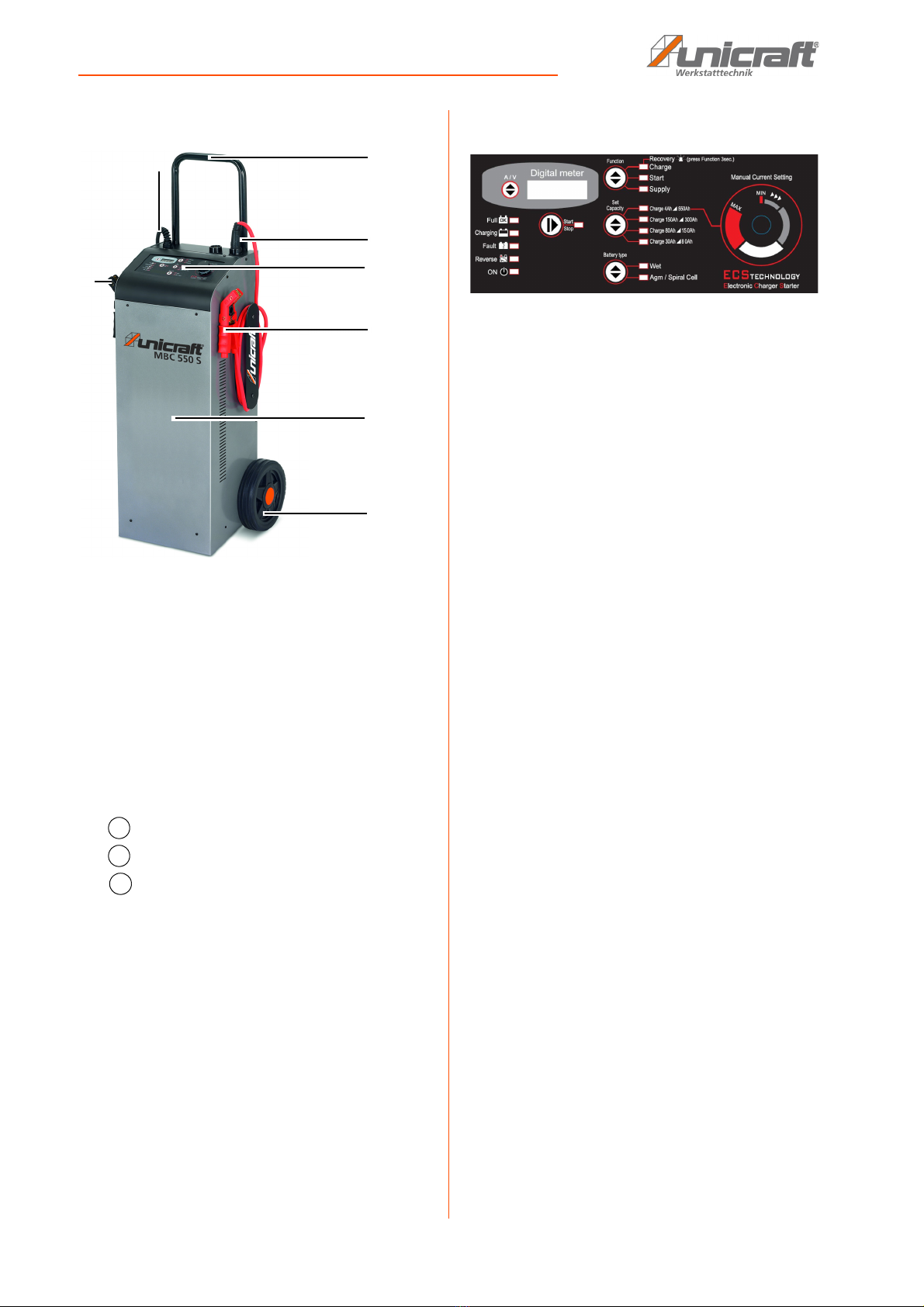
Settings and functions
MBC-Series | Version 1.05 7
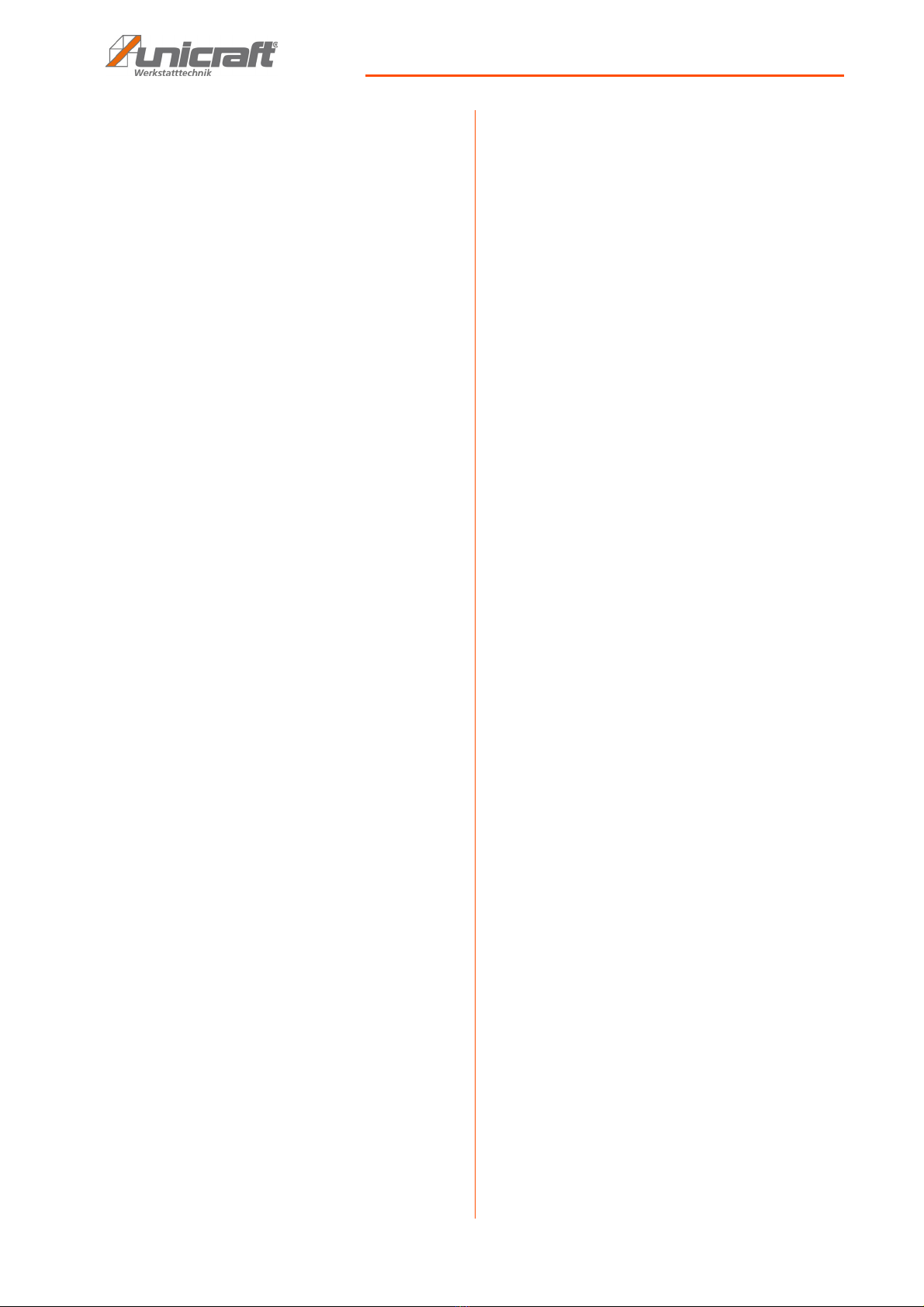
7.3 Digital Display
„A/V“ button:
The „A/V” selector button selects voltage or current dis-
play or allows the user to change the display messages
language. Pressing A/V toggles from voltage display U
to current display A, and finally the „Language“ menu.
