CMOSTEK CMT2310A User manual

Features
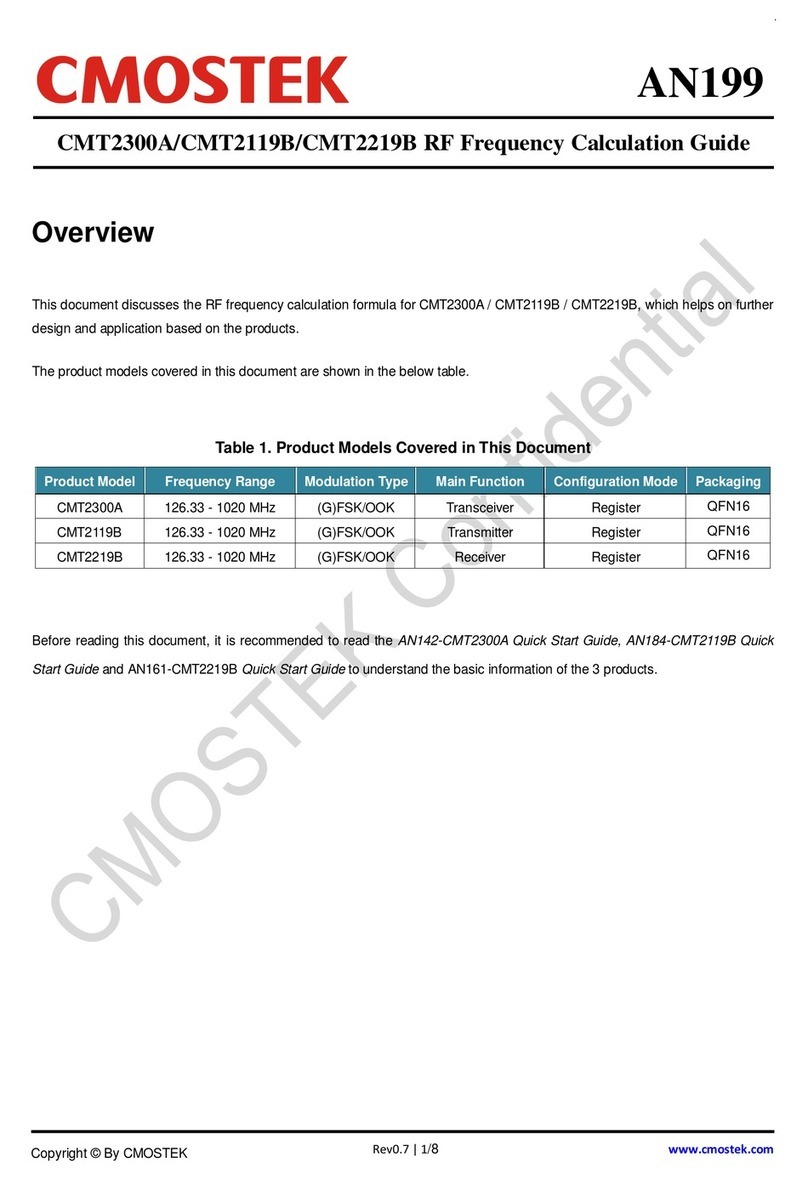
Frequency range: 113 – 960 MHz
Modulation/demodulation: OOK, 2 (G)FSK, 4 (G)FSK
Data rate: 0.1 - 1000 kbps
Sensitivity: 2 FSK, -122 dBm DR=2.4 kbps, 433.92 MHz
4 FSK, -88 dBm DR=1 Mbps, 433.92 MHz
OOK, -94 dBm DR= 300 kbps, 433.92 MHz
Adjacent channel rejection : 62 dBc, BW = 4.8 kHz,
Channel space = 12.5 kHz
Blocking: 76 dBc , ±1 MHz offset, BW = 4.8 kHz
Operating voltage range: 1.8 - 3.6 V
Tx current: 30 mA @ 13 dBm, 433.92 MHz, FSK
82 mA @ 20 dBm, 433.92 MHz, FSK
Rx current: 9.6 mA (DCDC) @433.92 MHz, FSK
No extra RF switching components required in single antenna mode
Multiple super-low power (SLP) Rx modes available
Sleep current
400 nA, Duty Cycle = OFF
800 nA, Duty Cycle = ON
Special features:
Quick and stable automatic frequency control (AFC)
3 varied clock data recovery systems (CDR)
Quick and accurate valid signal detection (PJD, RSSI)
Super-low power (SLP) and Duty Cycle receiving
Fast Tx or Rx frequency hopping
Carrier sense multiple access (CSMA)
Automatic ACK and re-sending
Antenna diversity
4-wire SPI interface
Supporting both direct and packet modes, with configurable
packet handler and 128-Byte FIFO
NRZ format, Manchester, whiten data coding, FEC
Application
Automatic meter reading
Home security and building automation
ISM-band data communication
Industrial monitoring and control
Remote control and security system
Remote key entry
Wireless sensor node
Tag reader and writer
Ordering Information
Product Model
Frequency
Package
Minimum
Order
Quantity
CMT2310A-EQR
113 - 960 MHz
QFN 24
3,000 pcs
Refer to Table 22 for more ordering information.
