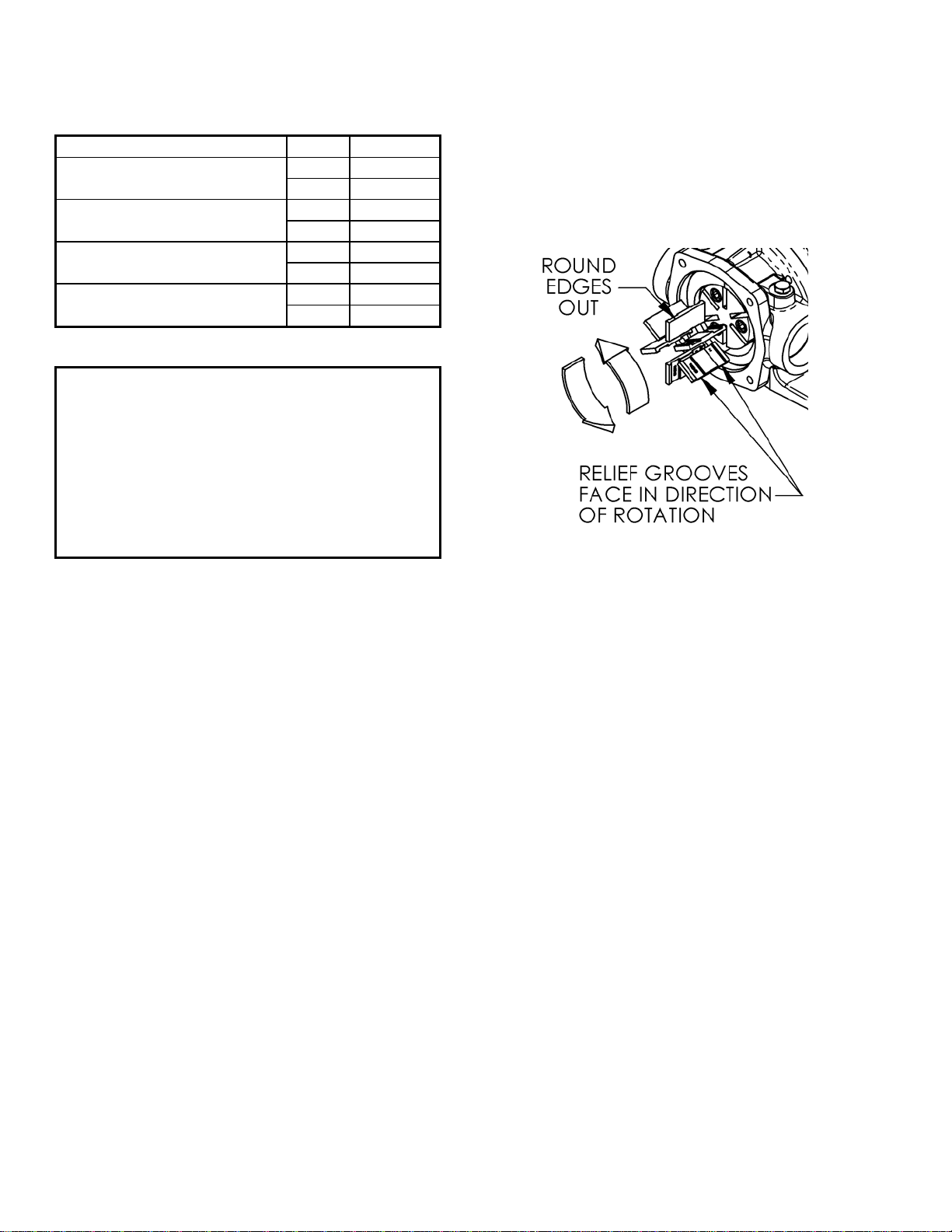
111-B00 Page 3/16
INSTALLATION
NOTICE:
Blackmer pumps must only be installed in systems
designed by qualified engineering personnel. System
design must conform to all applicable regulations and
codes and provide warning of all system hazards.
NOTICE:
This pump shall be installed in accordance with all
applicable local, state and national regulations.
