SmartSight - Asyril SA
Programming Guide
000.100.531 SmartSight - Programming Guide 3/31
Table of Contents
1. INTRODUCTION..............................................................................................................................................4
1.1. GENERAL INFORMATION...........................................................................................................................4
1.2. OTHER MANUALS......................................................................................................................................5
2. GENERAL INTRODUCTION............................................................................................................................6
2.1. OVERVIEW................................................................................................................................................6
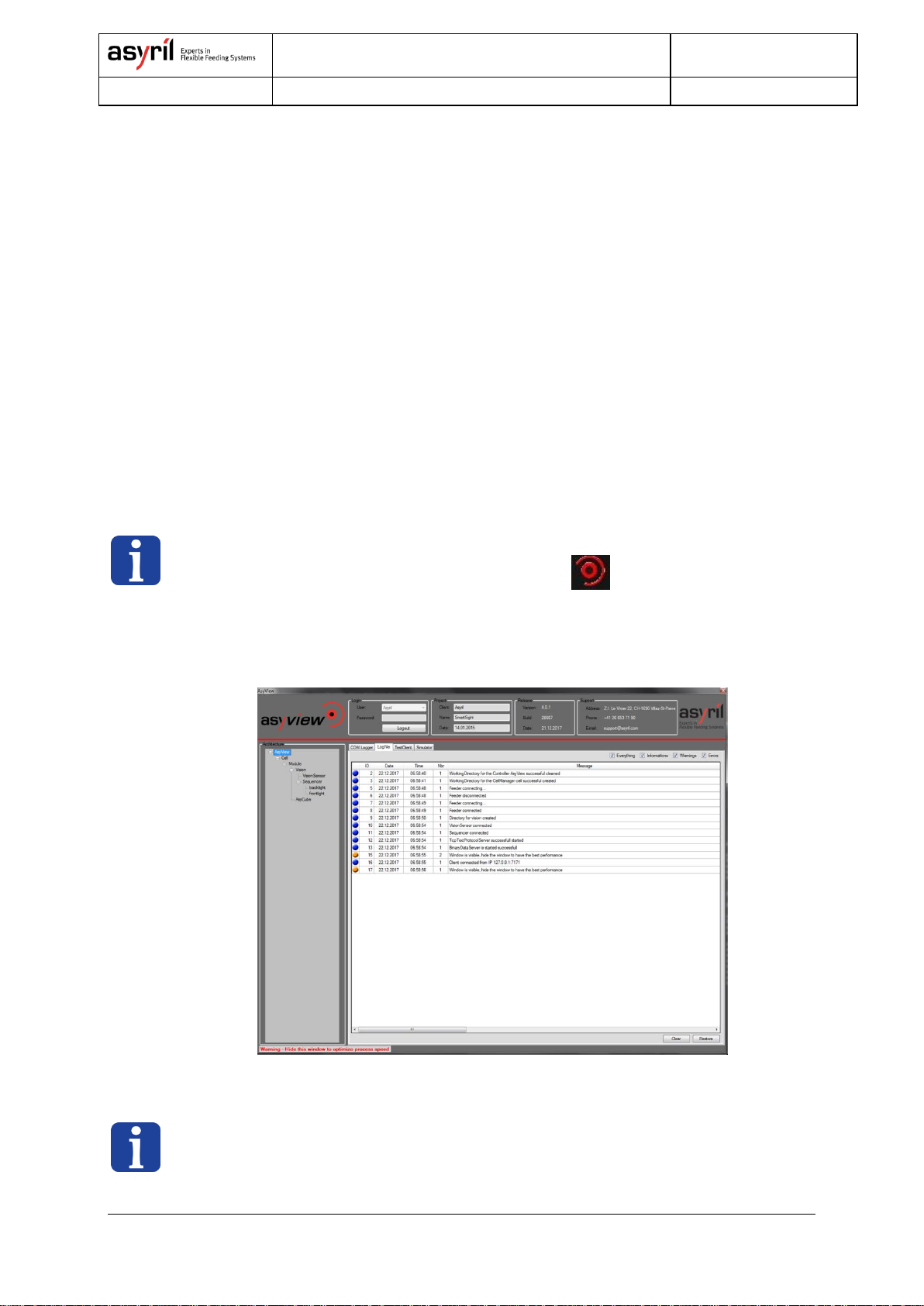
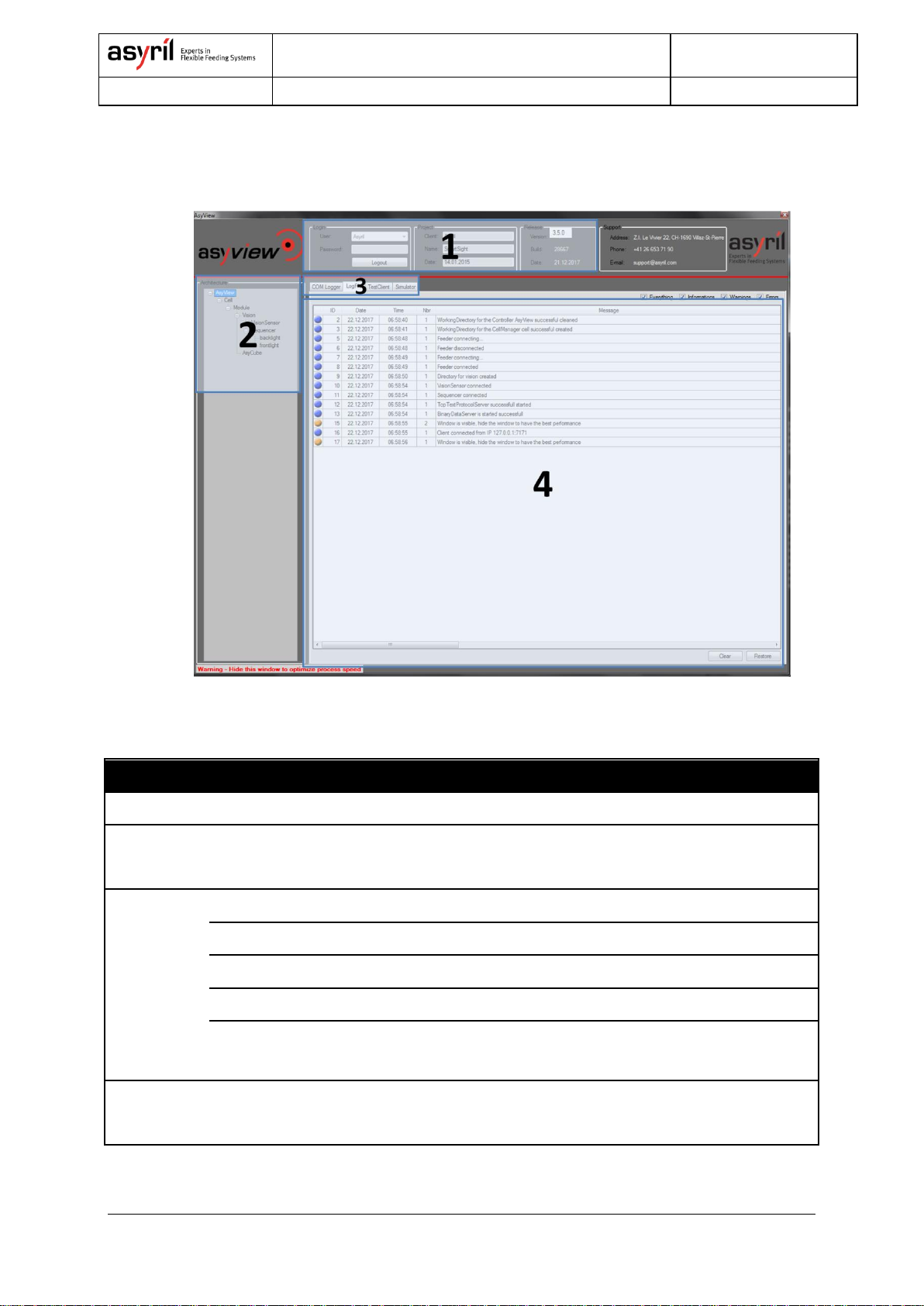
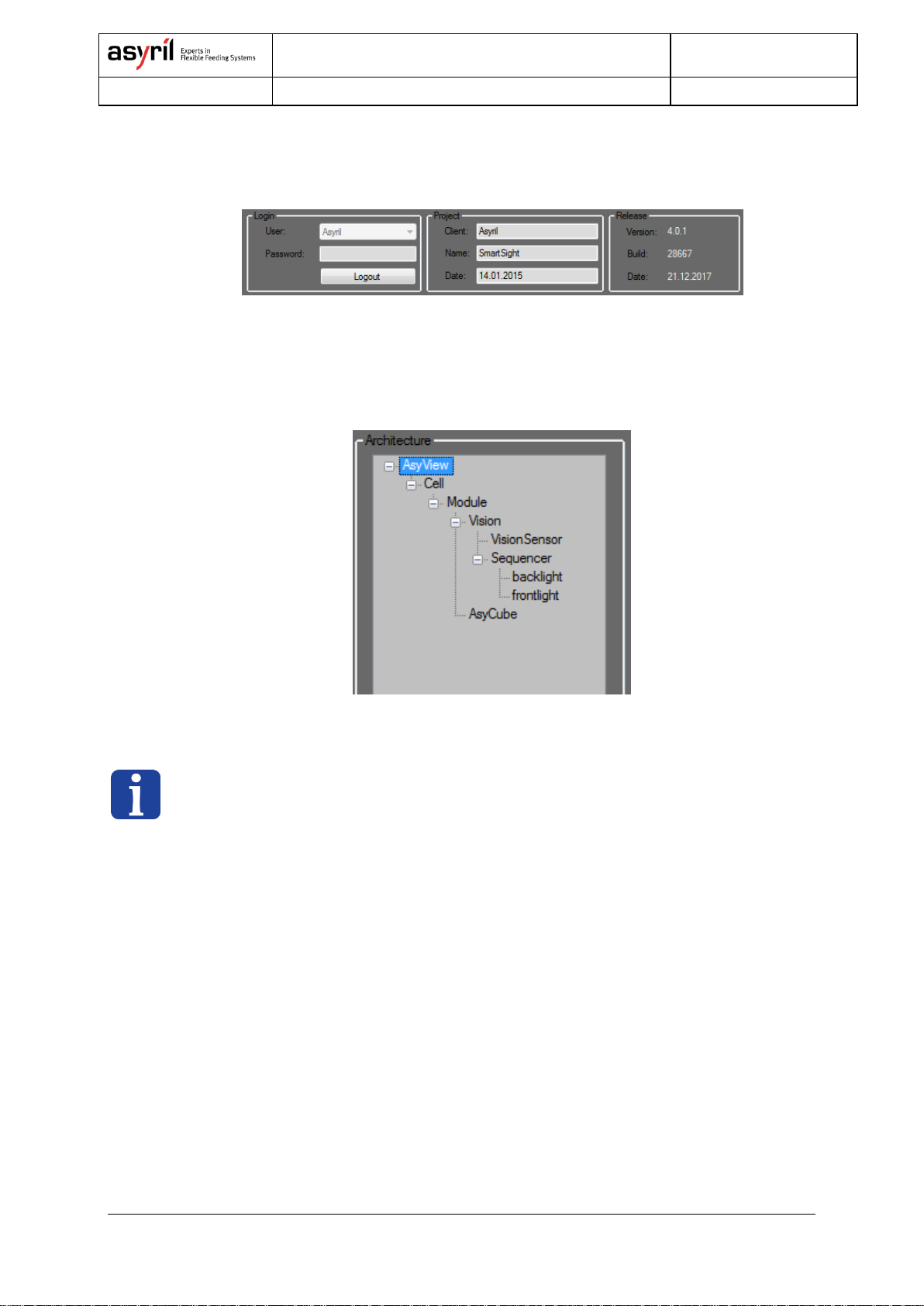