Description
The CMT2310A is an ultra-low power, high-performance, OOK / 2
(G)FSK / 4 (G)FSK based RF transceiver, applicable to various
applications within the 113 - 960 MHz frequency band. The
product is part of the CMOSTEK NextGenRFTM product family
which covers a complete product line consisting of transmitters,
receivers and transceivers. The high-density integration of
CMT2310A simplifies the required BOM in system design. With Tx
power reaching +20 dBm and sensitivity reaching -122 dBm, it can
achieve optimized performance of application RF links. Through
providing multiple data packet formats and code methods, this
product ensures the flexible supporting of various applications.
Besides, the CMT2310A provides functions such as 128-byte
Tx/Rx FIFO, multiple GPIO and interrupt configurations,
Duty-Cycle mode, LBT(listen before talk), high-precision RSSI,
LBD, power on reset, low-frequency clock output, quick frequency
hopping, squelch, etc., which allows more flexible application
design and gains more product differentiation capability.
High-performance Sub-1GHz RF Transceiver
CMT2310A
C
Copyright © By CMOSTEK
QF24 (4X4)

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page2/50
www.cmostek.com
Table of Content
1 Electrical Specifications............................................................................................................................................................................... 4
1.1 Recommended Operating Conditions............................................................................................................................................ 4
1.2 Absolute Maximum Ratings........................................................................................................................................................... 4
1.3 RF Power Consumption..................................................................................................................................................................5
1.4 Receiver..........................................................................................................................................................................................6
1.5 Transmitter.....................................................................................................................................................................................8
1.6 RF Frequency Synthesizer...............................................................................................................................................................9
1.7 Settling Time.................................................................................................................................................................................. 9
1.8 Crystal Oscillator.......................................................................................................................................................................... 10
1.9 Low-frequency Oscillator............................................................................................................................................................. 10
1.10 Low Battery Detection..................................................................................................................................................................11
1.11 Digital Interface............................................................................................................................................................................11
1.12 Typical Parameter Chart............................................................................................................................................................... 11
2 Pin Descriptions......................................................................................................................................................................................... 14
3 Typical Application Schematic...................................................................................................................................................................15
3.1 Direct Tie Schematic Diagram...................................................................................................................................................... 15
4 Function Description..................................................................................................................................................................................18
4.1 Transmitter...................................................................................................................................................................................19
4.2 Receiver........................................................................................................................................................................................19
4.3 Additional Functions....................................................................................................................................................................19
4.3.1 Power-On Reset (POR)............................................................................................................................................................19
4.3.2 Crystal Oscillator.....................................................................................................................................................................20
4.3.1 Temperature Compensated Crystal Oscillator (TCXO)........................................................................................................... 21
4.3.2 Sleep Timer..............................................................................................................................................................................21
4.3.3 Low Battery Detection.............................................................................................................................................................21
4.3.4 Received Signal Strength Indicator(RSSI)...............................................................................................................................22
4.3.5 Phase Jump Detector(PJD)...................................................................................................................................................... 22
4.3.6 Automatic Frequency Control (AFC)...................................................................................................................................... 22
4.3.7 Clock Data Recovery (CDR)................................................................................................................................................... 23
4.3.8 Fast Frequency Hopping..........................................................................................................................................................23
5 Chip Operation...........................................................................................................................................................................................23
5.1 SPI Interface................................................................................................................................................................................. 23
