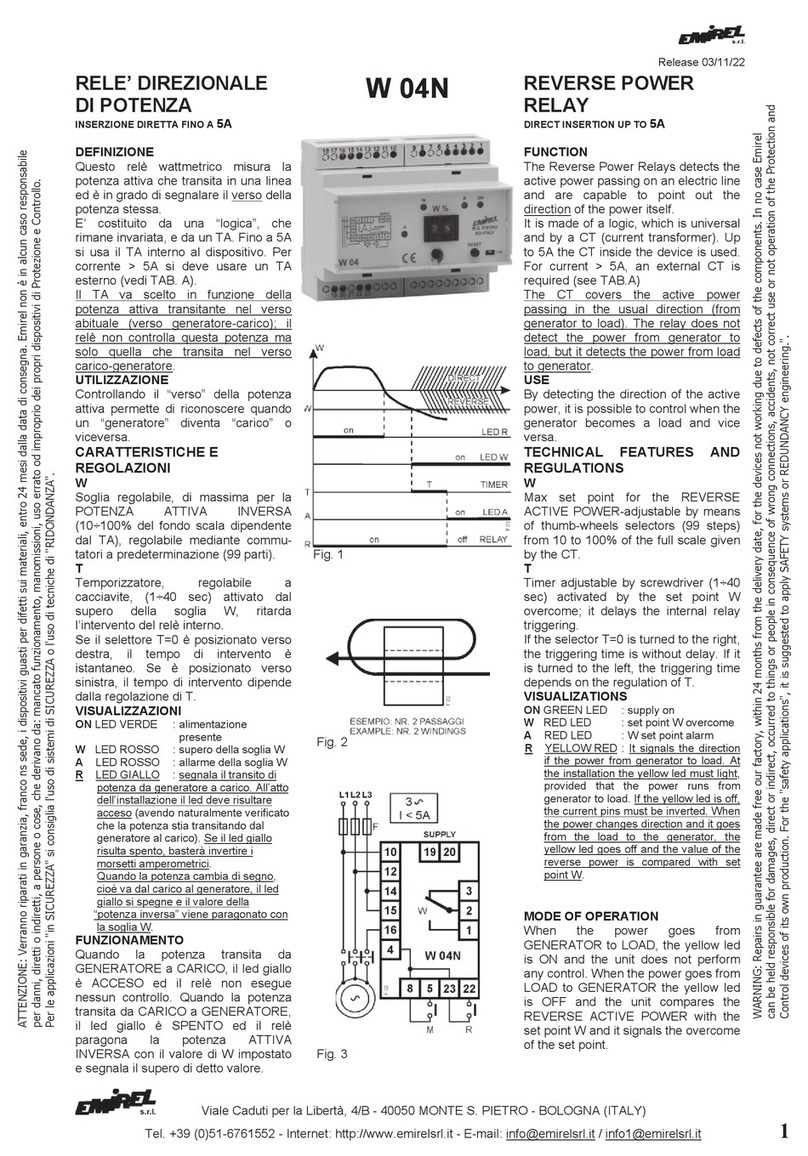
Thytronic NA016 User manual

NA016 - Manual - 05 - 2022
MANUAL
NA016
PHASE & RESIDUAL OVERCURRENT
PROTECTION RELAY

2
NA016 - Manual - 05 - 2022
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION 4
Scope and liability...........................................................................................................................................................................................4
Applicability......................................................................................................................................................................................................4
Conformity ........................................................................................................................................................................................................4
Technical support............................................................................................................................................................................................4
Copyright...........................................................................................................................................................................................................4
Warranty...........................................................................................................................................................................................................4
Safety recommendations...............................................................................................................................................................................4
Insulation tests ................................................................................................................................................................................................4
Product identification .....................................................................................................................................................................................5
Environment .....................................................................................................................................................................................................5
Graphical conventions ...................................................................................................................................................................................5
Glossary/definitions ........................................................................................................................................................................................5
2 GENERAL 9
Preface............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 9
Photo ................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 9
Main features................................................................................................................................................................................................ 10
3 TECHNICAL DATA 11
3.1 GENERAL............................................................................................................................................................................................................11
Mechanical data ...........................................................................................................................................................................................11
Insulation ........................................................................................................................................................................................................11
EMC tests for interference immunity.........................................................................................................................................................11
Voltage dip and interruption........................................................................................................................................................................11
EMC tests for interference immunity.........................................................................................................................................................11
Emission..........................................................................................................................................................................................................12
Mechanical tests...........................................................................................................................................................................................12
Climatic tests..................................................................................................................................................................................................12
Safety ..............................................................................................................................................................................................................12
Certifications..................................................................................................................................................................................................12
3.2 INPUT CIRCUITS .............................................................................................................................................................................................. 13
Auxiliary power supply
U
aux ...................................................................................................................................................................... 13
Phase current input circuits....................................................................................................................................................................... 13
Residual current input circuit..................................................................................................................................................................... 13
Binary input circuits..................................................................................................................................................................................... 13
3.3 OUTPUT CIRCUITS........................................................................................................................................................................................... 13
Output relays................................................................................................................................................................................................. 13
3.4 MMI.....................................................................................................................................................................................................................14
3.5 COMMUNICATION INTERFACES ...................................................................................................................................................................14
Local port........................................................................................................................................................................................................14
Remote ports..................................................................................................................................................................................................14
3.6 GENERAL SETTINGS ........................................................................................................................................................................................14
3.7 PROTECTIVE ELEMENTS .................................................................................................................................................................................14
Phase overcurrent - 50/51............................................................................................................................................................................14
Residual overcurrent - 50N/51N .................................................................................................................................................................15
3.8 CONTROL AND MONITORING........................................................................................................................................................................16
Trip Circuit Supervision - 74TCS..................................................................................................................................................................16
Circuit Breaker monitoring ..........................................................................................................................................................................16
Oscillography (DFR) ......................................................................................................................................................................................16
3.9 MEASURES ........................................................................................................................................................................................................16
4 FUNCTION CHARACTERISTICS 17
4.1 HARDWARE DESCRIPTION.............................................................................................................................................................................17
Power supply board......................................................................................................................................................................................17
CPU board...................................................................................................................................................................................................... 18
Input board .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 18
MMI (keyboard, LED and display) ............................................................................................................................................................. 18
4.2 SOFTWARE DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................................................................. 19
Kernel ............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 19
Drivers............................................................................................................................................................................................................ 19
Application..................................................................................................................................................................................................... 19
Base protocol (kernel)................................................................................................................................................................................. 19
Calibration (kernel)....................................................................................................................................................................................... 19
Communication (drivers)............................................................................................................................................................................. 19
MMI (drivers) ................................................................................................................................................................................................ 19
Data Base (application/drivers)................................................................................................................................................................. 20
Self-test (application) .................................................................................................................................................................................. 20

