© 2005 D420 - 06/05 2 of 24
Table of Contents
Table of Contents ...........................................................2
Display and DIP Switches ..............................................2
Dip Switch Settings ................................................2
Access Level...........................................................3
Display and Symbols Description ...........................4
User Interface ........................................................5
Display Menus................................................................6
View Menu ..............................................................6
Adjust Menu............................................................7
Miscellaneous Menu .............................................10
Testing the Control ....................................................... 11
Sequence of Operation................................................. 12
tekmarNet®4 Communication ............................... 12
Outdoor Reset ...................................................... 12
Boiler Temperature Control .................................. 14
tekmar Stager Operation ...................................... 17
Zone Load Shedding ............................................ 17
Domestic Hot Water Temperature Operation ....... 17
DHW with Low Temperature Boilers ..................... 19
Setpoint Temperature Operation...........................19
Pump Operation....................................................20
Error Messages ............................................................21
Troubleshooting ............................................................23
Warranty .......................................................................24
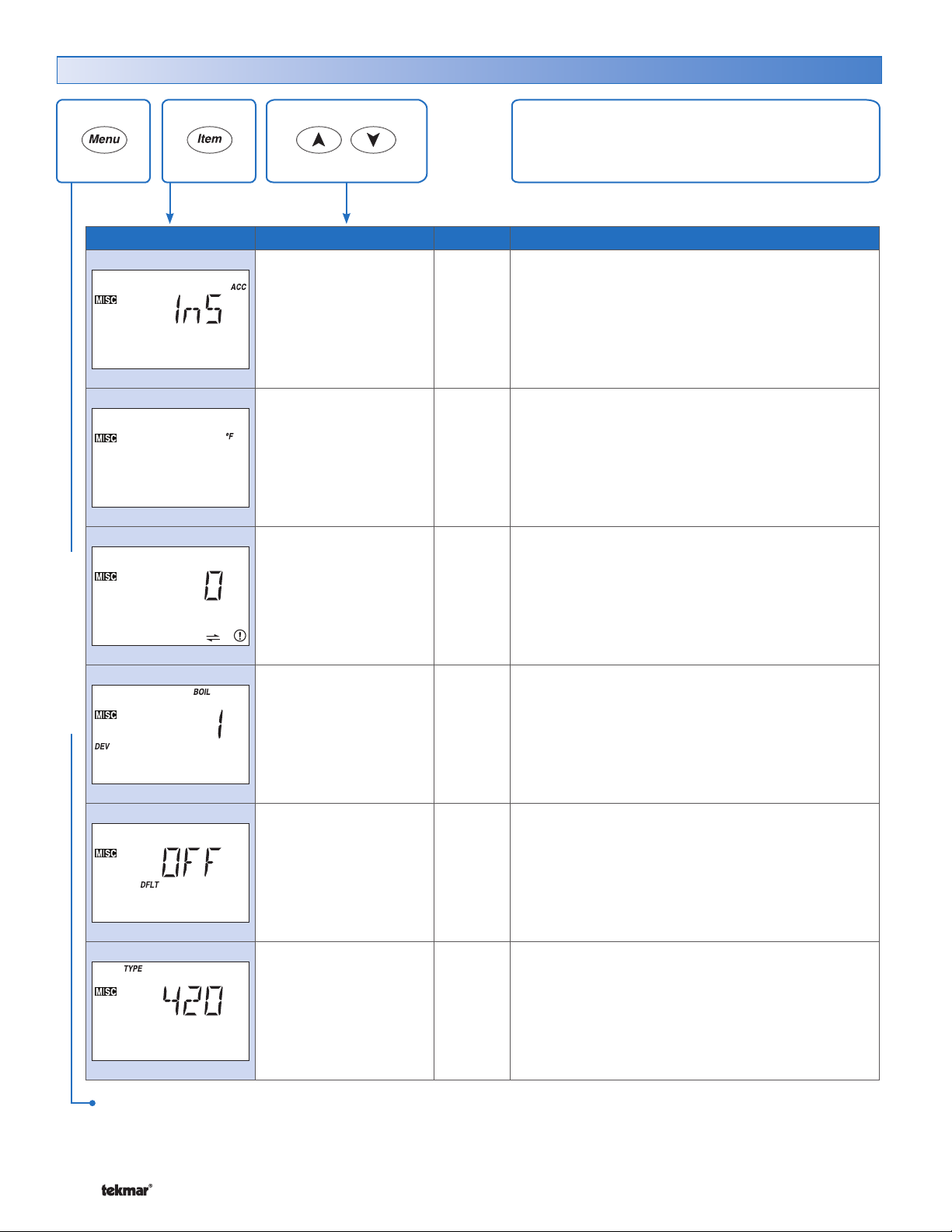
Set the DIP switch settings prior to making adjustments
to the control through the user interface. Setting the DIP
switches determines which menu items are displayed in
the user interface.
If you change a DIP switch setting while the control is
powered up, the LCD display returns to the View menu.
Lock/Unlock
Use the Lock/Unlock DIP switch to lock and unlock the Access
Level of the 420 and all connected tN4 devices, including
tN4 thermostats. For details, see “Access Levels”
• Once locked, the access level in all devices cannot be
viewed or changed.
• To determine if the control is currently locked a small
segment representing a padlock is viewed in the bottom
right hand corner of the display.
• To unlock the Access Level, set the DIP switch to
Unlock.
• To lock the Access Level, set the DIP switch to Lock.
Dip Switch Settings
Display and DIP Switches
51
52 53 54 55 56 57 58 60 61 62 63 64
Boiler DHW Setpoint C
59
C Com Boil OutVlv
Demand Demand 24 V (ac) DHW
R
65
+
Mod (dc)
–
DHW Primary
10 A
max.
66 67 68 69
N
Pump NPump
tN4
H7006B
Boil On-Off / Mod
Off / tekmar Stager
PoweredOutput 1 VA
DHW Valve:
24 V (ac) 8 VA
Made in Canada
Meets Class B: Canadian
ICES & FCC Part 15
Test
Boiler Reset Module 420
Item
Menu
tektra 991-01
Demands: 20 - 260 V (ac)
Relay Rating: 115 V (ac) 5 A
/
Do not apply power
6B
Boil On-Off / Mod
Off / tekmar Stager
/