This menu will show the message „LANGUAGE = ITA-
LIAN" or another language, depending on the selection.
Change messages language:
To enter the language selection mode, press the „A/V“
button and hold it down when the display is showing the
message „LANGUAGE = ITALIAN“. The language set-
ting is Italian by default; to scroll the language menu
press the „A/V“ button next to the display and the langu-
age shown will change instantly.
Languages supported:
- Italian
- English
Once the language is set, to quit the menu press the
„A/V“ button for a few seconds.
7.4 Functions and operating modes
All operating modes are suitable for 12V and 24V batteries!
Charge:
Battery charging mode. There are 11 phases to char-
ging the battery:
- Phase 1: Analysis 1. If the battery output is less than
10.5V the unit proceeds with the next analysis.
Outputs below 5V will cause the device to revert to
stand-by.
- Phase 2: Analysis 2. (sulphated battery). The display
shows the message "ANALYSIS" alternating with the
instantaneous voltage or current. After this step the
unit either starts the charging cycle directly or it dis-
plays the message "SULPHATED BATTERY" to inform
the operator that the battery must be recovered.
- Phase 3: Desulphation. Pulsed voltage to prevent sul-
phation of the battery.
- Phase 4: Controlled current. Charges the battery up to
the programmed limit value.
- Phase 5: Analysis 3 (elements short circuited). Checks
whether the battery has short circuited elements or is
damaged and reports the error, if present
- Phase 6: Deep Cycle Charging. Central charging cycle.
- Phase 7: Constant Voltage. Keeps the battery at the
charging end voltage.
- Phase 8: Analysis4. Checks whether the battery has
short circuited elements or is damaged and reports
the error, if present.
- Phase 11: Pulsed current cycle. Cycle that simulates the
normal life cycle of the battery.
Start: Method of starting a vehicle with a flat battery. Pos-
sibility of starting also remotely using a pushbutton
external to the battery charger. Composed of the
following steps:
- Step 1: Battery analysis. The device's „Start“ LED
flashes.
- Step 2: Fast Charging. The device enters this step if
the „START“ LED is steady on. It sets the charge
end voltage associated with the selected battery
type with the current limit defined for the „START“
step.
- Step 3: Engine Boost. When the battery charger de-
tects an engine cranking attempt it switches to the
next step. If the battery voltage reading is above
13.5V the scrolling message „START“ appears on
the display, also before the next step.
- Step 4: Boost. The scrolling message „START“ ap-
pears on the display: the battery charger is now
delivering the maximum power.
Supply:
Power supply mode to assist in vehicle programming.
This mode does not contain any charging steps, and it
consists exclusively of a stabilized power supply deli-
vering the nominal battery voltage. The purpose is that
of supplying current to support the battery to prevent it
from being drained during operations that require power
for short or long periods.
Recovery:
Method of recovery for sulphated batteries accessible
by means of a prolonged press of the "Function" button.
On the screen the message RECOVERY alternates with
the instantaneous voltage or current reading; during this
step the "Charge" LED flashes.
The battery charger performs a special charging cycle
in which higher than average voltages are forced to at-
tempt recovery of the battery. In this mode no error mes-
sages are generated during the charging cycle; a mes-
sage is displayed at the end of the cycle to indicate
whether or not the battery has been recovered on the
basis of the current absorption. Mode with 6 charging
steps, as described below:
- Step 1: Analysis1. Outputs below 2V will cause the de-
vice to revert to stand-by.
- Step 2: Desulphation. Pulsed voltage to prevent sul-
phation of the battery.
- Step 3: Controlled current. Charges the battery up to
the programmed limit value.
- Step 4: Deep Cycle Charging. Central charging cycle.