3
NA016 - Manual - 05 - 2022
Development tools ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 20
4.3 I/O DESCRIPTION..............................................................................................................................................................................................21
Metering inputs .............................................................................................................................................................................................21
Signal processing..........................................................................................................................................................................................21
Use of measured values...............................................................................................................................................................................22
Binary inputs ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 23
Output relays..................................................................................................................................................................................................24
LED indicators................................................................................................................................................................................................25
Communication interfaces...........................................................................................................................................................................26
4.4 PROTECTIVE ELEMENTS .................................................................................................................................................................................27
Rated values...................................................................................................................................................................................................27
Phase overcurrent - 50/51........................................................................................................................................................................... 29
Residual overcurrent - 50N/51N .................................................................................................................................................................31
4.5 CONTROL AND MONITORING....................................................................................................................................................................... 33
Data Logger................................................................................................................................................................................................... 33
Trip circuit supervision - 74TCS.................................................................................................................................................................. 33
Circuit breaker supervision .........................................................................................................................................................................35
Test..................................................................................................................................................................................................................36
Oscillography ................................................................................................................................................................................................36
5 MEASURES, LOGIC STATES AND COUNTERS 37
Measures........................................................................................................................................................................................................37
Circuit breaker ...............................................................................................................................................................................................37
Counters..........................................................................................................................................................................................................37
Fault recording - SFR....................................................................................................................................................................................37
Event recording - Events..............................................................................................................................................................................37
Setting changes - Settings ......................................................................................................................................................................... 38
Info.................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 38
Protections trip ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 38
Self-test.......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 38
Oscillography - DFR ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 39
6 INSTALLATION 41
6.1 PACKAGING.......................................................................................................................................................................................................41
6.2 MOUNTING........................................................................................................................................................................................................41
6.3 ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS ......................................................................................................................................................................... 43
6.4 NOMINAL CURRENT InAND IEn SETTING ................................................................................................................................................. 48
6.5 NOMINAL CURRENT InSETTING FOR LPCT .............................................................................................................................................. 50
6.6 LED ALLOCATION..............................................................................................................................................................................................51
6.7 FINAL OPERATIONS .........................................................................................................................................................................................51
7 PROGRAMMING AND SETTINGS 52
7.1 SW ThyVisor ......................................................................................................................................................................................................52
ThyVisor installation......................................................................................................................................................................................52
ThyVisor use...................................................................................................................................................................................................52
7.2 MMI (Man Machine Interface) ..................................................................................................................................................................... 53
Reading variables (READ)........................................................................................................................................................................... 53
Setting modifying (SET) ............................................................................................................................................................................... 53
Test...................................................................................................................................................................................................................54
Communication..............................................................................................................................................................................................55
Reset................................................................................................................................................................................................................55
DEFAULT (Option) ..........................................................................................................................................................................................55
Data/time setting (Time) ...............................................................................................................................................................................55
7.3 MENU TREE........................................................................................................................................................................................................56
7.4 MAINTENANCE................................................................................................................................................................................................ 58
7.5 REPAIR............................................................................................................................................................................................................... 58
7.6 PACKAGING...................................................................................................................................................................................................... 58
8 APPENDIX 59
8.1 APPENDIX A1 - Inverse time IEC curves .................................................................................................................................................... 59
Mathematical formula ................................................................................................................................................................................. 59
Phase overcurrent 50/51 - Standard inverse time curve (IEC 60255-3/BS142 type A)..................................................................... 60
Phase overcurrent 50/51 - Very inverse time curve (IEC 60255-3/BS142 type B) ..............................................................................61
Phase overcurrent 50/51 - Extremely inverse time curve (IEC 60255-3/BS142 type C).....................................................................62
8.2 APPENDIX B1 - I/O Diagram .......................................................................................................................................................................... 63
8.3 APPENDIX B2 - Interfaces ..............................................................................................................................................................................64
8.4 APPENDIX B3 - Connection diagrams ..........................................................................................................................................................65
8.5 APPENDIX C - Dimensions............................................................................................................................................................................. 68
8.6 APPENDIX D - EC Declaration of conformity .............................................................................................................................................. 69

