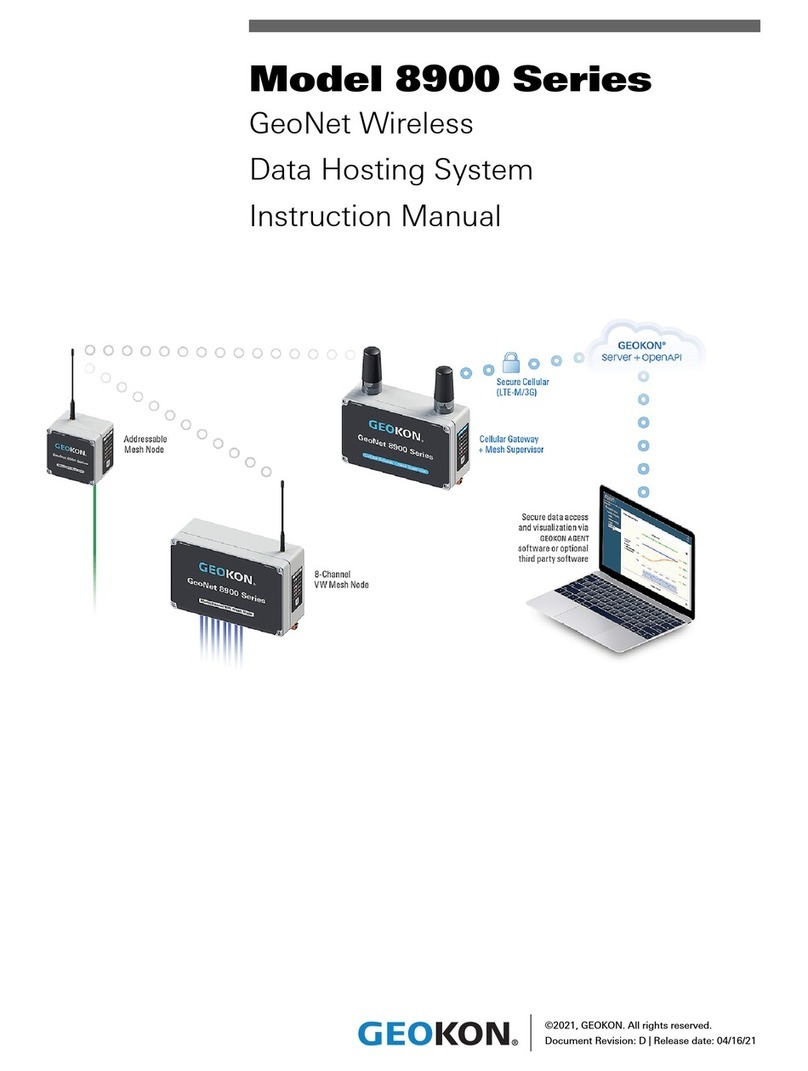
SS Telecoms SS-15 BRI User manual

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM)
USER MANUAL
USER MANUAL

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 2 of 26
CONTENTS
1.
INTRODUCTION 3
2.
WHAT IS SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM)? 3
3.
PACKAGE CONTENT 4
4.
INSTALLATION 5
4.1
IDENTIFYING THE CONNECTORS 5
4.2
CONFIGURING THE SIM CARDS 6
4.3
INSERTING THE SIM CARDS 6
4.4
CONNECTING THE CABLES 8
4.5
INSTALLING THE EXTERNAL ANTENNAS 9
4.6
JUMPER SETTINGS 11
4.7
POWER UP SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) 12
4.8
LED INDICATORS 13
4.9
PINOUT FOR THE CONNECTORS 14
4.10
MOUNTING THE SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) EQUIPMENT 16
4.11
INSTALLING THE PROGRAMMING TOOL 16
5.
OPERATION AND MODES OF CONNECTION 17
5.1
ROUTING FOR LEAST COSTS 17
5.2
MODES OF CONNECTION 18
6.
OPERATING ENVIRONMENT 24
7.
BENEFITS 25
6.
CONTACT DETAILS 26

