Page 7
Before calling a technician, check ...
- If the appliance does not turn on.
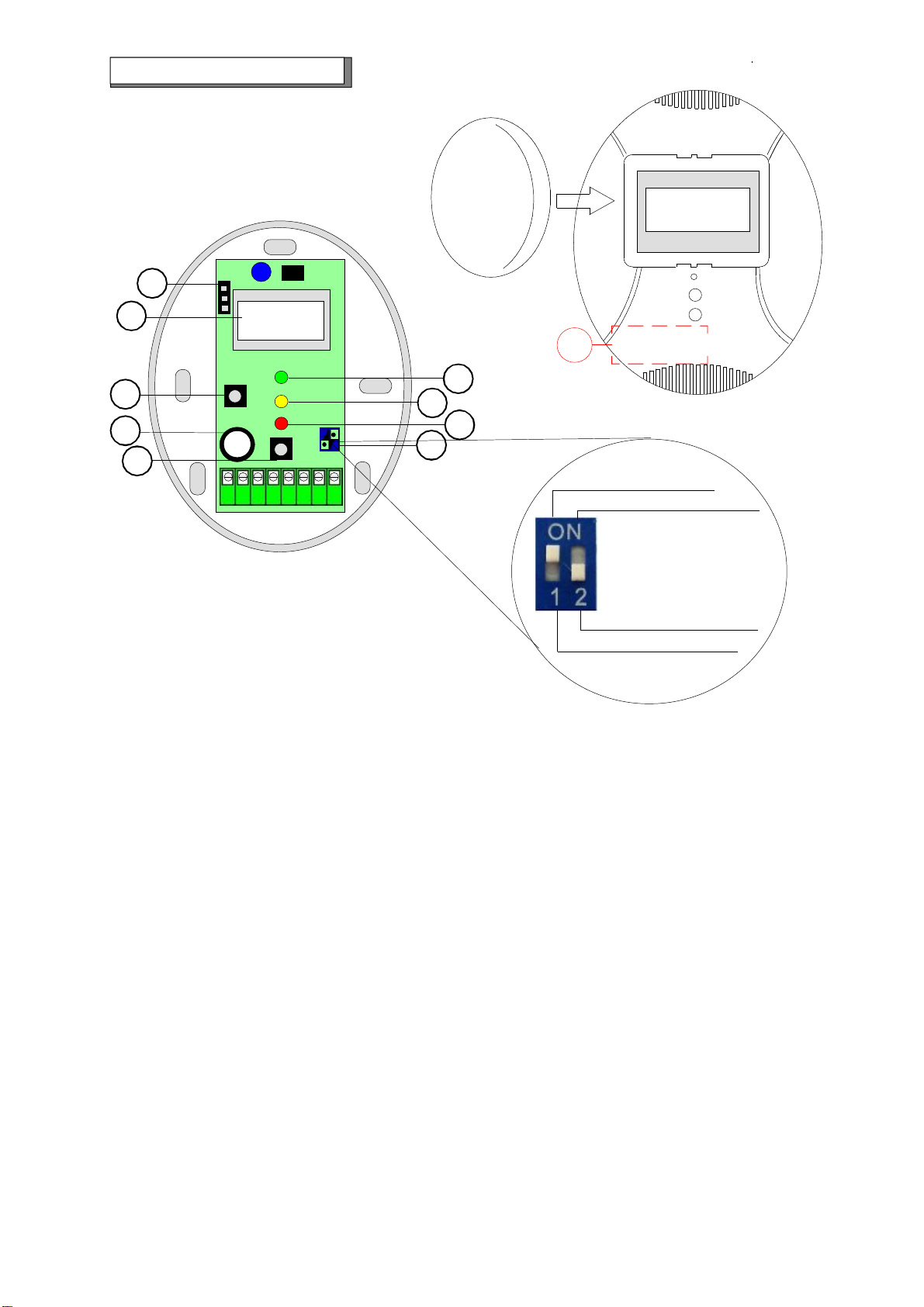
Check that the 230 VAC voltage is present at the ends of the connection terminals.“If battery powered, 12 VDC
voltage is present, and see that the battery is charged.
- If the Fault LED lights up.
If YELLOW LED lights continuously, check that the installation date has not exceeded six years.
If YELLOW LED flashes, check that the anti-seismic sensor has not tripped.“To reset the seismic sensor, simply
press the reset button.