INTRODUCTION 4
NA016 - Manual - 05 - 2022
1 INTRODUCTION1 INTRODUCTION
Scope and liability
This document describes the functions, the technical data of NA016 devices; instructions for mount-
ing, setting and commissioning are included.
This manual has been checked out, however, deviations from the description cannot be completely
ruled out, so that no liability in a legal sense for correctness and completeness of the information or
from any damage that might result from its use is formally disclaimed.
The information given in this document is reviewed regularly; any corrections and integration will be
included in subsequent editions that are identified by the date of revision.
We appreciate any suggestions for improvement.
We reserve the right to make technical improvements without notice.
Applicability
This manual is valid for NA016 devices with firmware version 1.01 and following.
Revision history is listed in appendix.
Conformity
The product complies with the CEE directives:
• EMC Council Directives: 2014/30/EEC
• Low voltage Directives: 2014/35/EEC
Technical support
Contact: THYTRONIC Technical Service www.thytronic.it
Copyright
All right reserved; It is forbidden to copy, modify or store material (document and sw) protected by
copyright without Thytronic consent.
Warranty
Thytronic warrants devices against defects in materials and workmanship under normal use for a
period of ONE (1) YEAR from the date of retail purchase by the original end-user purchaser (“War-
ranty Period”).
Safety recommendations
The warming contained in this document are all-important for safety; special attention must be paid
to the following symbols:
Installation and commissioning must be carried out by qualified person; Thytronic assumes no re-
sponsibility for damages caused from improper use that does not comply all warning and caution in
this manual.
In particular the following requirements must be met:
• Remove power before opening it.
• Verify the voltage absence by means suitable instrumentation on relay connections; attention must
be paid to all circuits supplied by external sources (binary input, CT, etc...)
• Care must be taken when handling metal parts (front panel, connectors).
Insulation tests
After insulation tests, hazardous voltages (capacitor charges,...) may be arise; it is advisable to grad-
ually reduce the test voltage avoiding to erase it abruptly.
WARNING Death, severe personal injury or substantial property damage can result if proper precautions
are not taken.
CAUTION Minor personal injury or property damage can result if proper precautions are not taken
CAUTION
Settings must be established on the basis of a coordination study.
Numerical values inside examples have educational purpose only; they don’t be used, in no way,
for actual applications.

INTRODUCTION 5
NA016 - Manual - 05 - 2022
Product identification
Each device is equipped with:
• Identification label installed on the front side with following informations: code number, phase and
residual nominal currents, auxiliary voltage range and CE mark:
• Test label with following informations: data, serial number and test operator signature.
Environment
The NA016 device must be employed according to the environment conditions shown (see technical
data).
In case of different environment conditions, appropriate provisions must be provided (conditioning
system, humidity control, etc...).
If contaminants are present (dust, corrosive substances, etc...), filters must be provided.
Graphical conventions
The CEI/IEC and ANSI symbols is employed where possible:
e.g.: 51 = ANSI code concerning the overcurrent element.
Following text formats are used:
The ThyVisor[1] menu:
Phase overcurrent -50/51
The parameter description (measures, thresholds, operate time,...) and related value:
First threshold 50/51 denite time
I>def
The display messages (MMI) are shown as:
NA016
Notes are highlighted with cursive letters inside colored bar
Note: Useful description note
Glossary/definitions
I
En Relay residual nominal current
I
Enp Residual CT primary nominal current
I
nRelay phase nominal current
I
np Phase CT primary nominal current
50/51 Phase overcurrent ANSI code
50N/51N Residual overcurrent ANSI code
74CT CT supervision
74TCS Trip Circuit Supervision
DFR Digital Fault Recorder (Oscillography)
SER Sequential Event Recorder
SFR Sequential Fault Recorder
ANSI American National Standard Institute
Note 1 The graphic interface and the operation of the ThyVisor software are described in the relative chapters
Standard CTs - Logger Standard CTs - No Logger
LPCT inputs - Logger LPCT inputs - No Logger
NA016#xx00
In5A 1A
50-51
50N-51N
5A
UAUX 24-230 Vac/dc
IEn 5A 1A 5A
1
2
3
4
5
NA016#xx10
In5A 1A
50-51
50N-51N
CB OPEN
CB CLOSED
TCS
5A
UAUX 24-230 Vac/dc
IEn 5A 1A 5A
1
2
3
4
5
NA016#xx01
InRated 50...500A/Extended 50...1250A
50-51
50N-51N
UAUX 24-230 Vac/dc
IEn 5A 1A 5A
1
2
3
4
5
NA016#xx11
InRated 50...500A/Extended 50...1250A
50-51
50N-51N
CB OPEN
CB CLOSED
TCS
UAUX 24-230 Vac/dc
IEn 5A 1A 5A
1
2
3
4
5

INTRODUCTION 6
NA016 - Manual - 05 - 2022
IEEE Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
IEC International Electrotechnical Commission
CENELEC Comité Européen de Normalisation Electrotechnique
52 o CB (Circuit Breaker) Circuit Breaker
52a Auxiliary contact in the breaker that is in the same position as the
breaker. It can be assigned to a binary input to locate the CB posi-
tion (Breaker failure and/or CB diagnostic functions). (52a open = CB
open)
52b Auxiliary contact in the breaker that is in the opposite position as the
breaker (52b open = CB closed)
K1...K4 Output relays
tTR1... tTR4 Output relay minimum pulse width
Latched Output relay with latched operation (manual reset) Output relay with
latched operation (automatic reset)
No-latched Output relay with no-latched operation (automatic reset)
CT or TA Current Transformer
LPCT Low Power Current Transformer
P1 IEC nomenclature for primary polarity mark of CTs (as an alternative to
a ANSI dot)
P2 IEC nomenclature for primary polarity mark of CTs (as an alternative to
a ANSI no-dot)
S1 IEC nomenclature for secondary polarity mark of CTs (as an alternative
to a ANSI dot)
S2 IEC nomenclature for secondary polarity mark of CTs (as an alternative
to a ANSI no-dot)
Self test Diagnostic
Start Leave an initial condition or reset condition (Pickup)
Trip Operation (with operate time)
Operating time Duration of time interval between the instant when the character-
istic quantity in reset condition is changed, under specified condi-
tions, and the instant when the relay operates
Dropout ratio The ratio of a reset value to an operate value in well-specified con-
ditions. The dropout ratio may be lower or greater than 1 according
as an over or under element is considered
Reset time Duration of the time interval between the instant when the charac-
teristic quantity in operate condition is changed, under specified
conditions, and the instant when the relay operates.
The stated reset time is related to a step variation of characteristic
quantity in operate condition to the reset condition.
Overshoot time The critical impulse time for a relay which is in its reset condition,
is the longest duration a specified change in the input energizing
quantity(ies) (characteristic quantity), which will cause the relay
to change to operate condition, can be applied without the relay
switches. The overshoot time is the difference from the operate time
and the critical impulse time.
The declared values for the overshoot time are applicable with the
lower setting value of the operation time.
MMI (Man Machine Interface) Operator front panel
ThyVisor Setting and monitoring software
Log file A text file that lists actions that have occurred (ThyVisor).
J2SE Java Platform Standard Edition
Sw Software
Fw Firmware
Upgrade Firmware upgrade
XML eXtensible Markup Language