5.1.1 Read/Write Register.................................................................................................................................................................23
5.1.2 Read/Write Register in Batch Mode (BURST)........................................................................................................................25
5.2 FIFO.............................................................................................................................................................................................. 26
5.2.1 FIFO Read Operation................................................................................................................................................................27
5.2.2 FIFO Associated Interrupt........................................................................................................................................................ 28
5.3 Operation State, Timing and Power Consumption....................................................................................................................... 29

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page3/50
www.cmostek.com
5.3.1 Startup Timing......................................................................................................................................................................... 29
5.3.2 Operation State........................................................................................................................................................................29
5.4 GPIO and Interrupt.......................................................................................................................................................................30
6 Data Packet and Packet Handler............................................................................................................................................................... 33
6.1 Direct Mode................................................................................................................................................................................. 33
6.2 Packet Mode................................................................................................................................................................................ 34
6.2.1 Rx processing..........................................................................................................................................................................34
6.2.2 Tx processing........................................................................................................................................................................... 35
7 Low Power Operating................................................................................................................................................................................ 36
7.1 Duty Cycle Operating Mode......................................................................................................................................................... 36
7.2 Super-low Power (SLP) Rx Mode.................................................................................................................................................. 36
7.3 Rx Automatic Frequency Hopping (RX AUTO HOP)...................................................................................................................... 38
7.4 TX Automatic Frequency Hopping (TX AUTO HOP)...................................................................................................................... 39
7.5 Automatically Re-sending (TX AUTO RESEND)..............................................................................................................................40
7.6 Carrier Sensing Multi-path Accessing (CSMA)..............................................................................................................................40
7.7 Antenna Diversity.........................................................................................................................................................................42
8 User Register..............................................................................................................................................................................................44
9 Ordering Information.................................................................................................................................................................................45
10 Packaging Information..............................................................................................................................................................................46
11 Top Marking.............................................................................................................................................................................................. 47
12 Revise History........................................................................................................................................................................................... 48
13 Contacts.................................................................................................................................................................................................... 50

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page4/50
www.cmostek.com
1 Electrical Specifications
The measurement conditions are: VDD= 3.3 V ,TOP= 25 °C ,FRF = 433.92 MHz, sensitivity is measured by receiving a PN9
sequence, matching to 50 Ω impedance and 0.1% BER if nothing else stated. All measurement results are obtained using the
evaluation board CMT2310A-EM if nothing else stated.
1.1 Recommended Operating Conditions
Table 1. Recommended Operating Conditions
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Operating supply voltage
VDD
1.8
3.6
V
Operating temperature
TOP
-40
85
℃
Supply voltage slope
1
mV/us
1.2 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Table 2. Absolute Maximum Ratings[1]
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Supply voltage
VDD
-0.3
3.6
V
Interface voltage
VIN
-0.3
3.6
V
Junction temperature
TJ
-40
125
℃
Storage temperature
TSTG
-50
150
℃
Soldering temperature
TSDR
Last for at least 30 seconds
Human body model (HBM)
255
℃
ESD rating[2]
Human body model (HBM)
-2
2
kV
Latch-up current
@ 85 ℃
-100
100
mA
Notes:
[1]. Exceeding the Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the equipment. This value is a pressure
rating and does not imply that the function of the equipment is affected under this pressure condition, but if it is exposed to
absolute maximum ratings for extended periods of time, it may affect equipment reliability.
[2]. The CMT2310A is a high performance RF integrated circuit. The operation and assembly of this chip should only be
performed on a workbench with good ESD protection.
Caution! ESD sensitive device.Precaution should be used when handling the device in order to
prevent performance degradation or loss of functionality.

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page5/50
www.cmostek.com
1.3 RF Power Consumption
Table 3. RF Power Consumption
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Typ.