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 3 of 26
1.
INTRODUCTION
By purchasing SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) you have opted for:
cutting down the costs of your cellular calls;
mobile-2-ISDN interface with LCR capabilities;
excellent quality of audio signal;
availability of SMS and data functions;
convenient, easy to use e-mail to SMS and SMS to e-mail feature;
perfect compatibility to ISDN private branch exchanges (PBX);
routing functions assured even when used as standalone unit;
full compatibility with GSM 900/1800 or 850/1900 networks;
saving of ports in your PBX exchange and
easy and quick installation and usage.
2. WHAT IS SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM)?
By interfacing between an ISDN phone exchange and the mobile telephony
network (GSM 900/1800 or 850/1900) cuts down the costs of fixed-to-GSM and
GSM–to-fixed calls.
ISDN 2 GSM was designed to be connected to any ISDN phone exchange so
it meets standard ISDN PBX requirements.
It may be used as GSM interface for an ISDN a phone exchange. Even when
used as standalone unit with an ISDN phone set it can still perform routing of
the calls for minimum costs. Also, by means of a terminal adapter it can be
used with analogue (standard) telephones or with a payphone.
The unit works primarily in voice mode by re-routing incoming or outgoing
calls through the corresponding wireless network. This way there is only cost
of a mobile-to-mobile call inside the same carrier network, instead of the cost
of a fixed-to-mobile call.
The interface enables several types of ISDN connections and may be used for
services such as call forwarding (conditioned or unconditioned), DISA and
voice messages.
When connected to a computer, the SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) equipment
may be used to receive and send out SMS’s.
By connecting SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) to an ISDN phone exchange, all
local extensions can make calls to GSM networks while keeping down the
costs. Also, when making a call the subscriber is no longer subjected to RF
radiations from the cell-phone. The external antennas can then also be
placed for optimal reception (higher intensity of the radio signal).
Since SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) can send billing pulses, a public telephone
(payphone) can also be used by means of terminal adapter.
Finally, ISDN 2 GSM may be used as small ISDN phone exchange by itself,
since it can interconnect up to 8 ISDN local phones and perform automated
routing of calls for minimum cost.
The unit includes the GSM modules, so it does not need supplementary
devices (such as an external GSM phone) to work. Its two SIM cards allow
routing the call through the corresponding GSM operator, for least cost.

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 4 of 26
Its installation is simple; you just insert the SIM cards and plug in the cables
(serial configuration, ISDN lines, external antennas, power adapter). This
comes very useful for the SOHO (small office/ home office) market.
3. PACKAGE CONTENT
Please ensure that all components are accounted for and that no damage has
been sustained during transport.
Item Image Pcs/ Note
SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM)
equipment
1
Serial programming cable
for SS-15
ISDN 2 GSM
1*
Power supply adapter
12VDC / 2,08A
1
External antennas
1-2 **
Wall mounting kit - 1 ***
CD with OAM software - 1 ****
User’s manual -

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 5 of 26
Notes:
* The package also contains two connecting cable for TE and NT
interfaces
** Depending on what SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) model of equipment it is
(with one or two GSM modules) you will have one or respectively two
antennas.
*** The kit for mounting SS-15 BRI on a wall includes dowels, woodscrews,
etc.
**** OAM software supplied with SS-15 BRI (isdncfg) includes functions for
configuring (programming) the ISDN to GSM interface, routing of calls,
sending and receiving SMS. It also includes online help with examples
4.
INSTALLATION
4.1
IDENTIFYING THE CONNECTORS
The back of the enclosure of the SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) unit features all
the supply/voice/data connectors:
Figure 1. Identifying the connectors
PWR: Female connector, jack type, for the power supply adapter
SERIAL: Female RJ-11 connector with special pin-out, for the serial cable
used for configuration (for the connection to PC is used a DB9
muffle)
NT: Network Termination for 4-wire ISDN phone line. Connects SS-15
BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) to the TE of the ISDN PBX or the ISDN phone
set (analogue phone may be used via terminal adapter)
SY: Synchronization, connections paralleled with TE slot. Used for
clock signal synchronization, when cascading several ISDN 2
GSM units together .
TE: Terminal Equipment connector for ISDN is used for connecting to
an ISDN phone exchange or to the ISDN public telephony network
and also, for connecting more than one SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM)
unit to the same PBX.
The two FME connectors for the external antennas are located on
top of the SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) equipment, while the slots for
the SIM cards and their pushbuttons can be found on the right
side of the enclosure, under the LED indicators.

