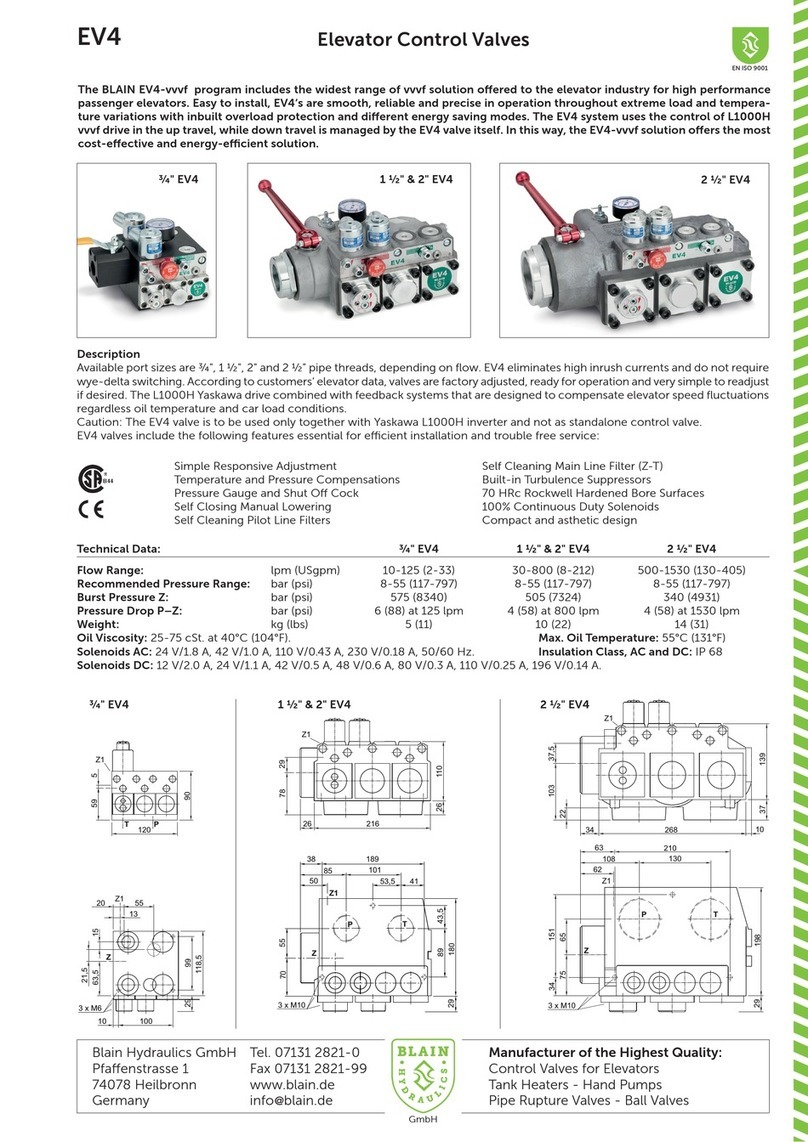
Control Elements
LV Check Valve
LH Manual Lowering
LK Slack Rope Valve (option)
LE Solenoid E
PB Pressure Gauge
LY Manual Down Speed
Adjust. (not with 1/2“ L 10)
Hydraulic Circuit
2 may 08 BLAIN HYDRAULICS Designers and Builders of High Quality Valves for Hydraulic Elevators Printed in Germany
LVO LUOLVB LVF
LFG
DS
LF
LFO
LB
MO
DG
DN
DF
DK
LV
PB
LYLH
DRLE MM
LK
Rest Position: The condition of rest of the L 10 valve is with the
solenoid LE de-energized and the main flow guide LV closed, pre-
venting flow from cylinder to tank.
Up Travel: During up travel with the pump running, oil flows through
port A, through flow guide LV and out through port Bto the main
cylinder. Solenoid LE is not energized.
Down Travel: For the elevator to travel downwards, in addition to the
down solenoids Cand Dof the EV 100 control valve, solenoid LE of
the Pressure Lock Valve is energized causing the flow guide LV to
open and allowing oil from the cylinder to flow in the direction, port B
to port A, of the Pressure Lock Valve and through the EV 100 control
valve to tank.
To slow down the elevator, solenoid Cof the EV 100 is de-energized.
Only upon completion of down levelling, is the solenoid LE of the L 10
togetherwith solenoid Dof theEV100 de-energized, causing bothflow
guides, Xof the EV 100 and LV of the L 10 to close.
ManualDown:Intheeventofanemergency,selfclosingManualDown
LH can be opened to pilot operated adjustable lowering speed valve
LY to lower the elevator. In the case of the operation of the safeties
in a 2:1 hydraulic lift system where the weight of the car is no longer
carried by the ropes, the optional Slack Rope Valve LK prevents the
ram being lowered when the manual lowering valve is opened which
would cause a slack rope condition.
Adjustments
Manual Down Speed LY (3/4“, 1½“, 2“ and 2½“ valves): ‘In‘
(clockwise) provides a slower, ‘out‘ a faster down lowering speed.
Slack Rope Valve LK: The LK is adjusted with a 3 mmAllan Key by
turning the screw LK ‘in‘ for higher pressure and ‘out‘ for lower pres-
sure. With LK turned all the way ‘in‘, then half a turn back out, the
unloadedcarshoulddescendwhentheLEsolenoidaloneisenergised.