(Disable DCDC)
Typ.
(Enable DCDC)
Unit
Sleep current [1]
ISLEEP
In sleep mode with sleep timer disabled
400
nA
In sleep mode with sleep timer enabled
800
nA
Ready current [1]
IReady
2.3
2.1
mA
RFS current [1]
IRFS
315 MHz
7.7
5.4
mA
433 MHz
8.0
5.8
mA
868 MHz
8.6
6.1
mA
915 MHz
8.7
6.1
mA
TFS current [1]
ITFS
315 MHz
7.7
5.4
mA
433 MHz
8.0
5.8
mA
868 MHz
8.6
6.1
mA
915 MHz
8.7
6.1
mA
RX current [1]
IRx
DR = 10 kbps
Dev =10 kHz
315 MHz
13.7
9.0
mA
433 MHz
13.8
9.6
mA
868 MHz
14.5
10.1
mA
915 MHz
14.5
10.1
mA
TX current [1]
ITx
20 dBm[2]
315 MHz
74
/
mA
433 MHz
82
81
mA
868 MHz
88
87
mA
915 MHz
88
87
mA
13 dBm [3]
315 MHz
26.7
/
mA
433 MHz
30
29
mA
868 MHz
33
32
mA
915 MHz
34
33
mA
10 dBm [3]
315 MHz
21
15
mA
433 MHz
25
24
mA
868 MHz
27
26
mA
915 MHz
27
26
mA
-10 dBm [3]
315 MHz
10.3
7
mA
433 MHz
11
10
mA
868 MHz
12
11
mA
915 MHz
12
11
mA
Notes:
[1]. 2 FSK, DR = 10 kbps, FDEV = 5 kHz, Vbat = 3.3 V.
[2]. Apply 20 dBm matching network.
[3]. Apply 13 dBm matching network.

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page6/50
www.cmostek.com
1.4 Receiver
Table 4. Receiver Specifications
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Data rate
DR
OOK
0.1
300
kbps
2 (G)FSK
0.1
500
kbps
4 (GFSK
0.1
1000
kbps
Deviation (RX)
FDEV
(G)FSK, 4 (G)FSK[1]
0.5
350
kHz
Sensitivity
@ 433 MHz
(direct tie
matching
network)
S433
FSK[2]
DR = 2.4 kbps, FDEV = 1.2 kHz, BW = 4.8 kHz
-122
dBm
DR = 10 kbps,FDEV = 5 kHz
-114
dBm
DR = 20 kbps, FDEV = 10 kHz
-112
dBm
DR = 50 kbps, FDEV = 25 kHz
-109
dBm
DR = 100 kbps, FDEV = 50 kHz
-106
dBm
DR = 200 kbps, FDEV = 100 kHz
-104
dBm
DR = 500 kbps, FDEV = 250 kHz
-98
dBm
OOK[2]
5 kbps
-110
dBm
50 kbps
-101
dBm
100 kbps
-97
dBm
200 kbps
-95
dBm
300 kbps
-94
dBm
4 FSK[2]
DR = 10 kbps, FDEV[3] = 10 kHz
-109
dBm
DR = 100 kbps, FDEV[3] =100 kHz
-99
dBm
DR = 1 Mbps, FDEV[3] = 250 kHz
-88
dBm
Sensitivity
@ 868 MHz
(direct tie
matching
network)
S868
FSK[2]
DR = 2.4 kbps, FDEV = 1.2 kHz, BW=4.8 kHz
-120
dBm
DR = 10 kbps,FDEV = 5 kHz
-111
dBm
DR = 20 kbps, FDEV = 10 kHz
-110
dBm
DR = 50 kbps, FDEV = 25 kHz
-107
dBm
DR = 100 kbps, FDEV = 50 kHz
-104
dBm
DR = 200 kbps, FDEV = 100 kHz
-102
dBm
DR = 500 kbps, FDEV = 250 kHz
-96
dBm
OOK[2]
5 kbps
-106
dBm
50 kbps
-98
dBm
100 kbps
-94
dBm
200 kbps
-93
dBm
300 kbps
-92
dBm
4 FSK[2]
DR = 10 kbps, FDEV[3] = 10 kHz
-106
dBm
DR = 100 kbps, FDEV[3] = 100 kHz
-96
dBm
DR = 1 Mbps, FDEV[3] = 250 kHz
-85
dBm
Notes:
[1]. BT = 0.5 by default for Gaussian modulation.
