AC310 Universal AC Drive Service Manual
5
1.2 Common Device Overhaul Method
1.2.1 Detect Diode
Digital multimeter diode file open-circuit voltage of about 2.8V, the red pen is
connected to the positive, the black pen is connected to the negative, the measurement
of the current provided by about 1mA, the display value for the diode forward voltage
drop approximation, the unit is mV or V. Silicon diode forward conduction voltage drop
of about 0.3 ~ 0.8V, reverse bias shows the diode open-circuit voltage. The germanium
diode germanium forward conduction voltage drop is about 0.1~0.3V. And the forward
voltage drop of the more powerful diode is smaller, and the reverse bias shows the open-
circuit voltage of the diode. If the measured value is less than 0.1V, it means that the
diode breaks down, at this time both forward and reverse conduction. If the forward
and reverse are open, it means that the diode is open.
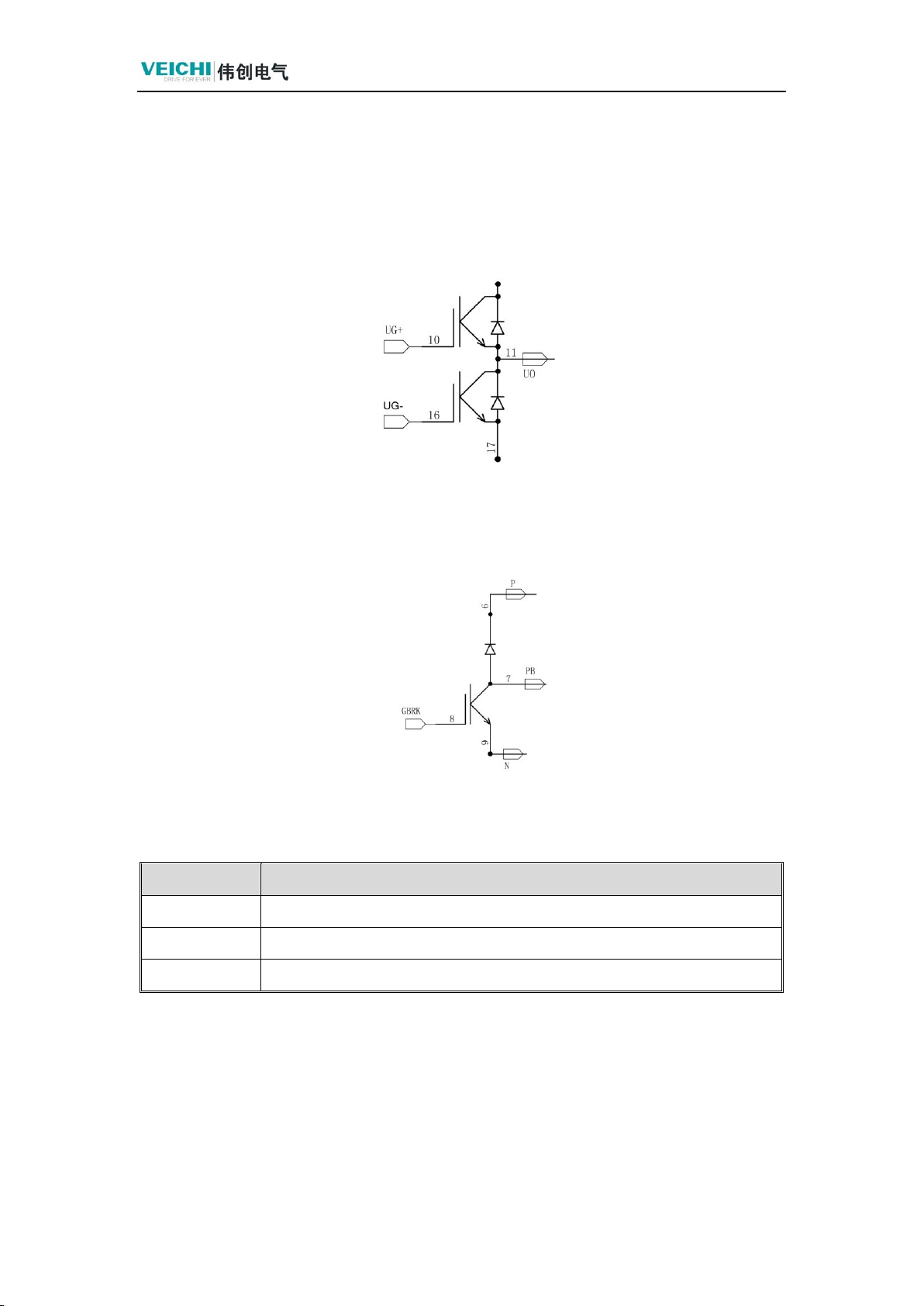
1.2.2 Detect Triode
The triode has two PN junctions, the emitter junction (be) and the collector
junction (bc), which can be measured in the same way as the diode. In the actual
measurement, the forward and reverse voltage drops between each two pins should
be measured, a total of 6 times, of which 4 times show open circuit, only two times
show the voltage drop value (why only 2 times show the data, because the triode is
in the triode, the voltage drop value is not displayed).
There are two times to show the voltage drop value (why only two times to show
the data, because the transistor in the measurement of the static value of the
equivalent diagram shown in the figure below), otherwise the transistor is bad or
special transistors (such as resistance transistors, Darlington transistors, etc., can be
distinguished by the model number and the ordinary transistors). In two
measurements with values, if the black or red pen is connected to the same pole, the
pole is the base pole, the smaller measurement value is the collector junction, and
the larger one is the emitter junction, because the base pole has been judged, and the
collector and emitter can be judged accordingly. At the same time, it can be judged:
if the black pen is connected to the same pole, the transistor is PNP type; if the red
pen is connected to the same pole, the transistor is NPN type; the one with a voltage