INTRODUCTION 7
NA016 - Manual - 05 - 2022
Symbols.ai
Symbols
I>> Start
I>> BF_OUT
IPh Block2
Logic internal signal (output); may be a logical state
(e.g.I>> Start
) or a numerical value
It is available for reading (ThyVisor + communication interface)
Logic external signal (intput); may be a command coming from a binary input or a sw command
It is available for reading (ThyVisor + communication interface)
Internal signal (e.g. Breaker Failure output state concerning to the 2nd threshold of the 50 element)
It is not available for reading (missing arrow)
AND and NAND logic gates
OR and NOR logic gates
Limit block (I>> threshold).
Computation block (Max phase current)
Threshold setting (e.g. pickup
I>>)
.
The value is available for reading and is adjustable by means ThySetter + MMI.
Switch
ON delay timer with reset (tON delay)
ON delay timer without reset (tON delay)
OFF delay timer (dropout) without reset (tDROP delay)
Curve type (definite/inverse time)
0T
IL3
Max[IL1 ,IL2 ,IL3 ]
IL2
IL1
tON tON tON tON
t
RESET
INPUT
OUTPUT
tDROP
tON tON
t
INPUT
OUTPUT
tON tON tON
t
INPUT
OUTPUT
0T
tON
& &
≥1≥1
EXOR logic gate
tDROP
=1
I >>
II ≥
I>>
tON
RESET
0T
0 T

INTRODUCTION 8
NA016 - Manual - 05 - 2022
Symbols1 .ai
tON tON tON
t
RESET
INPUT
OUTPUT
tDROP
tDROP
tDROP tDROP
Minimum pulse width operation for output relays (tTR
)
tTR
t
tTR
INPUT
OUTPUT
tTR
0 T
tTR
t
tTR
INPUT
OUTPUT
Latched operating mode for output relays and LEDs
Pulse operating mode for output relays
t
INPUT
OUTPUT
Latched
tTR
T0
RESET
OFF delay timer (dropout) with reset (tDROP delay)

Headquarter: 20139 Milano - Piazza Mistral, 7 - Tel. +39 02 574 957 01 ra - Fax +39 02 574 037 63
Factory: 35127 Padova - Z.I. Sud - Via dell’Artigianato, 26 - Tel. +39 049 894 770 1 ra - Fax +39 049 870 139 0
www.thytronic.it thytronic@thytronic.it www.pro-n.it
2 GENERAL2 GENERAL
Preface
The relay type NA016 can be used in radial networks as feeder or power transformer protection.
In solidly grounded systems the residual overcurrent protection can be used on feeders of any length,
while in ungrounded or Petersen coil and/or resistance grounded systems, the residual overcurrent
protection can be used on feeders of small length in order to avoid unwanted trippings due to the
capacitive current contribution of the feeder on external ground fault.
The NA016 protection relay may be shipped with traditional CTs or low power (LPCT) current inputs.
Following input circuits are available:
• Three phase current and one residual current inputs with nominal currents independently select-
able at 1 A or 5 A using DIP-switch (CT inputs) or 50...1250 primary amperes (LPCT inputs).
• Three binary inputs.
In addition to the main protection element, the Trip Circuit Supervision (TCS) is also provided.
Setting, programming and reading operations must be effected by means of Personal Computer with
ThyVisor software or by means of remote communication interface (RS485 bus); all operations must
be performed through MMI.
The NA016 hardware case is suitable for flash and rack mounting
Other options are:
• Auxiliary power supply operating range.
• Communication protocols (Modbus or IEC60870-5-103).

Headquarter: 20139 Milano - Piazza Mistral, 7 - Tel. +39 02 574 957 01 ra - Fax +39 02 574 037 63
Factory: 35127 Padova - Z.I. Sud - Via dell’Artigianato, 26 - Tel. +39 049 894 770 1 ra - Fax +39 049 870 139 0
www.thytronic.it thytronic@thytronic.it www.pro-n.it
Photo
Main features
• Metallic case.
• Backlight LCD 2x16 Display.
• Eight LEDs that may be joined with matrix criteria to many and various functions.
• RESET key to clear LED indications and latched output relays.
• Free settable three binary inputs.
• Independently settable for start, trip, self-test and control four output relay (K1...K4) Each output
relay may be set with normally energized or normally de-energized operating mode and manual or
automatic reset (latched/no-latched).
• Rear RS485 port, with ModBus protocol.
• RS232 front serial port (local communication for ThyVisor).
• Real time clock with super capacitor backup.
The most significant constructive features are:
• Galvanically insulated input and output circuits (communication and binary circuits included).
• Fast sampling rate for inputs.
• Optimum filtering of input signals through combined use of analog and digital filters.
• Traditional electromechanical-type final output contacts with continuous monitoring of control coil
continuity.
• Auxiliary supply comprising a switching-type voltage stabilizing circuit having a very wide working
range and a very small power dissipation
• Nominal frequency: 50 or 60 Hz.
The most significant operating features are:
• Programming of operating modes and parameters by means of the front keys and alphanumeric
display, with a programming procedure based on carrying out guided selections and on explicit and
immediate signalling of the operations being performed, so that such procedure can be carried out
without coding tables or mnemonic informations.
• The feature modification operations do not interrupt the normal functions of the relay.
• Impossibility of programming unacceptable parameter values, thanks to the automatic limitation of
top and bottom scale values for the relative setting ranges.
• Currents are sampled 64 times per period and measured in the effective value (RMS) of the funda-
mental component using the DFT (Discrete Fourier Transform) algorithm and digital filters.
• The fault recorder (SFR) runs continuously capturing in circular mode the last twenty events upon
trigger of binary input/output and/or element pickup (start-trip).
• The event recorder (SER) runs continuously capturing in circular mode the last three hundred
events upon trigger of binary input/output.
• Recording of the last setting changes (Logger).
• Digital fault recorder (DFR) in COMTRADE format (oscillography).