[2]. In case of unspecified BW value, a crystal of 10 ppm is used and the BW value is automatically calculated by RFPDK.
[3]. For 4 FSK, FDEV represents the frequency difference between the frequency points at the far ends (left and right) and the
centered frequency point.

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page7/50
www.cmostek.com
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Receiver
channel
bandwidth
BW
Receiver channel bandwidth
1.3
1168
kHz
RSSI range
RSSI
By a step of 1 dB
-127
20
dBm
Co-channel
rejection
@ 433 MHz,
868 MHz
CCR
DR = 2.4 kbps; FDEV = 1.2 kHz;
BW = 4.8 kHz
CW interference, BER < 0.1%
-7
dBc
Adjacent
channel
rejection
@ 433 MHz
ACR-I43
3
DR = 2.4 kbps; FDEV = 1.2 kHz;
BW = 4.8 kHz, Channel Space = 12.5 kHz,
CW interference, BER < 0.1%
62
dBc
Adjacent
channel
rejection
@ 868 MHz
ACR-I86
8
DR = 2.4 kbps;FDEV = 1.2 kHz;
BW = 4.8 kHz, Channel Space = 12.5 kHz,
CW interference, BER < 0.1%
56
dBc
Blocking
@ 433 MHz
BI433
DR = 2.4 kbps; FDEV = 1.2 kHz;
BW = 4.8 kHz,
CW interference, BER < 0.1%
±1 MHz offset
76
dBc
±2 MHz offset
80
dBc
±10 MHz offset
84
dBc
Blocking
@ 868 MHz
BI868
DR = 2.4 kbps; FDEV = 1.2 kHz;
BW = 4.8 kHz,
CW interference, BER<0.1%
±1 MHz offset
66
dBc
±2 MHz offset
76
dBc
±10 MHz offset
83
dBc
Image Rejection
@ 433 MHz
IMR433
DR = 2.4 kbps; FDEV = 1.2 kHz;
BW = 4.8 kHz
CW interference, BER < 0.1%
Before calibration
30
dBc
After calibration
56
dBc
Image Rejection
@ 868 MHz
IMR868
DR = 2.4 kbps; FDEV = 1.2 kHz;
BW = 4.8 kHz
CW interference, BER < 0.1%
Before calibration
26
dBc
After calibration
51
dBc
Input 3rd order
intercept point
@ 433 MHz
IIP3433
DR = 2.4 kbps; FDEV = 1.2 kHz;
two-tone test with 10 MHz and 20 MHz deviations.
-13
dBm
Input 3rd order
intercept point
@ 868 MHz
IIP3868
DR = 2.4 kbps; FDEV = 1.2 kHz;
two-tone test with 10 MHz and 20 MHz deviations.
-12
dBm
Receiver input
impedance
Zin
RXP and RXN
Differential input impedance
433 MHz
150 Ω // 0.8 pF
868 MHz
134 Ω // 1.0 pF

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page8/50
www.cmostek.com
1.5 Transmitter
Table 5. Transmitter Specifications
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Output power
POUT
Specific peripheral components are
required according to different frequency
bands.
