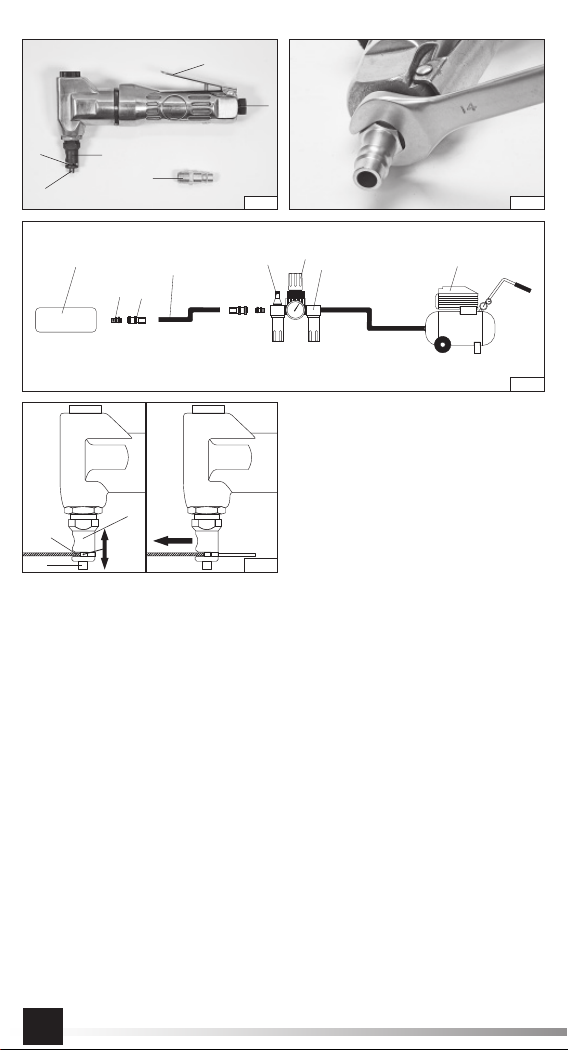
INSTRUKCJA ORYGINALNA
6
PL
Zagrożenia związane z wyrzucanymi częściami
Odłączyć narzędzie od źródła zasilania
przed wymianą narzędzia wstawionego
lub akcesoria. Uszkodzenie obrabianego
przedmiotu, akcesoriów lub nawet narzę-
dzia wstawianego może spowodować wy-
rzucenie części z dużą prędkością. Zawsze
należy stosować ochronę oczu odporną na
uderzenia. Stopień ochrony należy dobierać
w zależności od wykonywanej pracy. Nale-
ży się upewnić, ze obrabiany przedmiot jest
bezpiecznie zamocowany. W przypadku pra-
cy narzędziem nad głową, stosować hełm
ochronny. Należy również brać pod uwagę
ryzyko wobec osób postronnych. Należy
się upewnić, ze obrabiany przedmiot jest
bezpiecznie zamocowany. Upewnić się, że
ostrza są skierowane w taki sposób, aby nie
powodowały zagrożenia.
Zagrożenia związane z pracą
Użytkowanie narzędzia może wystawić ręce
operatora na zagrożenia, takie jak: zmiaż-
dżenie, uderzenie, odcięcie, ścieranie oraz
gorąco. Unikać kontaktu z ostrzami narzę-
dzia za każdym razem gdy narzędzie jest
podłączone do zasilania. Cięcie nożycami
powoduje powstawanie ostrych krawędzi.
Należy ubierać właściwe rękawice do ochro-
ny rąk. Operator oraz personel konserwujący
powinni być fi zycznie zdolni do poradzenia
sobie z ilością, masą oraz mocą narzędzia.
Trzymać narzędzie poprawnie. Być gotowym
na przeciwdziałanie normalnym lub gwałtow-
nym ruchom oraz mieć obie ręce dostępne.
Zachować równowagę oraz zapewniające
bezpieczeństwo ustawienie stóp. Należy
zwolnić nacisk na urządzenie startu i stopu
w przypadku przerwy w dostawie energii
zasilającej. Używać tylko środków smar-
nych zalecanych przez producenta. Unikać
bezpośredniego kontaktu z narzędziem
wstawianym podczas oraz po pracy, może
być gorące. Zawsze powinny być stosowa-
ne ostre narzędzia. Unikać niewygodnych
postaw, a także pozycji, które nie pozwolą
przeciwdziałać normalnemu lub nagłemu ru-
chowi narzędzia. Nieoczekiwany ruch narzę-
dzia lub pęknięcie ostrzy może spowodować
obrażenia. Cięcie niektórych metali może
spowodować powstawanie iskier lub po-
wodować wysoką temperaturę, które mogą
spowodować pożar lub wybuch. Przed roz-
poczęciem cięcia ściany zbiornika w którym
wcześniej była przechowywana łatwopalna
ciecz, należy zbiornik całkowicie opróżnić,
a następnie wywietrzyć opary. Istnieje ryzyko
wyładowań elektrostatycznych podczas cię-
cia plastiku lub innych materiałów nieprze-
wodzących.
Zagrożenia związane z powtarzalnymi ruchami
Podczas stosowania narzędzia pneumatycz-
nego do pracy polegającej na powtarzaniu ru-
chów, operator jest narażony na doświadcze-
nie dyskomfortu dłoni, ramion, barków, szyi
lub innych części ciała. W przypadku użyt-
kowania narzędzia pneumatycznego, ope-
rator powinien przyjąć komfortową postawę
zapewniającą właściwe ustawienie stóp oraz
unikać dziwnych lub nie zapewniających rów-
nowagi postaw. Operator powinien zmieniać
postawę podczas długiej pracy, pomoże to
uniknąć dyskomfortu oraz zmęczenia. Jeżeli
operator doświadcza symptomów takich jak:
trwały lub powtarzający się dyskomfort, ból,
pulsujący ból, mrowienie, drętwienie, piecze-
nie lub sztywność. Nie powinien ich ignoro-
wać, powinien powiedzieć o tym pracodawcy
i skonsultować się z lekarzem.
Zagrożenia związane z akcesoriami
Odłączyć narzędzie od źródła zasilania przed
zmianą narzędzia wstawionego lub akceso-
ria. Stosować akcesoria i materiały eksploata-
cyjne tylko w rozmiarach i typach, które są za-
lecane przez producenta. Ostrza mogą stać
się gorące podczas używania, nie dotykać
ich. Nie używać popękanych lub zniekształ-
conych akcesoriów lub narzędzi wstawianych.
Zagrożenia związane z miejscem pracy
Poślizgnięcia, potknięcia i upadki są głów-
nymi przyczynami obrażeń. Wystrzegać
się, śliskich powierzchni spowodowanych
użytkowaniem narzędzia, a także zagrożeń
potknięciem spowodowanym instalacją po-
wietrzną. Postępować ostrożnie w niezna-
nym otoczeniu. Mogą istnieć ukryte zagro-
żenia, takie jak elektryczność lub inne linii
użytkowe. Narzędzie pneumatyczne nie jest
przeznaczone do stosowania w strefach za-
grożonych wybuchem i nie jest izolowane od
kontaktu z energią elektryczną. Upewnić się,
że nie istnieją żadne przewody elektryczne,
rury gazowe, itp., które mogą powodować
zagrożenie w przypadku uszkodzenia przy
użyciu narzędzia.
Zagrożenia związane z oparami i pyłami
Pył i opary powstałe przy użyciu narzędzia
pneumatycznego mogą spowodować zły
stan zdrowia (na przykład raka, wady wro-
dzone, astma i/ lub zapalenie skóry), nie-