Contents
1. OUTLINE................................................................................................................3
1.1. Mobile Introduction..................................................................................................................................3
1.2. Motherboard Components Distribution.................................................................................................5
2. SIGNAL FLOW AND FAULT ANALYSIS.............................................................5
2.1. RF Part.......................................................................................................................................................5
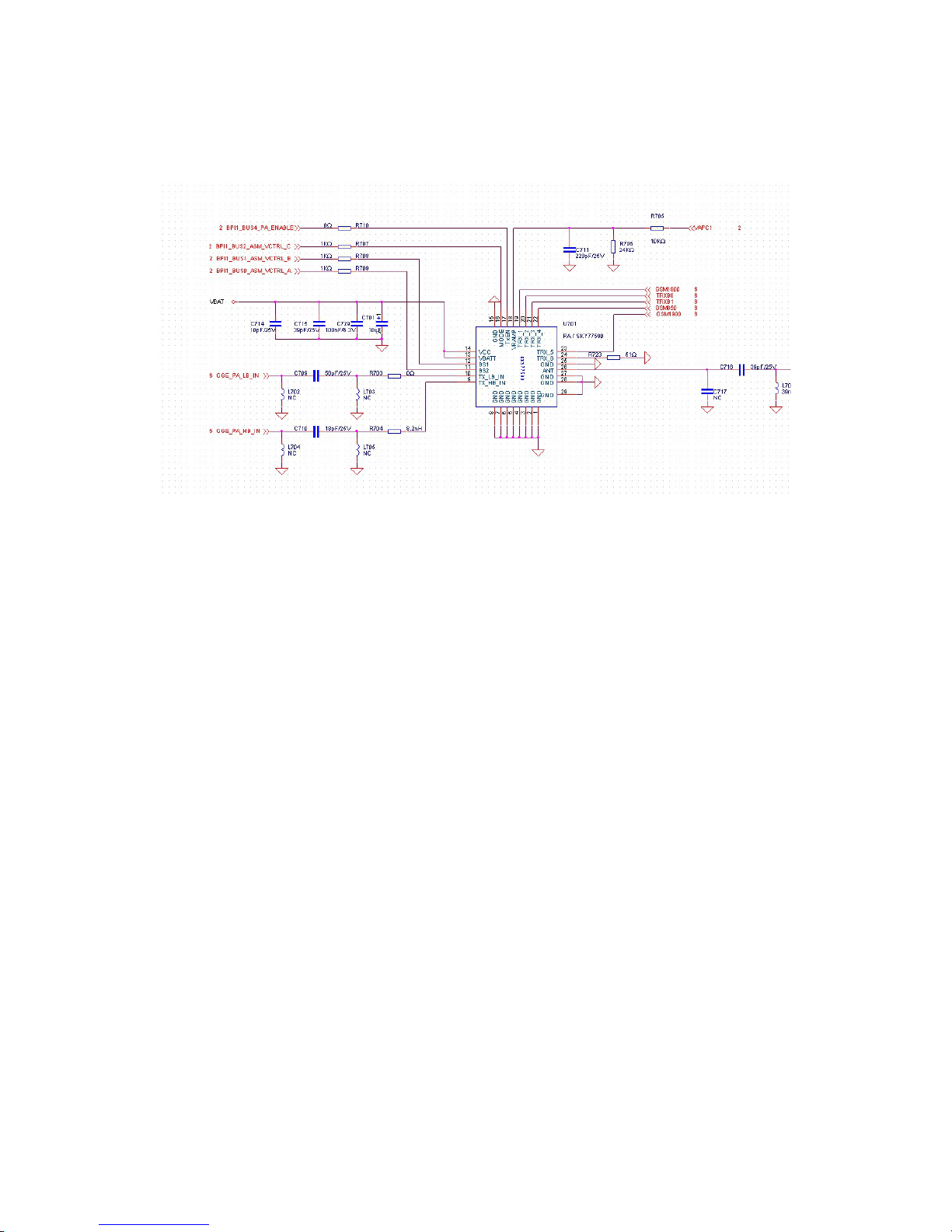
2.1.1. Block Diagram of the RF Section.......................................................................................................5
2.1.2. Signal flow of the RF Transmitting Part.............................................................................................6
2.1.2.1. Transmitting Path...............................................................................................................................6
2.1.2. Signal Flow of the RF Receiving Part................................................................................................7
2.1.3.1. Receiving Path Components...........................................................................................................7
2.2. Baseband part..........................................................................................................................................10
2.2.1 Block diagram of the Baseband part.....................................................................................................10
2.2.2 Power Management...............................................................................................................................11
2.2.3 Audio Section........................................................................................................................................12
2.2.3.1 Audio Codec Circuit.....................................................................................................................12
2.2.3.2 MIC& Receiver Loop...................................................................................................................13
2.2.3.3 Headset Loop................................................................................................................................13
2.2.4 Baseband Fault issues...........................................................................................................................14
2.2.4.1 Analysis of the keyboard fault......................................................................................................15
2.2.4.2 Analysis of Display module circuit..............................................................................................15
2.2.4.3 FM Module...................................................................................................................................16
2.2.4.4 Camera Module............................................................................................................................16
2.2.4.5 IO Interface...................................................................................................................................17
2.2.4.6 SIM Card Circuit..........................................................................................................................17
2.2.4.7 BT/WIFI/GPS Circuit...................................................................................................................18
2.2.4.8 G-sensor Circuit............................................................................................................................18
2.2.4.9 M-sensor Circuit.......................................................................................................................18
2.2.4.10 Gyroscope Circuit....................................................................................................................19
Page 2 of 21