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 6 of 26
4.2 CONFIGURING THE SIM CARDS
The SIM cards that will be used with SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) must be
activated by the corresponding GSM operator. It must also be properly
configured before insertion in the GSM slot of the equipment. The
configuration of the SIM cards is performed using a GSM phone.
Disable request for PIN code – If the “PIN Code Request” option is disabled,
any value can be inserted in the “Pin Code” field of the Programming Tool.
When entering the correct PIN code, it will be stored in the equipment
memory. The SS-15 unit must be connected with the computer that runs the
Programming Tool through a serial connection in order to modify the “PIN
Code” (for more details refer to the User Manual for the isdncfg program).
Disable GSM services – most GSM operators assure several services
(redirection of calls, vocal mailbox) concerning the handling of incoming calls.
These are very useful when the cell-phone is busy or disconnected; it is an
advantage to use the call forwarding features provided by the GSM carrier. But
when the SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) interface is used together with a phone
exchange it is generally better to disable those services because it can be
performed locally with fewer costs.
Disable Auto-re-dialling and Auto-answer – these options must be disabled if
they are provided by your GSM operator.
Turn off roaming - international roaming services allows one to make calls with
the same GSM subscription when travelling in other countries (where the service
provider has signed a roaming contract with the GSM operator). The roaming
option should be disabled, because SS-15 BRI was designed to work with PBX
or ISDN phones in stationary applications.
If roaming remains enabled, it is possible that when the local GSM carrier is
interrupted, the ISDN 2 GSM interface will connect to a foreign mobile operator
and the costs of the calls will be much higher.
Settings for configuration of the SIM cards
Description Option
Select “OFF” for “Dial again –
Interval”. If this option exists
Select “OFF” for “Auto Answering” Required
Select “OFF” for “Call Waiting” Required
4.3 INSERTING THE SIM CARDS
The ISDN 2 GSM interface needs SIM cards for the corresponding GSM
operators.
Each SIM card must be inserted in the corresponding slot of the SS-15 BRI
(ISDN 2 GSM) unit. Depending upon the equipment model, it may feature one
or two GSM modules, hence one or two slots for SIM cards.

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 7 of 26
The slots for SIM cards are located on
the upper right side of the SS-15 BRI
enclosure, under the LED indicators. To
insert/ remove the SIM, use the
removable tray (SIM holder) which is
activated by a small yellow pushbutton.
Note: To push the ejector button,
because of its small size, one may need
to use a tool with a small, hard tip (keys,
pen, screwdriver or tweezers). Handle
the SIM cards with care.
Figure 2. Location of SIM slots
WARNING: Unplug the SS-15 unit from the main outlet before insert or
replace a SIM card.
For each of the SIM card, follow these steps:
1. Press the little button to eject the SIM holder.
2. Pull out (extract) the tray (SIM holder).

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 8 of 26
3. Insert SIM card into the holder, as shown – with cut corner upwards and
with contacts facing you.
4. Push the holder tray with the SIM inside back into the corresponding slot
of the SS-15 unit
The steps described above should also be followed when the SIM cards
already installed into SS-15 need to be replaced.
4.4 CONNECTING THE CABLES
Connect the data, phone and power cables as shown in the drawing below:

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 9 of 26
Other ISDN interfaces
Figure 3. Connecting the cables
Use ISDN cables to connect the unit to the ISDN PBX (or other ISDN
terminals). Connect the cables from the corresponding ISDN device to the
SS-15 BRI unit. For more detailed information on correct connections refer to
par. 5.2. “Modes of connection”.
1. For each SS-15 BRI ISDN interface, insert one end of the 4-wire ISDN
phone cable in the TE or NT connector of the SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM). The
opposite other end of the cable must be connected to the corresponding local
or junction interface of the ISDN PBX or to the ISDN phone. The pinout ofRJ-
45 connectors for TE and NT interfaces is shown in tables in par.4.9 “Pinout
for connectors” .Select the individual NT, TE or SY connections in
accordance with par. 5.2. „Modes of connection”. In order to achieve a good
operation, the pattern of connections required for the application needs to be
known(links required by the ISDN phone exchange or telephone terminals).
2. Serial programming connection – To be able to adjust configuration of the
ISDN 2 GSM interface using the Programming Tool, the equipment must be
connected to a PC. The connection is performed by means of a special cable
that connects to the „SERIAL” slot of the SS-15 device. The serial connection
is also necessary for sending and receiving SMS messages from the PC.
3. Insert the jack of the power supply adapter (shipped in the SS-15 BRI
package) into the PWR connector. Do not plug the adapter into the
receptacle of the 230V ac mains outlet yet.
If starting up SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) and the antennas are not connected,
the transmitter of theGSM module could be damaged.
4.5 INSTALLING THE EXTERNAL ANTENNAS
SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) features two RF connectors on top for connecting
the antennas for the wireless network. The following may be used:
the wideband antenna supplied with the package, with cable and magnetic
base (see below characteristics) or