- If the detector goes into alarm repeatedly.
Check for gas leaks.
Check that, together with the alarm signal, the FAULT light does not turn on, in this case proceed as described
in the previous paragraph.
- If the detector goes into alarm and does not close the connected equipment.
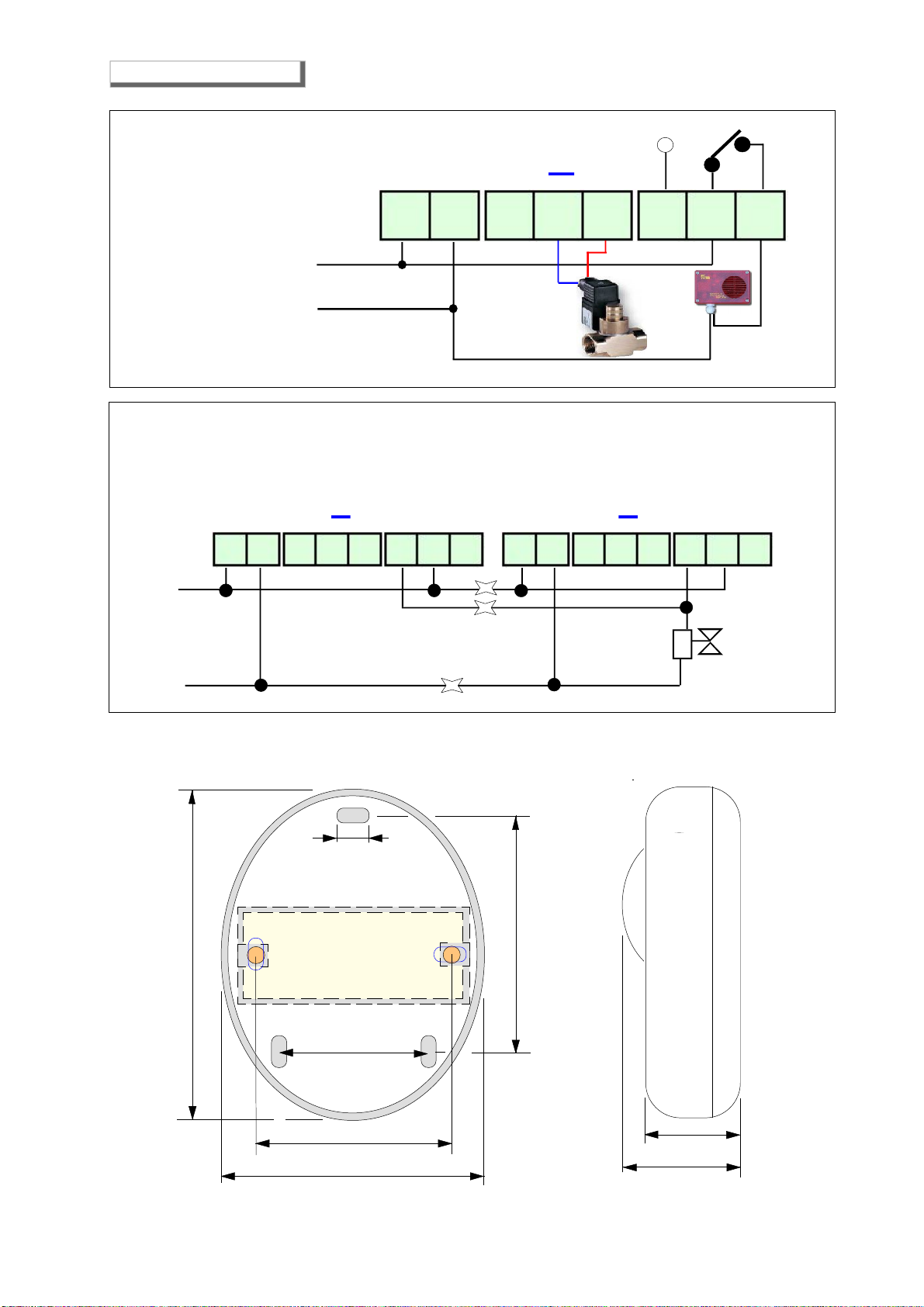
Check that the connections are correct, and that the jumper that brings voltage to the relay common has been
made, all relays are voltage free. Check the connection drawing
- If a 12 VDC solenoid valve is connected to the detector and it does not work well
Check that there are no drops in the power supply voltage.