TECHNICAL DATA 11
NA016 - Manual - 05 - 2022
3 TECHNICAL DATA3 TECHNICAL DATA
3.1 GENERAL
Mechanical data
Mounting Flush, Rack
External dimensions 177 x 107 x 105 (high x width x depth)
Terminals screw connection
Mass 1.2 kg
Reference standards EN 60529, EN 60529/A1
• Degrees of protection provided by enclosures (IP Code)
• Front IP52
• Terminals IP20
Insulation
Reference standards EN 60255-5 IEC 60255-5
High voltage test (50 Hz 60 s)
• Auxiliary power supply 2 kV
• Input circuits 2 kV
• Output circuits 2 kV
• Output circuits (between open contacts) 1 kV
• Communication interfaces 500 V
Impulse voltage withstand test (1.2/50 ms):
• Auxiliary power supply 5 kV
• Input circuits 5 kV
• Output circuits 5 kV
• Output circuits (between open contacts) 2.5 kV
Insulation resistance >100 MW
EMC tests for interference immunity
Reference standards
• Product standard for measuring relays EN 50263
• Generic standards immunity for industrial environments EN 61000-6-2
• Electromagnetic compatibility requirements for measuring relays and protection equipment
EN 60255-26
• Apparati di automazione e controllo per centrali e stazioni elettriche
• Compatibilità elettromagnetica - Immunità ENEL REMC 02
• Normativa di compatibilità elettromeccanica per apparati e sistemi
ENEL REMC 01
Voltage dip and interruption
Reference standards EN 61000-4-29
IEC 60255-22-11
Voltage dips, short interruptions and voltage variations on dc input power port immunity tests
Auxiliary power supply in dc energizing quantity
• Interruption (UT=40%) 100 ms
• Interruption (UT=0%) 50 ms
• Voltage variations (UT=80...120%) 10 s
EMC tests for interference immunity
Reference standards EN 60255-22-1 IEC 60255-22-1
EN 61000-4-12 EN 61000-4-12
Damped oscillatory wave
• 0.1 MHz and 1 MHz common mode 2.5 kV
• 0.1 MHz and 1 MHz differential mode 1.0 kV
• Ring wave common mode 2.0 kV
• Ring wave differential mode 1.0 kV
Reference standards EN 60255-22-2 IEC 60255-22-2
EN 61000-4-2 IEC 61000-4-2
Electrostatic discharge
• Contact discharge 6 kV
• Air discharge 8 kV
Reference standards EN 60255-22-3 IEC 60255-22-3
EN 61000-4-3 IEC 61000-4-3
Radiated radio-frequency fields
• 80...1000 MHz AM 80% 10 V/m
• 900 MHz Pulse modulated 10 V/m

TECHNICAL DATA 12
NA016 - Manual - 05 - 2022
Reference standards EN 60255-22-4 IEC 60255-22-4
EN 61000-4-4 IEC 61000-4-4
Fast transient burst (5/50 ns)
• Auxiliary power supply 2 kV
• Input circuits 4 kV
Reference standards EN 60255-22-5 IEC 60255-22-5
EN 61000-4-5 IEC 61000-4-5
High energy pulse
• Uaux (line-to-ground 10 ohm, 9 mF) 2 kV
• Uaux (line-to-line 0 ohm, 18 mF) 1 kV
• I/O ports (line-to-ground 40 ohm, 0.5 mF) 2 kV
• I/O ports (line-to-line 40 ohm, 0.5 mF) 1 kV
Reference standards EN 60255-22-6 IEC 60255-22-6
EN 61000-4-6 IEC 61000-4-6
Conducted radio-frequency fields
• 0.15...80 MHz AM 80% 1kHz 10 V
Reference standards EN 60255-22-7 IEC 60255-22-7
EN 61000-4-16 IEC 61000-4-16
Power frequency immunity tests
• Dc voltage 30 V
• 50 Hz continuously 30 V
• 50 Hz 1 s 300 V
• 0.015...150 kHz 30 V
Reference standards EN 61000-4-8 IEC 61000-4-8
Magnetic field 50 Hz
• 50 Hz continuously 100 A/m
• 50 Hz 1 s 1 kA/m
Reference standards EN 61000-4-10 IEC 61000-4-10
Damped oscillatory magnetic field
• Damped oscillatory wave 0.1 MHz 30 A/m
• Damped oscillatory wave 1 MHz 30 A/m
Emission
Reference standards EN 60255-25 IEC 60255-25
EN 61000-6-4 IEC 61000-6-4
EN 55011 CISPR 11
Electromagnetic emission tests
• Conducted emission auxiliary power supply 0.15...0.5 MHz 79 dB mV
• Conducted emission auxiliary power supply 0.5...30 MHz 73 dB mV
• Radiated emission 30...230 MHz 40 dB mV/m
• Radiated emission 230...1000 MHz 47 dB mV/m
Mechanical tests
Reference standards EN 60255-21-1 EN 60255-21-2 RMEC01
Vibration, shock, bump and seismic tests on measuring relays and protection equipment
• EN 60255-21-1 Vibration tests (sinusoidal) Class 1
• EN 60255-21-2 Shock and bump test Class 1
Climatic tests
Reference standards IEC 60068-x ENEL R CLI 01 CEI 50
Operating temperature -25...+70 °C
Storage temperature -40...+85 °C
Permissible relative humidity 10...95 %
Atmospheric pressure 70...110 kPa
Safety
Reference standards EN 61010-1
Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control and laboratory use
Pollution degree 3
Reference voltage 250 V
Overvoltage category III
Certifications
Reference standards
Product standard for measuring relays EN 50263
CE Conformity
• EMC Directive 2014/30/EEC
• Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EEC
• Type tests IEC 60255-6