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 10 of 26
other kinds of external antennas with higher gain or directivity (Yagi), if the
need arises.
The following table shows the main characteristics of the dual-band stick
antennas with magnetic base (currently supplied with the SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2
GSM) package).
Frequency bands GSM 890-960 MHz
PCN 1710-1880 MHz
PCS1850-1990 MHz
Gain 2 dBi
Polarization Vertical
Base Magnetic, 2,8cm
Cable Type RG174, length
2,5 m
Connector Female FME
The two antennas must be threaded to the FME male connectors located on
top of the SS-15 ISDN 2 GSM unit, as shown in the following drawing.
Figure 4. Connecting external antennas.
Plug the cable connector and tighten the flange lightly, by hand.
Do NOT use a spanner or screw key, which could damage the antenna
connectors.
The external antennas must be installed in a place with a good GSM signal
strength. The antenna has vertical polarization; it must be placed in vertical or
horizontal position, depending of the local field condition.
If the SIM cards used are for different GSM operators, it may be necessary to
place each antenna in a location with maximum strength of the received signal
from the respective GSM carrier.
SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) and its antennas must be located as far as possible
from equipment that is sensitive to electromagnetic interferences (radios, audio
or video appliances, computer monitor, TV receivers etc). If placing the SS-15

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 11 of 26
BRI interface or its antennas too close to such appliances, their operation could
be affected.
Note1: The antennas of the SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) interface send out RF
energy so they should NOT be placed very close to people. Since the GSM
interface transmits for longer periods of time, being used by several people
(most of the calls of local subscribers are routed through it) the radiation will be
accordingly higher than for a cell-phone used only infrequently, by a single
person.
Note2: Remember to connect the antennas before powering up the SS-15 BRI,
to avoid damage to the transmitters of the GSM modules.
4.6 JUMPER SETTINGS
The SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) features several jumpers located on the printed
circuit board, inside the enclosure. These jumpers control functions seldom
needed, therefore, under normal operation these settings do not need to be
changed.
4.6.1. Bootloader enable
Use
If an abnormal interruption occurred in the loading of an image file, use the JP5
jumper.
To fix this problem, set the jumper on the JP5 pins to force the bootloader to
start. In order to load a new image file please refer to the isdncfg OAM manual.
Remember to take the jumper off pins JP5 before resuming normal operation
of the ISDN 2 GSM equipment.
Location
Figure 6. JP5 jumper location
Jumper JP5 is located near the top left corner of the printed circuit board of the
SS-15 BRI. Immediately to the right of JP5 the connector for the external
antenna can be seen. JP5 is alone (no other jumpers close to it) and it is in a
vertical position.
4.6.2. Terminal resistors
Use
These pairs of jumpers (JAN1 and JAN2 for the NT interface, JAT1 and JAT2 for
the TE interface) configure the impedance matching (termination) resistors for
the respective interfaces.
By default, these jumpers are ON so the terminal resistors are connected. The
jumpers should be taken OFF if terminal resistors are not required.

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 12 of 26
When several ISDN devices are connected to an ISDN line, the line must end
with impedance matching resistors, also called terminal resistors. This is
required, for instance, when cascading several SS-15 interfaces and using
synchronization.
One solution for termination is to use a terminal block with matching resistors
inside. But if the last device is an SS-15 BRI, the termination resistors that are
included with the equipment can be used. Remember, out of several SS-15 BRI
units cascaded on the ISDN line, only the last unit must have the termination
resistors enabled.
Location
Figure 7. Location of JAT1, JAT2, JAN1 and JAN2 jumpers
The pairs of jumpers (JAN1 and JAN2 for the NT interface, JAT1 and JAT2 for
the TE interface) are located towards the right edge of the SS-15 BRI printed
circuit board, at middle-bottom. Each pair of jumpers is near a black rectangle
(ISDN transformers). JAN1 and JAN2 are the first pair; below them is the
second pair, JAT1 and JAT2 respectively. The jumpers are in horizontal
position.
4.7 POWER UP SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM)
Insert the jack of the power supply adapter into the PWR connector.
Plug the adapter into the receptacle of the 230V AC mains outlet. The SS-15
BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) will start working immediately. The green LED indicator
(PWR) should be lighting up.
Warning: To avoid accidents or damage to the equipment, follow the installation
steps described earlier. The supply plug of the adapter must be the last
connection made. Do NOT connect the cables for serial configuration, phone or
PBX while the SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) unit is powered. Also, don’t take out
the antennas whole SS-15 is working.

