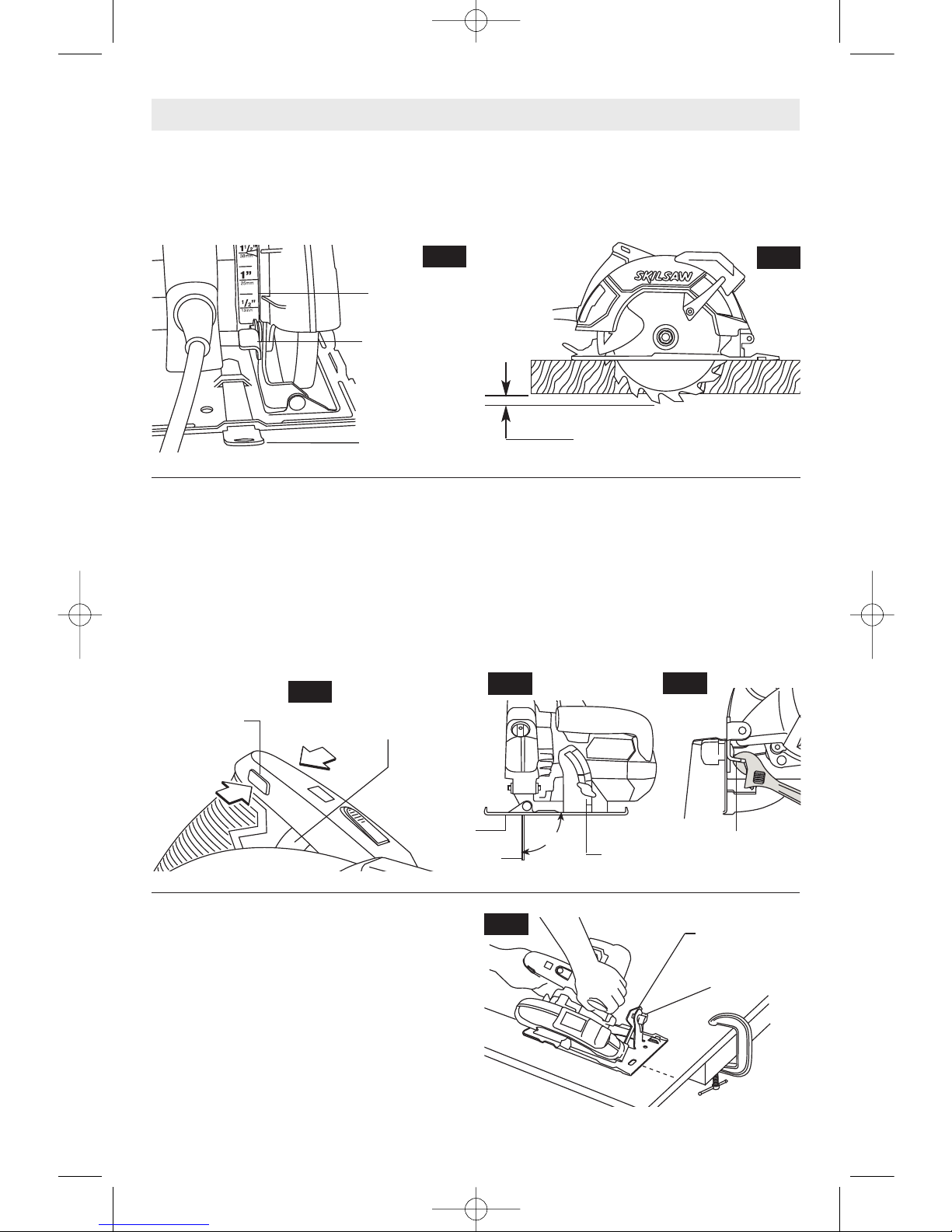
Blade depth and bevel adjusting locking
levers must be tight and secure before
making cut. If blade adjustment shifts while
cutting, it may cause binding and kickback.
Use extra caution when making a “Plunge
Cut” into existing walls or other blind
areas. The protruding blade may cut objects
that can cause kickback.
The blade washers and the bolt on your
saw have been designed to work as a
clutch to reduce the intensity of a kickback.
Understand the operation and settings of
the VARI-TORQUE CLUTCH. The proper
setting of the clutch, combined with firm
handling of the saw will allow you to control
kickback.
-4-
SM 1619X02967 05-08 4/30/08 11:34 AM Page 4