Install ground and wire to local and
National Electrical Code requirements.
Install an all-leg disconnect switch near
the unit motor.
Disconnect and lockout electrical power
before installation or service
Hazardous voltage.
Can shock, burn or
cause death.
Electrical supply MUST match motor nameplate
specifications.
Motors equipped with thermal protection automatically
disconnect motor electrical circuit when overload exists.
Motor can start unexpectedly and without warning.
An external bypass valve and/or internal
relief valve MUST be installed in the
system to protect the pump from
excessive pressure.
Hazardous pressure
can cause personal
injury or property
damage
Incorrect bypass valve or internal relief
valve settings can cause pump
component failure, personal injury, and
property damage.
Hazardous pressure
can cause personal
injury or property
damage
NOTICE:
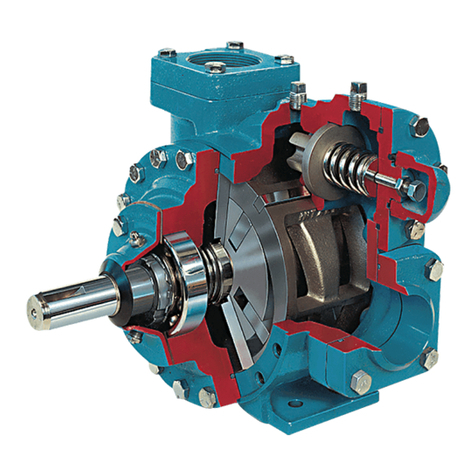
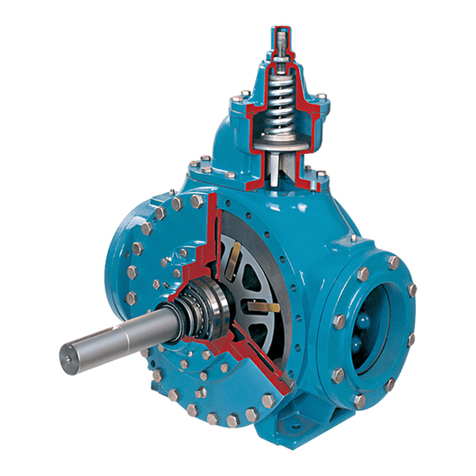
Blackmer ProVane pumps may or may not be fitted with
an internal relief valve. If an internal relief valve is not
supplied, an external bypass valve MUST be used.
PRE-INSTALLATION CLEANING
NOTICE:
This pump contains some residual test fluid and rust
inhibitor. If necessary, flush pump prior to use.
Foreign matter entering the pump WILL cause extensive
damage. The supply tank and intake piping MUST be
cleaned and flushed prior to pump installation and operation.
LOCATION AND PIPING
Pump life and performance can be significantly reduced when
installed in an improperly designed system. Before starting
the layout and installation of the piping system, review the
following suggestions:
1. Locate the pump as near as possible to the source of
supply to avoid excessive inlet pipe friction.
2. The inlet line should be at least as large as the intake
port on the pump. It should slope downward to the pump,
and should not contain any upward loops. Eliminate
restrictions such as sharp bends; globe valves,
unnecessary elbows, and undersized strainers.
3. Install a system bypass valve that returns excess flow to
the supply tank or pump inlet piping as appropriate for
the pumping system. Insure that the bypass valve
pressure setting is appropriate for the pump and system
component working pressures.
4. It is recommended a strainer be installed in the inlet line
to protect the pump from foreign matter. The strainer
should be located at least 24" (0.6m) from the pump, and
have a net open area of at least four times the area of
the intake piping. Strainers must be cleaned regularly to
avoid pump starvation.
5. The intake system must be free of all leaks.
6. When pumping liquids at elevated temperature,
provisions should be made to compensate for expansion
and contraction of the pipes, especially when long pipe
lines are necessary. Steel pipe expands approximately
3/4” (1.9 cm) per 100 feet (30.49 m) per 100°F (37.8°C)
rise in temperature.