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 13 of 26
4.8 LED INDICATORS
The SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) equipment
has three LED’s as optical status
indicators, shown in the figure to the right.
Figure 7: Location of the LED status
indicators: form top downwards the GSM
LED, the ISND LED and the power supply
LED.
The first two are bi-colour (red / green)
while the Power led lights only green.
Functions of LED`s status
Each LED may light green or red, continuously or blinking with different
frequencies, as shown in the table below:
LED STATUS SIGNIFICANCE
This dual colour LED shows the status of GSM modules. It
lights green to indicate GSM 0 and red to indicate GSM 1.
Topmost
(GSM)
Blinking fast,
5 Hz The GSM module is initializing
Blinking,
1 Hz Wrong PIN number (PIN error)
Blinking slow,
0.5 Hz
GSM module is searching for the
network (antenna not installed, or
SS-15 not in the coverage area of
the GSM network )
Off GSM module has registered to the
network and is in standby
On,
continuously GSM module is busy (in a call or
just allocated)
Middle
(ISDN)
Information about synchronization of ISDN interfaces. Here
green color indicates the NT interface and red color refers to
the TE interface of SS-15.
Blinking 0.25 sec then
one sec off
Interface not synchronized. For
example, if green LED lights 0,25
sec then red LED lights 0,25 sec it
means both interfaces are not
synchronized.
Off The ISDN interface is
synchronized
Lower
(Power) Lights continuously green
The supply voltage is present
Off There is no-supply voltage

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 14 of 26
4.9 PINOUT FOR THE CONNECTORS
The SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) features four
data connectors at the bottom of its case. All
connectors are of the same type, female RJ-
45, but they have different functions. Please
read the paragraph carefully and perform the
connections accordingly.
Serial connector
For programming the SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) the special connection cable
must be used. The special serial cable is included in the package of the SS-
15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) equipment.
The end towards the SS-15 BRI features an RJ11 connector while the end
towards the COM port of the computer features a standard female DB-9
connector.
In the drawing below the pin numbering can be seen (from left to right) of the
RJ11 female connector of the SS-15 BRI and the corresponding male RJ11
male connector on the serial programming cable.
Figure 8.Serial connector
See table below for pinout of cable and its connectors.
RJ11 Symbol DB-9 Signal
1 DSR 6 Data Set Ready, input
2 RxD 3 Receive Data, input
3 GND 5 Signal Ground
4 TxD 2 Transmit Data, output
5 DTR 4 Data Terminal Ready, input
6 CTS 8 Clear To Send, input
TE connector – used for connecting the SS-15 BRI TE interface.
The TE interface of the SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) unit is used for connection
to NT interfaces of the ISDN private branch exchange or of the ISDN public
telephony network. TE interfaces are provided with embedded termination
resistors. These resistors may be enabled by means of corresponding
jumpers, the pair JAT1 and JAT2.

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 15 of 26
See table below for pinout of TE interface.
Pin Signal
1 Not connected
2 Not connected
3 Tx
4 Rx
5 Rx
6 Tx
7 Not connected
8 Not connected
NT connector – used for connecting the SS-15 BRI NT interface.
The NT ISDN interface of the SS-15 BRI is to be used for connection to TE
interfaces of the ISDN PBX or to ISDN terminals.
For pinout of NT interface of the SS-15 BRI:
Pin Signal
1 Not connected
2 Not connected
3 Rx
4 Tx
5 Tx
6 Rx
7 Not connected
8 Not connected
SY connector
The Synchronization connector is internally paralleled to the TE interface of the
SS-15 BRI.
This is used when connecting several SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) units together,
to ensure synchronous operation of all devices.
Figure 9. Usage of SY connector