TECHNICAL DATA 13
NA016 - Manual - 05 - 2022
3.2 INPUT CIRCUITS
Auxiliary power supply
U
aux
Voltage
Nominal value (range)[1] 24...230 V~/-
Operative range 19...265 V~/19...300 V-
Inrush current (max)
• 24 V- 3 A, 1 ms
• 48 V- 5 A, 1 ms
• 110 V- 10 A, 1 ms
• 230 V~ 40 A, 1 ms
Frequency (for alternate voltage supply) 45...66 Hz
Max distortion factor ( for alternating voltage supply) 15%
Max alternating component (for dc voltage supply):
• Full wave rectified sine wave 100 %
• Sine wave 80 %
Power consumption:
• Maximum (energized relays, three LEDs, backlight ON) 4.5 W (UAUX = 24 V-)
• Maximum (energized relays, three LEDs, backlight ON) 9 VA (UAUX = 230 V~)
Phase current input circuits
Standard CTs:
Connections M4 terminals
Relay nominal phase current In1 A or 5 A selectable by DIP-switch
Permanent overload 25 A
Thermal overload (1 s) 500 A
Dynamic overload (half cycle) 1250 A
Rated consumption (for any phase) ≤0.002 VA with In=1 A
≤0.04 VA with In=5 A
LPCT - Low Power Current Transformers:
Connections RJ45 plug
Relay nominal phase current In100 A
Extended primary current 50 A...1250 A selectable by DIP-switch
Max primary current 12.5 kA
Nominal secondary voltage (with Inp = 100 A) 22.5 mV
Residual current input circuit
Relay nominal residual current IEn 1 A or 5 A selectable by DIP-switch
Permanent overload 25 A
Thermal overload (1 s) 500 A
Dynamic overload (half cycle) 1250 A
Rated consumption ≤0.006 VA with IEn=1 A
≤0.12 VA with IEn=5 A
Binary input circuits
Quantity 2
Type optocoupler
Operative range 24...265 V~/-
Min activation voltage UDIGmin 18 V
Max consumption, energized 3 mA
3.3 OUTPUT CIRCUITS
Output relays
Quantity 4
Type of contacts changeover (SPDT, type C)
Nominal current 8 A
Nominal voltage/max switching voltage 250 V~/400 V~
Breaking capacity:
• Direct current (L/R = 40 ms) 50 W (K1, K2, K4 trip)
• Direct current (L/R = 40 ms) 30 W (K3 signalling)
• Alternating current (l= 0,4) 1250 VA
Make 1000 W/VA
Short duration current (0,5 s) 30 A
Minimum switching load 300 mW (5 V/ 5 mA)
Life:
• Mechanical 106operations
Electrical 105operations
Minimum pulse width (K1tTR...K4tTR) 0.01...0.50 s (step 0.01 s)
Note 1 The different versions must be select on order

TECHNICAL DATA 14
NA016 - Manual - 05 - 2022
3.4 MMI
Display 16x2 LCD backlight module
LEDs
Quantity 8
• ON/fail (green) 1
• Start (yellow) 1
• Trip (red) 1
• Trip I>, I>>, I>>> (red) 1
• Trip IE>, IE>> (red) 1
• 52a - Circuit Breaker position (red) 1
• 52b - Circuit Breaker position (red) 1
• TCS - Trip Circuit Supervision (red) 1
Keyboard 8 keys[1]
3.5 COMMUNICATION INTERFACES
Local port
Connection RJ10
Baud rate 19200 bps
Parity None
Protocol Modbus RTU®
Remote ports
RS485
• Connection screw terminals
• Baud rate 1200...57600 bps
• Protocol[2] ModBus®RTU
IEC 60870-5-103
3.6 GENERAL SETTINGS
Relay nominal frequency fn50, 60 Hz
Phase CT primary nominal current Inp [3] 1 A...1000 A
1...99 A (step 1 A)
100...1000 A (step 5 A)
Residual CT primary nominal current IEnp [4] 1 A...1000 A
1...99 A (step 1 A)
100...1000 A (step 5 A)
3.7 PROTECTIVE ELEMENTS
Phase overcurrent - 50/51
I> Element
I> Curve type (I>Curve)Inverse[5] IEC/BS A, B, C
50/51 First threshold inverse time (I>inv) 0.100...2.50 In
0.100...0.999 In (step 0.001 In)
1.00...2.50 In (step 0.01 In)
Operating time (t>inv) 0.02...60.0 s
0.02...9.99 s (step 0.01 s)
10.0...60.0 s (step 0.1 s)
Nota 1 The “ O” and “ I” keys are not actives
Note 2 The different versions must be select on order
Note 3 The nominal current settings doesn’t concern the 50/51 protection elements; they must agree with nominal primary current for traditional CT
inputs or dip-switch 50...1250 A for LPCT inputs for a right reading of the phase current primary values (Reading Direct).
Note 4 The nominal current settings doesn’t concern the 50N/51N protection elements; they must agree with nominal primary current of the CT inputs
for a right reading of the residual current primary values (Reading Direct).
Note 5 Standard Inverse Time (IEC 255-3/BS142 type A or SIT): t = 0.14 · t>inv / [(I/I>inv)0.02 - 1]
Very Inverse Time (IEC 255-3/BS142 type B or VIT): t = 13.5 · t>inv / [(I/I>inv) - 1]
Extremely Inverse Time (IEC 255-3/BS142 type C or EIT): t = 80 · t>inv / [(I/I>inv)2 - 1]
t:operate time
I>inv:pickup value
t>inv:operate time setting
Asymptotic reference value: 1.1 I>inv
Minimum operate time: 0.1 s
Equation is valid for 1.1 ≤ I/I>inv ≤ 20:
- with traditional CTs and setting I>inv ≥ 2.0 In, the measuring upper limit is 40 In
- with LPCT sensors and setting I>inv = 1.0 In and In = 625 A the measuring upper limit is 12500 A