7. Expansion joints, placed at least 36" (0.9m) from the
pump, will compensate for expansion and contraction of
the pipes. Contact the flexible connector/hose
manufacturer for required maintenance/care and design
assistance in their use.
8. ALL piping and fittings MUST be properly supported to
prevent any piping loads from being placed on the pump.
9. Install pressure gauges in the NPT ports provided in the
pump casing (if equipped) to check pump at start up.
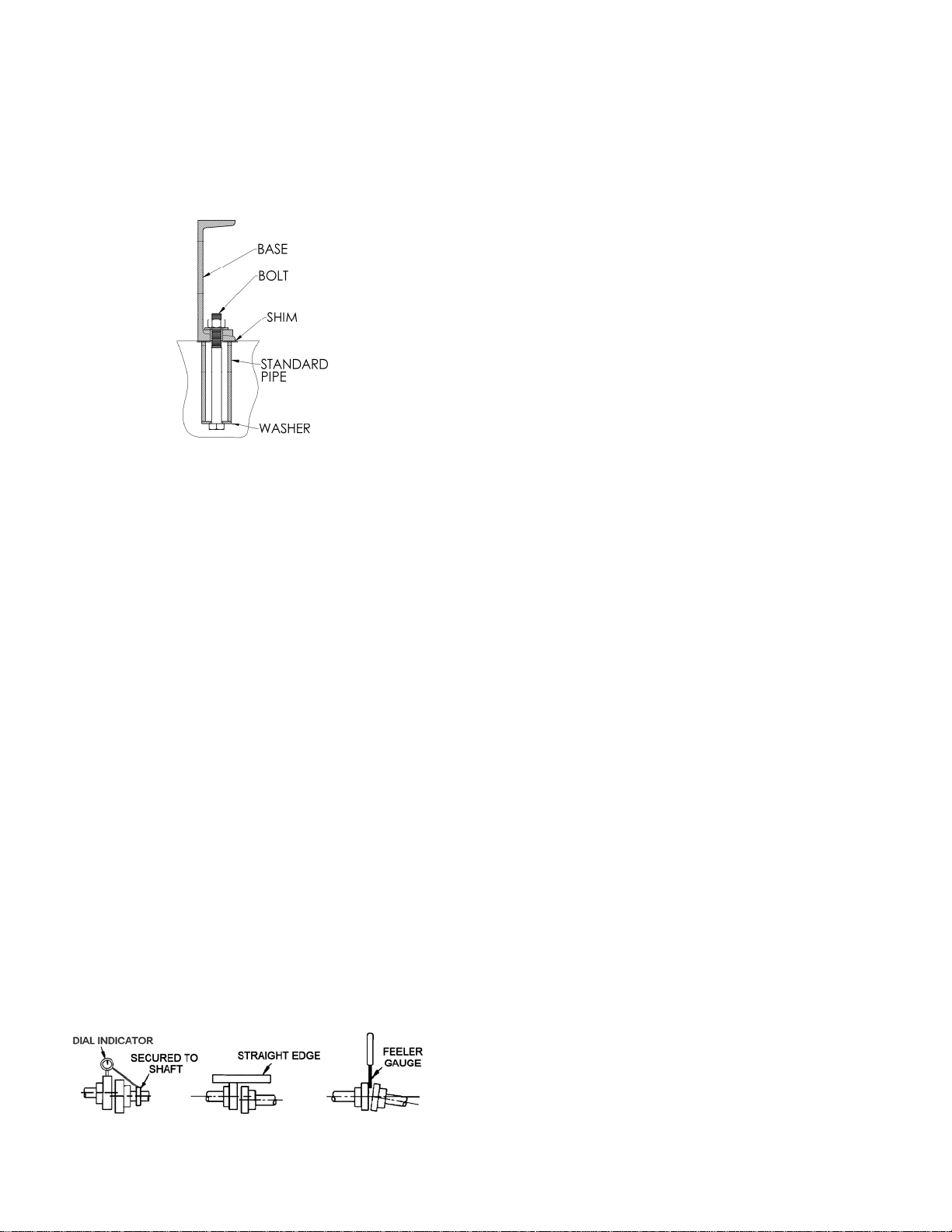
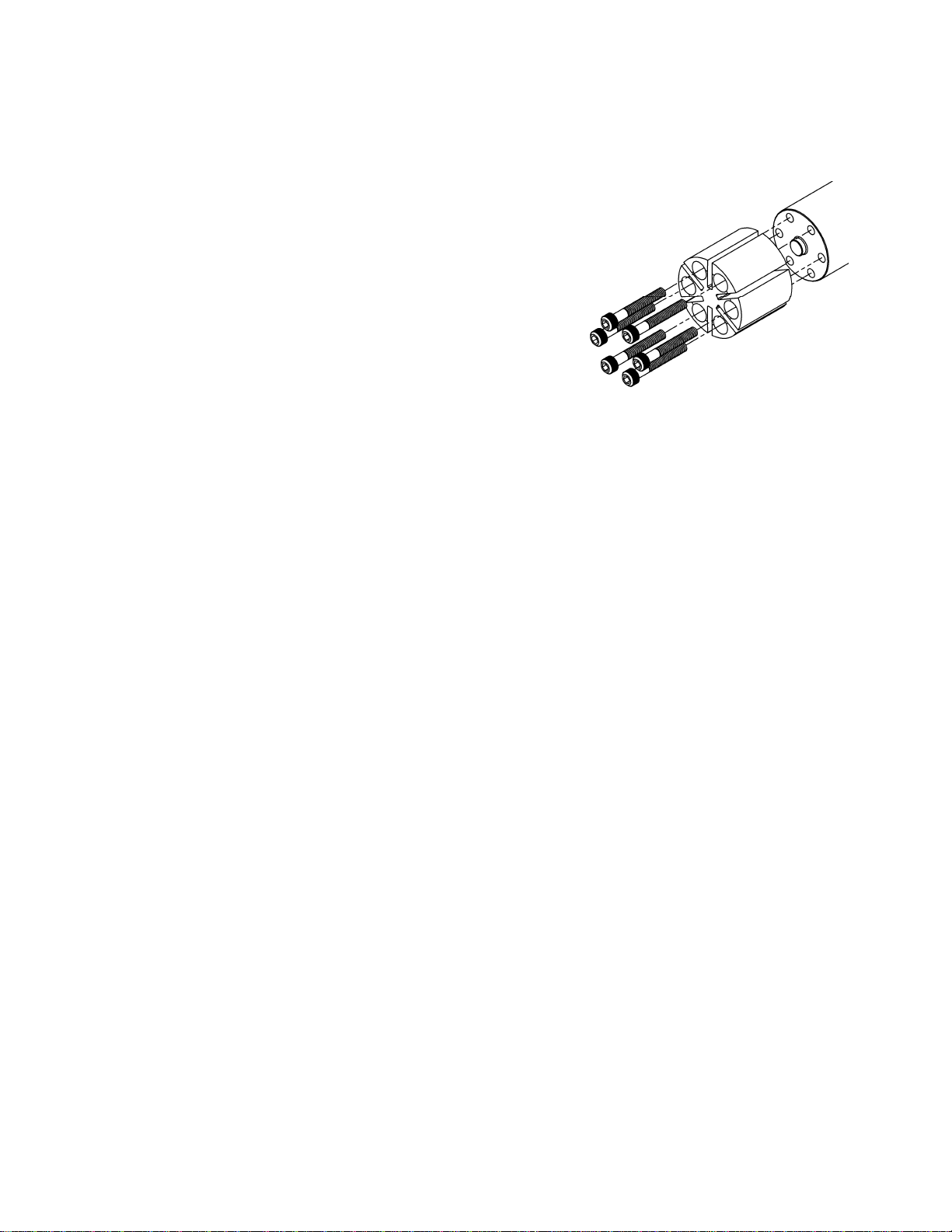
10. Check alignment of pipes to pump to avoid strains which
might later cause misalignment. See Figure 1. Unbolt
flanges or break union joints. Pipes must not spring
away or drop down. After pump has been in operation
for a week or two, completely recheck alignment.
Figure 1