Should the car not descend, LK must be backed off until the car just
begins to descend, then backed off a further half turn to ensure that
with cold oil, the car can be lowered as required.
T
GB L10
Connections
AControl Valve Connection
B Cylinder Side Connection
TTank Return Line
Pressure Lock Valve
No. Parts List
LF Flange
LFO 0-Ring- Flange
LB Ball
LVF Spring - Flow Guide
LFG Flow Guide
LVO Seal - Flow Guide
LVB Body - Flow Guide
LUO O-Ring - Flow Guide
LH Manual Down - Self Closing
LY Manual Down SpeedAdjuster
HO Seal - Manual Low. (5.28x1.78)
MM Nut Solenoid
M Coil Solenoid (indicate voltage)
MD Emergency Dual Power Coil
DR Tube - Solenoid
MO 0-Ring Solenoid
DF Spring Solenoid
DN Needle Solenoid
DK Core Solenoid
DG Seat Housing (with screen)
DS Seat Solenoid
B
PB
AZ
L10 EV 100
LY
LE
LV
LK LH
T
HO
L 10 1 1/2“ - 2 1/2“
Do not reduce G 1/2“ - Use 1/2“ tubing ( 18 x 1,5)
Drucksperrventil
Ruhezustand: In der Ruhestellung ist beim L 10 der Hauptkolben LV
geschlossenunddas Magnetventil LE stromlos, wodurcheinÖldurch-
fluss vom Zylinder zum Tank verhindert wird.
Hubfahrt: Mit laufender Pumpe fließt Öl durch Anschluss Aüber
den Hauptkolben LV und durch Anschluss Bzum Zylinder. Magnet-
ventil LE steht nicht unter Strom.
Senkfahrt: Damit der Aufzug abwärts fährt, muss das Magnetventil
LE des L 10 Drucksperrventils zusätzlich zu den Magnetventilen C
undDdesEV100 Ventils unter Strom gesetzt werden.Ölfließtausder
Vorsteuerkammer des L 10 Hauptkolbens LV über Magnetventil LE.
LV öffnet, wodurch ein Durchfluss vom Zylinder zum Tank über das L
10 Richtung Anschluss B zu A sowie den EV 100 entsteht.
Um den Aufzug zu verlangsamen, wird Magnetventil Cdes EV 100
stromlos. Erst am Ende der Schleichfahrt wird das Magnetventil LE
desL10 Ventilszusammen mit Magnetventil DdesHauptsteuerventils
stromlos, was das vollständige Schließen der beiden Kolben, LV im L
10 und Xim EV 100 Ventil, bewirkt.
Notablass: Um den Aufzug im Notfall absinken zu lassen, kann der
Notablass LH geöffnet werden. Um bei einem 2:1-Aufzug der im
„Fang“ ist, zu vermeiden, dass beim Öffnen des Notablassventils
LH der Aufzugs-Kolben absinkt und die Seile schlaff werden, ist die
Kolbensicherung KS vorgesehen.
Einstellungen
Notablass Geschwindigkeit LY (3/4“,1½“,2“und2½“Ventilen): ‘Hi-
nein‘(Uhrzeigersinn)bewirkteinelangsamere,‘heraus‘eineschnellere
Ablassgeschwindigkeit.
Kolbensicherung LK: Eingestellt wird die Kolbensicherung durch
das Hinein- (höherer Druck) oder Herausdrehen (niederer Druck)
der Einstellschraube LK. Mit LK ganz hineingedreht, dann eine hal-
be Umdrehung zurück, soll der unbeladeneAufzug abwärts fahren,
während nur Spule LE unter Strom steht. Bleibt der Aufzug noch
stehen,somußdieEinstellschraube LK herausgedreht werden bis der
Aufzuggeradenochfährt, dann eine halbe Umdrehung herausdrehen,
damit sich der Aufzug auch bei kaltem Öl absenken läßt.
D
Steuerelemente
LV Rückschlagventil
LH Notablass
LK Kolbensicherung (Option)
LE Magnetspule E
PB Druckanschluss
LY Notablasseinstellung
(nicht bei 1/2“ L 10)
Anschlüsse
AAnschluß Steuerventil
B Anschluß Zylinderseite
TRückleitung Tank
Hydraulikschema
G 1/2“ nicht reduzieren - 1/2“ Rohr verwenden (18 x 1,5)
M Standard Coil
MD Double Coil
Nr. Benennung
LF Flansch
LFO O-Ring - Flansch
LB Kugel
LVF Feder - Hauptkolben
LFG Kegel - Hauptkolben
LVO Dichtung - Hauptkolben
LVB Körper - Hauptkolben
LUO O-Ring - Hauptkolben
LH Notablass - selbstschließend
LY Notablasseinstellung
HO Dichtung - Notablass
MM Mutter - Magnetventil
M
Magnetspule (Spanng. angeben)
MD Notstromspule
DR Rohr - Magnetventil
MO 0-Ring Magnetventil
DF Feder - Magnetventil
DN Nadel Magnetventil
DK Kern - Magnetventil
DG Sitzhalter mit Sieb - Mag.
DS Sitzscheibe - Magnetventil