It's cannot be directly connected to the GS920 detector 12 VDC solenoid valves or sirens with an absorption
greater than 300mA.
A battery must be used to connect a solenoid valve with higher absorption.“A 12 VDC impulse operated manual
reset solenoid valve can be directly connected to the detector.
Do not tamper with the detector.
In order not to cause the device to unbalance, and electric shocks.
MMdegree Accel(cm/s2)
1 1 Not perceived, except by a few people in particularly favorable circumstances.
2 2 Perceived by people resting on the upper floors of houses or in favorable.
3 3 Perceived in homes. Swinging of hanging objects. Vibration as when passing light trucks.
Estimated duration. Sometimes not recognized as an earthquake.
4 15-20 Swinging of hanging objects. Vibrations such as when heavy trucks pass or jolts such as a heavy ball hitting walls.
Oscillation of stationary vehicles. Movements of dishes, doors and windows.
Clink of glasses. Vibrations of crockery. In its upper stage, the creaking of wooden walls and structures.
5 30-40 Resentful to the outside; management estimate. Wake up of sleeping people. Movement of the surface of liquids,
spillage of some from containers. Moving or overturning of small unstable objects. Swing of doors that open and close.
Movement of window shutters and cadres. Stopping, starting, changing the pitch of grandfather clocks.
6 60-70 Heard by everyone. Fright, escape to the outside. Stagger of people on motorcycles.
Breakage of display cases, dishes, glassware.
Trinkets, books, etc. fell off the shelves. and paintings from the walls. Moving or overturning furniture.
Cracks in weak plaster and type D' masonry. Ringing of bells (churches, schools).
7 100-150 Difficult tostand upright. Resented by vehicle drivers. Flickering of hanging objects. Breakage of furniture. Damageto typeD' masonry,
including cracks. Breakage of weak chimneys locatedon the ridge of the roofs. Fall of plaster, bricks, stones, tiles, cornices (also of isolated parapets and architectural
ornaments). Some damage to the masonry type C*. Formation of waves on the water mirrors, clouding ofthe water. Small landslides and excavations in sand and
gravel deposits. Loud ringing of bells. Damage to lined irrigation channels.
8 250-300 Resentful in driving vehicles. Damage to walls type C*, partial collapses. Some damage to masonry type B*, not type A*. Fall of stucco
and some masonry walls. Rotation and fall of chimneys, industrialchimneys, monuments, towers, elevated tanks. Constructionswithtimber structures removed from
the foundationsif not bolted; wallpanels thrown out.Breakage of deteriorated palisades. Breakingtreebranches. Variations inflowortemperatureof springsand wells.
Cracks in the ground and on steep slopes.
9 500-550 General panic. Destruction of type D masonry, severe damage to type C masonry sometimes with complete collapse; serious damage
to type B masonry; general damage tofoundations; timber structures released fromfoundations if not bolted; timber structures tested.Serious damageto the tanks.
Rupture of underground pipes. Relevant crevasses in the ground. In alluvial areas expulsion of sand and mud, formation of sand craters.
10 >600 Destruction of most of the masonry and timber structures, with their foundations. Destruction of some robust wooden structures, with
their foundations. Destruction of somesturdy woodenstructures and bridges.Serious damage to dams,bridles,embankments. Large landslides. Dewatering of canals,
rivers, lakes, etc. Horizontal translation of sands and clays on beaches and flat regions. Weakly deflected rails.
11 --- Heavily deflected rails. Underground pipes completely out of service.
12 ---- Almost total destruction. Displacement of large rock masses. Deformed reference lines. Objects thrown into the air.
DETECTOR TRIGGERED
1) Put out all open flames, including smoking materials
2) Put out all free flames.
3) Close the main gas tap or the LPG cylinder.
4) Do not turn lights on or off; do not operate electrically powered appliances or devices
5) Open doors and windows to increase the ventilation of the environment.
If the alarm ceases, it is necessary to identify the cause and take action accordingly.
If the alarm continues and the cause cannot be identified or eliminated, leave the property and, from
the outside, notify the emergency services (fire fighters, distributors, etc.).
ATTENTION ! operations to be carried out in the event of an alarm
Effects of the Mercalli scale
If other problems arise, it is necessary to call a specialised and/or authorised technician and/or the
Distributor of BEINAT S.r.l. should be contacted directly.