INSTRUKCJA ORYGINALNA 7
PL
w przypadku przerwy w dostawie energii
zasilającej. Używać tylko środków smarnych
zalecanych przez producenta. Należy sto-
sować okulary ochronne, zalecane jest sto-
sowanie dopasowanych rękawic oraz stroju
ochronnego. Należy mieć świadomość, że
obrotowe narzędzie wstawiane pozostaje w
ruchu po tym jak zostanie zwolnione urzą-
dzenie startu i stopu.
Zagrożenia związane z powtarzalnymi ruchami
Podczas stosowania narzędzia pneumatycz-
nego do pracy polegającej na powtarzaniu ru-
chów, operator jest narażony na doświadcze-
nie dyskomfortu dłoni, ramion, barków, szyi
lub innych części ciała. W przypadku użyt-
kowania narzędzia pneumatycznego, ope-
rator powinien przyjąć komfortową postawę
zapewniającą właściwe ustawienie stóp oraz
unikać dziwnych lub nie zapewniających rów-
nowagi postaw. Operator powinien zmieniać
postawę podczas długiej pracy, pomoże to
uniknąć dyskomfortu oraz zmęczenia. Jeżeli
operator doświadcza symptomów takich jak:
trwały lub powtarzający się dyskomfort, ból,
pulsujący ból, mrowienie, drętwienie, piecze-
nie lub sztywność. Nie powinien ich ignoro-
wać, powinien powiedzieć o tym pracodawcy
i skonsultować się z lekarzem.
Zagrożenia związane z akcesoriami
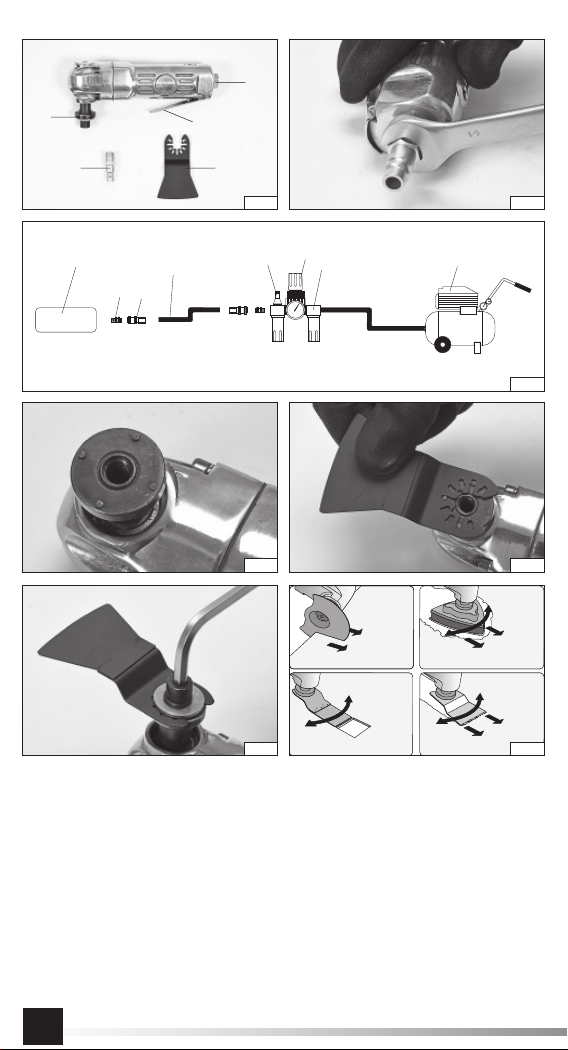
Odłączyć narzędzie od źródła zasilania
przed zmianą narzędzia wstawionego lub
akcesoria. Unikać bezpośredniego kontaktu
z narzędziem wstawianym podczas oraz po
pracy, może być gorące lub ostre. Stosować
akcesoria i materiały eksploatacyjne tylko w
rozmiarach i typach, które są zalecane przez
producenta. Nie stosować akcesoriów inne-
go typu lub innego rozmiaru. Nie stosować
ściernic do szlifowania lub cięcia. Sprawdzić
czy maksymalna prędkość pracy narzędzia
wstawianego (ściernice listkowe, pasy ścier-
ne, dyski z włóknami, tarcze polerskie) jest
większa niż prędkość znamionowa szlifi erki
lub polerki. Samomocujące dyski polerują-
ce powinny być mocowane koncentrycznie
na tarczy polerskiej. Dokonać sprawdzenia
akcesorium przed użyciem. Nie stosować
akcesoriów, które zostały upuszczone lub,
które posiadają ubytki, pęknięcia lub jakie-
kolwiek uszkodzenia.