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 16 of 26
For details see Chapter 4.2, about modes of connecting the SS-15 ISDN 2
GSM unit.
4.10 MOUNTING THE SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) EQUIPMENT
When selecting the location for mounting the SS-15 BRI refer to the
recommendations in par. 6.1.
The SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) equipment can be placed either in vertical
position on a wall or horizontally on a desk or in a shelf.
The SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) and its antennas must be located as far as
possible from equipment that is sensitive to electromagnetic interferences
(radios, audio or video appliances, computer monitor, TV receivers etc). Also,
the GSM antennas must be mounted in a place with maximum strength of the
received signal.
For mounting the SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) on a wall the mounting kit must be
used (plastic dowels, woodscrews, etc) provided by SS Telecoms.
Mark the position of a pair of holes
on the wall, spaced at 55 mm
apart.
Drill the holes in the wall.
Forcibly insert into the holes the
plastic dowels.
Thread the metallic woodscrews
into the plastic dowels leaving the
end to protrude outside for some 5
mm.
Hang the case of SS-15 BRI
(ISDN 2 GSM) in the two metallic
woodscrews and push it down a
little to get it fixed.
Figure 10. Mounting SS-15 on a wall
4.11 INSTALLING THE PROGRAMMING TOOL
The Programming Tool called ISDNCFG is required in order to configure and
control the SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) equipment.
It also allows the sending and receiving of SMS messages from the computer
that is connected to the SS-15 BRI via serial cable.
This Operation, Administration, and Maintenance program runs under the
Windows Operating System.
To install the program, connect the SS-15 BRI to the PC that will be used for
programming, by means of the special serial cable for configuration.

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 17 of 26
Figure 11. Configuring SS-15 via serial connection
Set the communication on the COM serial channel where the SS-15 BRI (ISDN
2 GSM) is connected.
Insert the diskette into the 3.5 inch diskette drive unit and copy the structure of
folders and files to the hard disk drive.
Run the ISDNCFG.EXE file from the folder on the hard disk
By means of the graphic interface of the configuration program begin to adjust
the SS-15 BRI settings (parameters for GSM modules, ISDN TE and NT
interfaces, routing table, CLIP table, name of connection, etc.)
Establish the settings according to the routing functions that the application
requires.
For details, refer to the Operating Manual for the Programming Tool. The
manual includes several examples of configuration of parameters for usual
applications.
5. OPERATION AND MODES OF CONNECTION
5.1 ROUTING FOR LEAST COSTS
No matter which mode of connection is used, the purpose of the SS-15 BRI is to
achieve Least Cost Routing of calls. The LCR function of the SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2
GSM) interface ensures that in each case calls (incoming or outgoing) are
routed through the direction with minimum costs. For example, if a local
subscriber of the PBX makes a call, the prefix will be analyzed and the call will
be routed accordingly, either to the public ISDN network or to one of the GSM
operators. This way, instead of paying for a fixed-to-mobile call, there will only be
the low cost of a fixed-to-fixed of mobile-to-mobile call inside the same network.
This holds true also for calls coming in from agents in the field who make calls
from mobile phone - they will pay just for a mobile-to-mobile call, avoiding
interconnection fees. Using the DISA feature, the mobile callers may get the
extension they want, without need for a human operator of the PBX.
Alternatively, the two GSM channels of the SS-15 BRI may feature SIM cards for
the same mobile provider, but with different subscriptions. The Programming
Tool will select the best subscription for any given moment of time (for example,
the operator that provides lower tariff by night or during weekends).
Another instance of getting lower tariff by using the SS-15 BRI is when several
subscribers of the PBX make calls to a certain mobile provider. Since most of
the calls to that provider will be routed through a specific GSM module of the