2.1.1. Asyview.......................................................................................................................................... 7
2.1.2. Asyview interface.......................................................................................................................... 7
2.1.3. Human Machine Interface –HMI ............................................................................................. 12
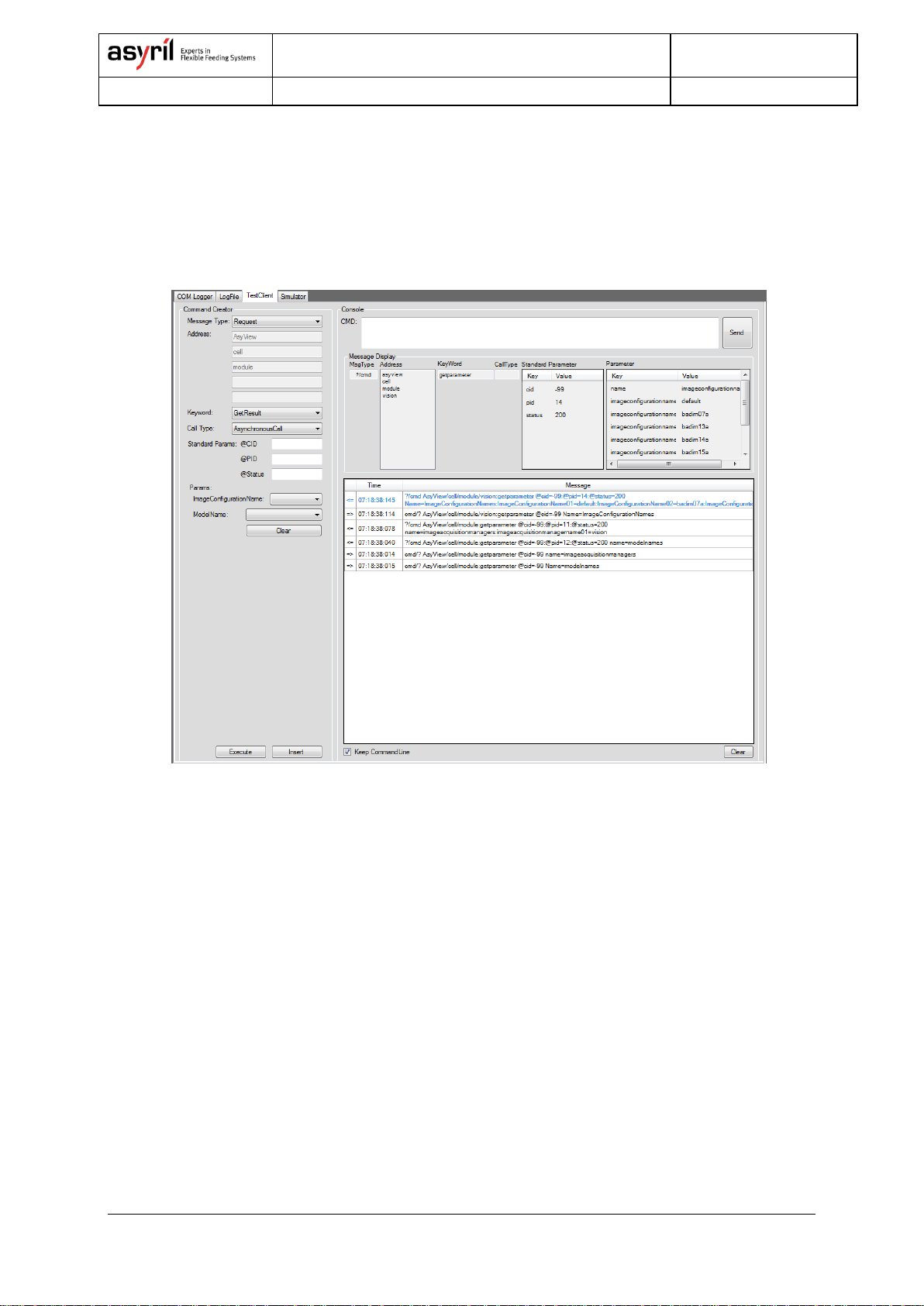
3. COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL...................................................................................................................13
3.1. TCP/IP PARAMETERS............................................................................................................................13
3.2. PROTOCOL.............................................................................................................................................13
3.2.1. Synchronous Mode .................................................................................................................... 14
3.2.2. Asynchronous Mode .................................................................................................................. 14
3.3. ARCHITECTURE AND ADDRESSING.........................................................................................................15
3.4. RESPONSE CODES.................................................................................................................................15
4. METHODS......................................................................................................................................................16
4.1. MODES ...................................................................................................................................................16
4.2. WORKING MODE....................................................................................................................................16
4.2.1. Active Working Mode................................................................................................................. 17
4.2.2. Passive Working Mode.............................................................................................................. 22
4.3. RECIPE...................................................................................................................................................23
5. INSTRUCTIONS.............................................................................................................................................24
6. TECHNICAL SUPPORT.................................................................................................................................29
6.1.1. For a better service … ............................................................................................................... 29
6.1.2. Contact......................................................................................................................................... 29
REVISION TABLE .................................................................................................................................................30