TECHNICAL DATA 15
NA016 - Manual - 05 - 2022
I>> Element
50/51 Second threshold definite time (I>>def)[1] 0.100...20.0 In
0.100...0.999 In (step 0.001 In)
1.00...9.99 In (step 0.01 In)
10.0...20.0 In (step 0.1 In)
I>>def Operating time (t>>def) 0.03...10.00 s (step 0.01 s)
I>> Reset time delay (t>>RES)0.00...1.00 s (step 0.01 s)
I>>> Element
50/51 Third threshold definite time (I>>>def) 0.100...20.0 In
0.100...0.999 In (step 0.001 In)
1.00...9.99 In (step 0.01 In)
10.0...20.0 In (step 0.1 In)
I>>>def Operating time (t>>>def) 0.03...10.00 s (step 0.01 s)
I>>> Reset time delay (t>>>RES)0.00...1.00 s (step 0.01 s)
Pickup time ≤ 0.03 s
Dropout ratio 0.95...0.98
Dropout time ≤ 0.04 s
Overshoot time 0.03 s
Pickup accuracy ± 4% ± 1% In
Operate time accuracy 5% or ± 10 ms
Residual overcurrent - 50N/51N
IE> Element
50N/51N First threshold definite time (IE>def) 0.005...5.00 IEn
0.005...0.999 IEn (step 0.001 IEn)
1.00...5.00 IEn (step 0.01 IEn)
IE>def Operating time (tE>def) 0.03...180 s
0.03...9.99 s (step 0.01 s)
10.0...99.9 s (step 0.1 s)
100...180 s (step 1 s)
IE> Reset time delay (tE>RES)0.00...1.00 s (step 0.01 s)
IE>> Element
50N/51N Second threshold definite time (IE>>def) 0.005...5.00 IEn
0.005...0.999 IEn (step 0.001 IEn)
1.00...5.00 IEn (step 0.01 IEn)
IE>>def Operating time (tE>>def) 0.03...10.00 s (step 0.01 s)
IE>> Reset time delay (tE>>RES) 0.00...1.00 s (step 0.01 s)
Pickup time ≤ 0.03 s
Dropout ratio 0.95...0.98
Dropout time ≤ 0.04 s
Overshoot time 0.03 s
Pickup accuracy ± 4% ± 1% IEn
Operate time accuracy 5% or ± 10 ms
Note 1 For all definite time elements the upper limit for measuring is 40 In for traditional CT input versions or 12.5 kA (primary current) for LPCT input
versions:
- 40 In for traditional CT input versions
- 12500 A (primary current) for LPCT input versions, so the maximum threshold adjustment depends on the In setting (Dip switch);
eg: with In = 1000 A the max setting for I>>def and I>>>def thresholds is 12500/1000 = 12.5 In

TECHNICAL DATA 16
NA016 - Manual - 05 - 2022
3.8 CONTROL AND MONITORING
Trip Circuit Supervision - 74TCS
Enable (74TCS) On / Off
Operating time 40 s
Reset time delay 6 s
Circuit Breaker monitoring
Circuit breaker diagnostic
Diagnostic (CB Diagnostic) On / Off
Oscillography (DFR)
Format COMTRADE
Number of records 2
Recording mode circular
Sampling rate 16 samples / power cycle
Set trigger:
• Pre-trigger time 0...63 T[1] [2]
• Trigger inputs IN1, IN2, IN3
• Triggeroutputs K1...K4
• Manual Trigger ThyVisor
• General Trigger general from start / trips Start, Trip
• Trigger from start / trips Start I>, I>>, ...Trip I>...
Set analog channels:
Analog 1...Analog 4
• Instantaneous currents value iL1, iL2, iL3, iE
• RMS value of the fundamental component for phase currents IL1, IL2, IL3
• RMS value of the fundamental component for residual current IE
Set digital channels:
• Inputs IN1, IN2, IN3
• Outputs K1...K4
• General from start / trips Start, Trip
3.9 MEASURES
RMS value of the fundamental component for phase currents (IL1, IL2, IL3)
RMS value of the fundamental component for residual current (IE)
Note 1 - T = number of power cycles
Example, with setting T=4 the pre-trigger is 80 ms with f = 50 Hz

FUNCTION CHARACTERISTICS 17
NA016 - Manual - 05 - 2022
4 FUNCTION CHARACTERISTICS4 FUNCTION CHARACTERISTICS
4.1 HARDWARE DESCRIPTION
The following figure illustrates the basic structure of the relay.
Printed boards hold the circuit components arranged according to a modular allocation of the main
functions.
Power supply board
All the components necessary for conversion and stabilization functions are present.
Two versions are envisaged suited to the input range 24...230 V.
The circuit provides stabilized voltages of +5 V and -5 V, required for the analogue measurement and
+3.3 V for supplying the digital circuits.
The circuit board additionally comprises:
INPUT CIRCUITS:
• Three binary input circuits,
The logical input circuits and the block circuits include photo-couplers which provide for galvanic
separation.
OUTPUT CIRCUITS:
• Four output relays (k1...K4).
hw.ai
RTC
CPU BOARD
POWER SUPPLY BOARD
INPUT MODULE
CTs
DSP
1A/5A
≈
≈
≈
≈
EEprom
RS485
RELAYS
K1...K4 Output contacts
RS232
MMI
LCD
LEDs
BINARY INPUTS
IN1
Input
IN2
IN3
POWER SUPPLY
+5 V
+10 V
0 V
+24 V
-10 V
POWER FAIL
RESET
Uaux
≈
≈
≈
LPCTs CURRENT INPUTS
IL1
IL2
IL3
L1
L2
SettingLPCT
800 A
400 A
200 A
100 A
50 A
L3
In=50...1250A

