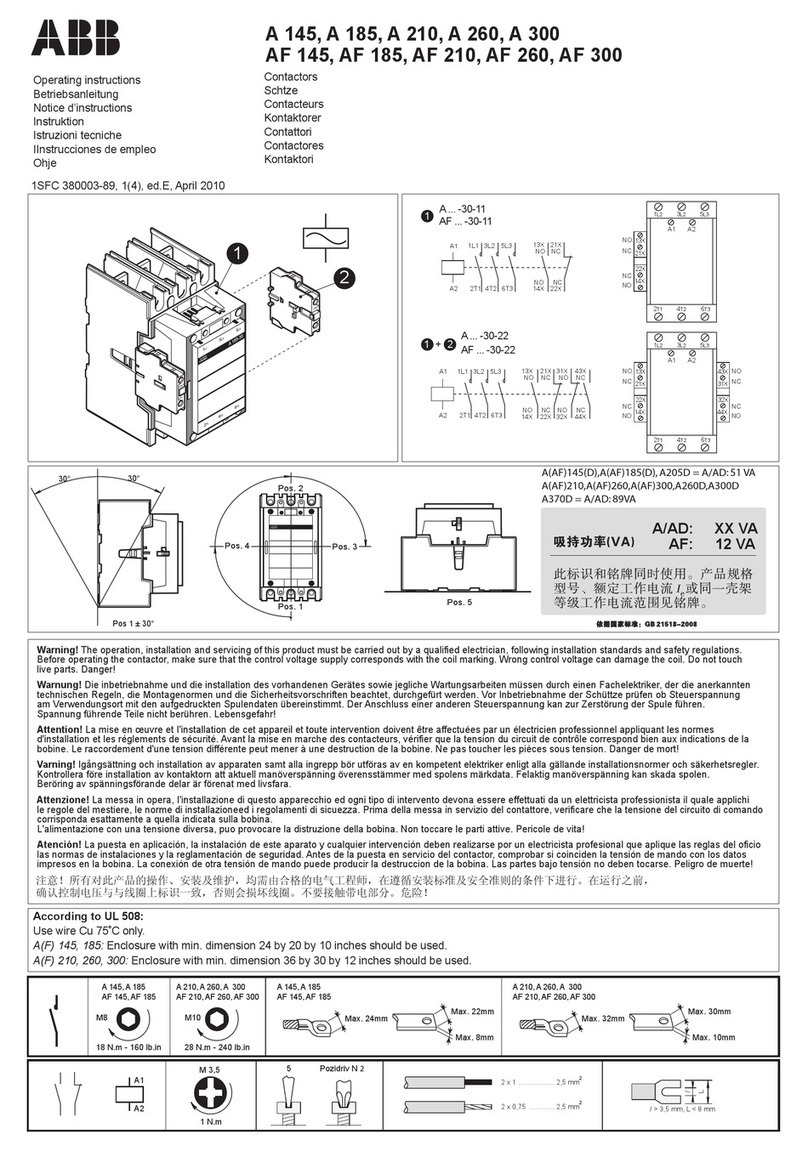
ABB ITH-T Series Guide
Other ABB Relay manuals

ABB
ABB HT595115 User manual

ABB
ABB MG-6 Manual

ABB
ABB 41-101U Manual

ABB
ABB RELION RET670 User manual

ABB
ABB Relion REG670 Instructions for use

ABB
ABB REC650 ANSI User manual

ABB
ABB REX 521 User manual

ABB
ABB REL 356 User manual

ABB
ABB Relion 615 series Instructions for use

ABB
ABB SPAJ 160 C Parts list manual