Zagrożenia związane z miejscem pracy
Poślizgnięcia, potknięcia i upadki są głów-
nymi przyczynami obrażeń. Wystrzegać
się, śliskich powierzchni spowodowanych
użytkowaniem narzędzia, a także zagrożeń
potknięciem spowodowanym instalacją po-
wietrzną. Postępować ostrożnie w niezna-
nym otoczeniu. Mogą istnieć ukryte zagro-
żenia, takie jak elektryczność lub inne linii
użytkowe. Narzędzie pneumatyczne nie jest
przeznaczone do stosowania w strefach za-
grożonych wybuchem i nie jest izolowane od
kontaktu z energią elektryczną. Upewnić się,
że nie istnieją żadne przewody elektryczne,
rury gazowe, itp., które mogą powodować
zagrożenie w przypadku uszkodzenia przy
użyciu narzędzia.
Zagrożenia związane z oparami i pyłami
Pył i opary powstałe przy użyciu narzędzia
pneumatycznego mogą spowodować zły stan
zdrowia (na przykład raka, wady wrodzone,
astma i/ lub zapalenie skóry), niezbędne są:
ocena ryzyka i wdrożenie odpowiednich środ-
ków kontroli w odniesieniu do tych zagrożeń.
Ocena ryzyka powinna zawierać wpływ pyłu
utworzonego przy użyciu narzędzia i możli-
wość wzburzenia istniejącego pyłu. Obsługę i
konserwację narzędzia pneumatycznego na-
leży przeprowadzać według zaleceń instrukcji
obsługi, pozwoli zminimalizować emisję opa-
rów i pyłu. Wylot powietrza należy tak kiero-
wać, aby zminimalizować wzbudzanie pyłu w
zakurzonym środowisku. Tam gdzie powstają
pył lub opary, priorytetem powinna być kontro-
la ich w źródle emisji. Wszystkie zintegrowane
funkcje i wyposażenie do zbierania, ekstrak-
cji lub zmniejszenia pyłu lub dymu powinny
być prawidłowo użytkowane i utrzymywane
zgodnie z zaleceniami producenta. Wybierać,
konserwować i wymieniać narzędzia wstawia-
ne według zaleceń instrukcji, aby zapobiec
wzrostowi oparów i pyłu. Używać ochrony
dróg oddechowych, zgodnie z instrukcjami
pracodawcy oraz zgodnie z wymogami higie-
ny i bezpieczeństwa. Należy ostrzec przed ry-
zykiem wybuchu lub pożaru spowodowanym
materiałem, który będzie obrabiany. Obróbka
niektórych materiałów wytwarza emisję pyłu
i oparów, powodujących powstawanie poten-
cjalnie wybuchowego środowiska.
Zagrożenie hałasem
Narażenie na wysoki poziom hałasu może
spowodować trwałą i nieodwracalną utratę
słuchu oraz inne problemy, takie jak szum w
uszach (dzwonienie, brzęczenie, gwizdanie
lub buczenie w uszach). Niezbędna jest oce-
na ryzyka oraz wdrożenie odpowiednich środ-
ków kontroli w odniesieniu do tych zagrożeń.
Odpowiednie kontrole w celu zmniejszenia