FUNCTION CHARACTERISTICS 18
NA016 - Manual - 05 - 2022
CPU board
This circuit board contains all the circuits necessary for performing the analogue and digital pro-
cessing of the signals.
Analog processing
The following are envisaged:
• Anti aliasing filter circuits, .
• Amplifier circuits for conditioning the input signals,
• Reference voltage adjustment circuits for the measurement A/D converter.
The relays usea a DSP processor operating at 40 MHzThe input currents are sampled at a frequency
of 64 samples per period by means of a dual conversion system which allows the attainment of infor-
mation pertaining to polarity and amplitude with high resolution. The measurement criterion allows
precise measurement of even those signals having a unidirectional component, such as transient
currents with overlapping exponential, which typically appear during faults.
The circuit board also houses the output relays with the corresponding command and control cir-
cuits, communication circuits, buttons, LCD display, LEDs and the key switch.
CPU
A 32 bit DSP is provided.
The following are envisaged:
• Real Time Clock circuits with oscillator and super capacitor,
• RS232 communication port,
• RS485 communication port,
Memories:
• Ram: high speed static memory
• Flash memory,
• EEprom memory: used for calibration data storage,
Input board
• Three CTs committed for phase currents acquisition,
• One CT committed for residual current acquisition.
The input circuits are suitable for 1 A or 5 A external CTs.[1]
MMI (keyboard, LED and display)
The MMI module (Man Machine Interface) includes:
• An eight keys 8 keyboard,
• a backlight LCD display,
• Eight signalling LEDs,
• RS232 communication port.
Note 1 The phase and residual nominal currents must be adjusted by means dip-switch.

FUNCTION CHARACTERISTICS 19
NA016 - Manual - 05 - 2022
4.2 SOFTWARE DESCRIPTION
The program which handles operation of the Pro-N relays is made up of three fundamental elements
shown in the following block diagram.
Kernel
The kernel represents the nucleus of the system: it includes the processing functions closest to the
electronic circuits; particularly the algorithms providing for the generation of the synchronisms (tim-
ers) for sampling the analogue signals and numerical processing.
The software is structured with interrupts operating with various priority levels in a non “pre-emp-
tive” task system. By means of Discrete Fourier Transform calculation, based on 32 samples/period,
information is deduced in relation to the amplitude and phase of all the current measurements; these
are constantly updated and at the disposal of all the protection and control application algorithms.
In addition, the kernel manages a service communication protocol known as Basic Protocol (BP).
Drivers
The driver library contains all the specialised modules for the command and control functions which
make up the connection ring between the kernel and the application. Examples of drivers include the
Modbus communication and LCD display modules.
Application
The application contains all the elements which carry out the protection and control functions.
The main modules are:
- diagnostic function,
- input management (logical inputs and block signal),
- protective functions,
- event recording,
- output management (output relays, LEDs and block signals).
Each element (Kernel, Drivers and Application) may, in turn, be split into modules:
Base protocol (kernel)
The module known as the Basic Protocol (BP) manages the service communication between the
kernel and the other modules through the communication buses:
- direct for internal functional call,
- SPI over synchronous serial,
- SCI over asynchronous serial.
The activities which may be performed by means of BP include:
- measurement configuration ,
- measurement reading,
- measurement enabling.
Calibration (kernel)
Calibration is performed using the base protocol functions for coordinating the calibration and test-
ing stages with the automatic testing equipement (ATE).
Communication (drivers)
The protective device implements the MODBUS RTU protocol for communicating via the RS232 inter-
face with the ThyVisor setting software and via the RS485 interface with the field bus.
All major codes according to the Modbus standard are envisaged; for a complete description and
map of the addresses, please refer to the appendix mentioned further in this manual.
MMI (drivers)
This handles the menus, available both on the panel and by means of Modbus messages, which
may be run from commands using the keyboard, LEDs and LCD display.
MMI information is stored in EEPROM and may be loaded remotely by means of the basic protocol
functions.
sw.ai
APPLICATION
DRIVERS
timers
KERNEL
sampling

FUNCTION CHARACTERISTICS 20
NA016 - Manual - 05 - 2022
Data Base (application/drivers)
Using modular criteria, the database is structured in three sections:
- RAM containing the volatile data,
- REE and PAR containing the data recorded in non-volatile memory.
Duplication of the data into two memory banks is envisaged with a continuous control system based
on the cross checking of the consistency of the stored data. Modification of the calibration pa-
rameters is split into two stages; in particular, data undergoing modification is placed in temporary
memory and subsequently confirmed permanently (Store command) or discarded (Clear command).
Instead, the area identified as REE is set aside for recording data which does not require the Store
command for storage, or date written directly by the application (e.g.: counters,...)
Self-test (application)
This function cyclically monitors the operation of the main hardware and software functions without
affecting the process cycle with any significant delays.
In particular, the functions monitored are the following,
- the reference voltage levels,
- output relay coil continuity,
- the program flow control by monitoring the execution times and stack area occupancy,
- checking the pilot wires (accelerated logic system),
- the consistency of the data in the REE and PAR blocks, duplicated in the EEPROM.
Development tools
For the development of the project, a CASE instrument has been developed, responsible for the opti-
mized production of software code for the management of collaboration, the database and the MMI
data and the Xml files used for communication. The automatic code generation criteria ensures the
quality of the result in terms of the reusability, verifiability and maintainability of the software life
cycle.
Table of contents
Other Thytronic Relay manuals

Thytronic
Thytronic DMC3S User manual

Thytronic
Thytronic SIF5600 User manual

Thytronic
Thytronic NA011 User manual

Thytronic
Thytronic NVA100X User manual

Thytronic
Thytronic SSG User manual

Thytronic
Thytronic DTB 49-50 User manual

Thytronic
Thytronic NA10 User manual

Thytronic
Thytronic NV10P User manual

Thytronic
Thytronic NA11 User manual

Thytronic
Thytronic NA30 User manual
Popular Relay manuals by other brands

Ei Electronics
Ei Electronics RadioLINK Relay Module Ei428 instruction manual

ENCARDIO RITE
ENCARDIO RITE EWN-01R user manual
System Sensor
System Sensor R-10TA Installation and maintenance instructions

Siemens
Siemens SIRIUS 3RA2811 Original operating instructions

Omron
Omron G7SA datasheet
Eaton
Eaton D85 Series instructions