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 18 of 26
SS-15 BRI, for that module a SIM with convenient tariff rate (low cost per minute
for a very large number of minutes used) may be used.
In case of connecting several SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) units to an ISDN phone
exchange, the possibilities of routing calls for least costs are even better. Firstly,
there is no limitation to two GSM modules - modules with SIM cards for two or
three mobile providers may be used, each with different subscription that allows
a better tariff rate.
Secondly, if all GSM modules in an SS-15 BRI interface are engaged (busy), the
call to a mobile network may not only be rejected but instead routed through
another SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) connected to the same PABX.
The Programming Tool uses CLIP to check the identity of the callers against a
data base. Thus calling can be restricted to certain selected (authorized)
subscribers, avoiding unnecessary costs.
Caller identification may be used for automated routing of calls.
All incoming calls that contain information about the phone number of the
subscriber (ID) will be checked by the Programming Tool against the CLIP
routing list. Depending upon the “Action” that has been set up, the program
will route the call accordingly, to the operator of the PBX, to a certain local
extension or will provide DISA tone.
DISA – direct inward access – allows callers to select the extension they want
without the help from an operator, via DTMF codes. Also, they can dial out of the
exchange.
If the incoming ID is missing, the default routing options apply.
With the “Nr. of Dialled Digits” option the SS-15 BRI makes the call
immediately after receiving the last digit - any digit sent afterwards will be
ignored.
5.2 MODES OF CONNECTION
There are a few options of connecting the SS-15 BRI equipment to an ISDN
phone exchange.
The ISDN 2 GSM interface can be connected either as TE, when it acts as a
terminal equipment, or as NT, when it simulates ISDN network.
It may also be used as a pass-through device that is “transparent” for the
calls. In this case the SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) equipment is inserted
between the public ISDN network and the PBX.
These three basic modes of connecting the SS-15 BRI can be combined in
different ways, as shown further.
a) SS-15 BRI connected via NT to a TE junction of the PABX
The NT connector of the GSM-2-ISDN linked to the TE of the PABX.
The TE of the PABX goes to the public ISDN. The TE interface can be
used to get the clock signal for synchronization, as shown below.

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 19 of 26
Figure 12. SS-15 BRI connected to TE junction of PBX
Outgoing from PABX
The PBX routes the calls to mobile networks through the SS-15 BRI unit. The
SS-15 BRI may use one or two directions for this (DIR0 for module GSM0,
one mobile network, DIR1 for module GSM1, the other mobile operator)
Incoming GSM to PABX
The decision is taken depending upon the CLIP GSM table or the GSM port
settings if the incoming phone number is not found in the table.
The call is sent only through the SS-15 BRI’s TE interface. In the CLIP-GSM
table, the “ACTION” field value must be set on “NT” and the “Port” field from
“GSM settings” menu will be set on “NT”.
b) The SS-15 BRI connected via TE to NT local of PABX and via NT to TE
junction of the PABX
The NT connector of the GSM-2-ISDN link to one TE junction of the PABX.
Other TE junction of the PABX goes to the public ISDN network. The TE
connector of the GSM-2-ISDN unit goes to the NT of a local board of the
PABX
Figure 13. SS-15 BRI connected to PBX with both NT and TE interfaces

SS-15 BRI (ISDN 2 GSM) USER MANUAL
DOC. NO: SS-15-14 (REV. 01) Page 20 of 26
Outgoing from PABX
The PABX unit verifies the number dialled and routes the call for the public
network through the dedicated interface and the call for the mobile network
through the SS-15 BRI’s NT interface. The SS-15 BRI unit selects one mobile
network operator to send the call.
Incoming to PABX
Calls get into PABX via TE connector. When an incoming GSM call comes in,
if the setting in the GSM window is Operator, the call will go to the local
extension from Target. From the PABX the call is considered to be a local call.
If the setting is DISA, the caller gets a DISA tone and can dial any local
subscriber. Calls can also be made from the public network, acting as a local
subscriber.
c) SS-15 connected to PBX on NT interface and to public ISDN via TE
interface
The public ISDN network is connected directly to the SS-15 BRI equipment
via TE interface. The NT connector is used to link to a TE junction of the
PABX.
Figure 14. SS-15 BRI inserted between PBX and public network
Outgoing calls
In this case calls coming from PABX junction through NT connector of ISDN-
2- GSM can be routed through one of the three directions: GSM0, GSM1 and
TE (which goes to the public ISDN network).
The routing is performed by the SS-15 ISDN-2- GSM unit.
Incoming to PABX from ISDN network
The calls from the public ISDN are transferred transparently towards the
PABX. For this, in the TE configuration window check “PassThrough” options.
Incoming to PABX from GSM network
The calls from GSM network are treated according to the specifications
presented in paragraph “a”.
Table of contents
Other SS Telecoms Data Logger manuals