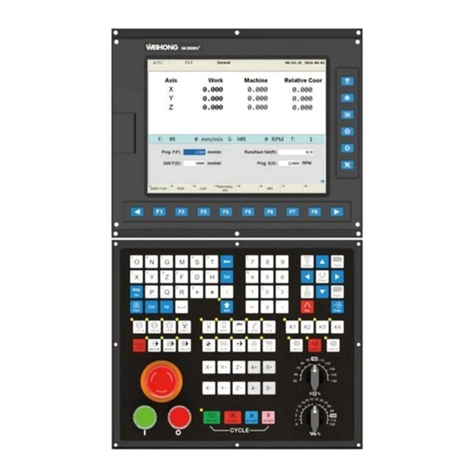
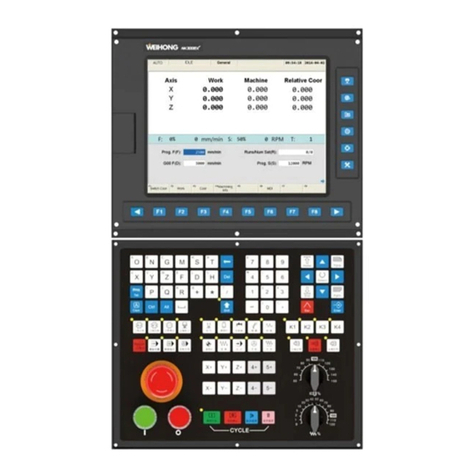
上海维宏电子科技股份有限公司
SHANGHAI WEIHONG ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD.
3.1 Load a Tool Path.............................................................................................................. 17
3.2 Set the Workpiece Origin ............................................................................................. 17
3.2.1 Set X-axis Workpiece Origin........................................................................... 18
3.2.2 Set Y-axis Workpiece Origin........................................................................... 19
3.2.3 Set Z-axis Workpiece Origin ........................................................................... 19
3.3 Set Valve Control Process ............................................................................................ 20
3.4 Simulate Machining........................................................................................................ 21
3.5 Set the Loading Point for Robots .............................................................................. 21
3.6 Execute Automatic Machining.................................................................................... 22
3.6.1 Use the Standard Machining Mode .............................................................. 22
3.6.2 Use the Remote Machining Mode................................................................. 22
4Common Operations................................................................................................................... 24
4.1 Customize Common Parameters............................................................................... 24
4.2 Execute I/O Port Related Operations...................................................................... 25
4.3 Check System Logs ......................................................................................................... 26
4.4 Generate an Installation Package.............................................................................. 27
4.5 Select a System Language ............................................................................................ 27
5Special Operations....................................................................................................................... 28
5.1 Select the Tool(s) ............................................................................................................ 28
5.2 Measure Height................................................................................................................ 29
5.2.1 Manually Measure Height................................................................................ 30
5.2.2 Measure Height before Cutting ..................................................................... 30
5.3 Execute Jiggle.................................................................................................................... 30
5.4 Execute Y1Y2 Jiggle ........................................................................................................ 31
5.5 Set Safety Light Curtains .............................................................................................. 32
6FAQs.................................................................................................................................................. 33
6.1 Questions during Returning to the Machine Origin........................................... 33