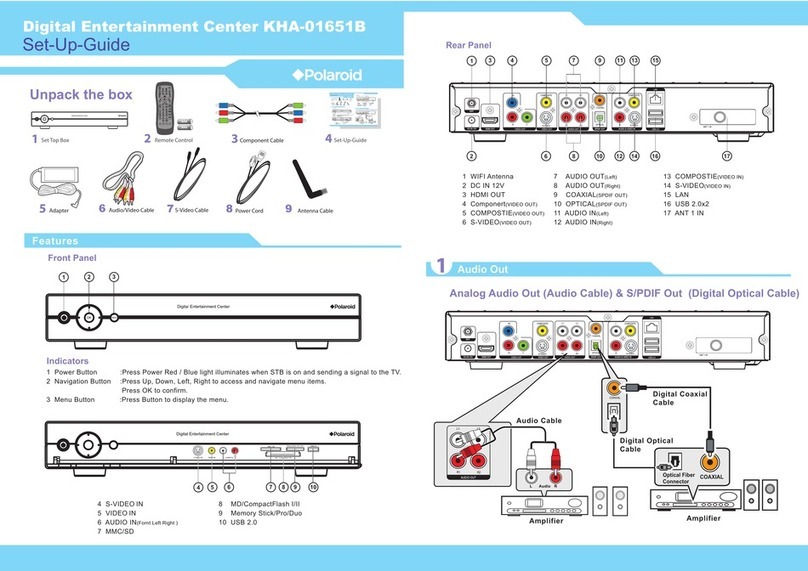
Installation Basics
A basic installation procedure involves the following:
Install the MoCA Point of Entry (POE) filter
Check QAM levels at each outlet
Boot the set-tops and verify the MoCA links
These topics are covered in the following sections.
Install POE Filter
The POE filter is a 1002 MHz low-pass filter which is installed at the subscriber drop.
It prevents interference between MoCA devices in homes connected to the same tap.
As shown in Basic Installation (on page 4), you should connect the POE filter
between the ground block and the splitter.
Verify QAM Levels
Verify that the QAM signal level of the highest frequency QAM channel (i. e.,
channel 158) is adequate at each outlet used in the installation. If this is not the case,
the home wiring should be corrected before continuing.
Verify MoCA Links
Set-tops should automatically form a MoCA network after two or more MoCA
devices boot up. Once a set-top has joined the network, its MoCA link indicator*
illuminates (see the front-panel call-outs in the set-top guides listed below):
Cisco Explorer 9800 Hybrid Video Gateway Series (part number OL-26440-01) for the
9865HDC set-tops
Cisco Explorer 8640HD, 8642HD, 8650HD, and 8652HD High-Definition DVR Set-
Tops Quick Reference (part number 78-4026879-01) for the 8640HD and 8642HD
set-tops
Cisco Explorer 8640HDC, 8642HDC, 8650HDC, and 8652HDC High-Definition Set-
Tops with Multi-Stream CableCARD (M-Card) Interface Quick Reference (part
number 78-4026878-01) for the 8642HDC set-tops
Cisco Explorer 4642HD and 4652HD High-Definition Set-Tops Quick Reference (part
number 78-4029078-02) for the 4642HD set-tops
Cisco Explorer 4642HDC and 4652HDC High-Definition Set-Tops with Multi-Stream
CableCARD Interface Quick Reference (part number 78-4029076-01) for the
4642HDC set-tops
* The 164x set-tops do not have a MoCA indicator. To verify the MoCA link, you must refer to DRIVERS
- MoCA SUMMARY PG 1 (see Node Summary and Network Summary (on page 8)).