-10
+20
dBm
Output power step
PSTEP
1
dB
GFSK Gaussian filter
coefficient
BT
0.3
0.5
1.0
-
Output power change in
different temperature
POUT-TOP
Temperature range: -40 to +85 C
1
dB
Spurious emissions
POUT = +13 dBm, 433 MHz, FRF < 1 GHz
-54
dBm
1 GHz to 12.75 GHz, including Harmonic
-36
dBm
Harmonic output[1]
for FRF= 315 MHz
H2315
2nd harmonic, +20 dBm POUT
-57
dBm
H3315
3rd harmonic,+20 dBm POUT
-75
dBm
Harmonic output[1]
for FRF= 433 MHz
H2433
2nd harmonic, +20 dBm POUT
-56
dBm
H3433
3rd harmonic,+20 dBm POUT
-71
dBm
Harmonic output[1]
for FRF= 868 MHz
H2868
2nd harmonic,+20 dBm POUT
-47
dBm
H3868
3rd harmonic, +20 dBm POUT
-72
dBm
Harmonic output[1]
for FRF= 915 MHz
H2915
2nd harmonic,+20 dBm POUT
-47
dBm
H3915
3rd harmonic,+20 dBm POUT
-73
dBm
Harmonic output[1]
for FRF= 315 MHz
H2315
2nd harmonic, +13 dBm POUT
-51
dBm
H3315
3rd harmonic,+13 dBm POUT
-72
dBm
Harmonic output[1]
for FRF= 433 MHz
H2433
2nd harmonic, +13 dBm POUT
-44
dBm
H3433
3rd harmonic, +13 dBm POUT
-58
dBm
Harmonic output[1]
for FRF= 868 MHz
H2868
2nd harmonic, +13 dBm POUT
-50
dBm
H3868
3rd harmonic,+13 dBm POUT
-71
dBm
Harmonic output[1]
for FRF= 915 MHz
H2915
2nd harmonic, +13 dBm POUT
-54
dBm
H3915
3rd harmonic,+13 dBm POUT
-73
dBm
Notes:
[1]. The harmonic level mainly depends on the quality of matching network. The parameters above are measured based on
CMT2310A-EM.

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page9/50
www.cmostek.com
1.6 RF Frequency Synthesizer
Table 6. RF Frequency Synthesizer
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Frequency range
FRF
Require different matching networks.
675
960
MHz
338
640
MHz
113
320
MHz
Frequency deviation
range
FDEV_RNG
[1]
675 ~ 960 MHz
600
kHz
450 ~ 640 MHz
400
kHz
338 ~ 450 MHz
300
kHz
225 ~ 320 MHz
200
kHz
169 ~ 225 MHz
150
kHz
135 ~ 169 MHz
120
kHz
113 ~ 135 MHz
100
kHz
Frequency resolution
FRES
60
Hz
Frequency tuning time
tTUNE
60
us
Phase noise
@ 433 MHz
PN433
10 kHz Frequency Offset
-101
dBc/Hz
100 kHz Frequency Offset
-114
dBc/Hz
1 MHz Frequency Offset
-129
dBc/Hz
10 MHz Frequency Offset
-134
dBc/Hz
Phase noise
@ 868 MHz
PN868
10 kHz Frequency Offset
-100
dBc/Hz
100 kHz Frequency Offset
-109
dBc/Hz
1 MHz Frequency Offset
-126
dBc/Hz
10 MHz Frequency Offset
-129
dBc/Hz
Notes:
[1]. For 2 FSK and 4 FSK, FDEV represents the frequency difference between the frequency points at the far ends (left and
right) and the centered frequency point.
1.7 Settling Time
Table 7. Settling Time
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Settling time
TSLP-RX
From Sleep to RX
660
us
TSLP-TX
From Sleep to TX
660
us
TSTB-RX
From Standby to RX
160
us
TSTB-TX
From Standby to TX
160
us
TRFS-RX
From RFS to RX
16
us
TTFS-RX
From TFS to TX
16
us
TTX-RX
From TX to RX
(Ramp down requires 2Tsymbol time)
2Tsymbol
+168
us

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page10/50
www.cmostek.com
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
TRX-TX
From RX to TX
220
us
Notes:
[1]. TSLP-RX and TSLP-TX mainly depend on crystal oscillating, which is largely related to crystal itself.
1.8 Crystal Oscillator
Table 8. Crystal Specification
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Crystal frequency [1]
FXTAL
32
MHz
Crystal frequency precision [2]
ppm_XTAL
0
20
100
ppm
Load resistance
CLOAD_XTAL
15
pF
Crystal equivalent resistance
RmXTAL
60
Ω
Crystal startup time [3]
tXTAL
200
us
Notes:
[1]. The CMT2310A can utilize external reference clock to directly drive XIN pin through the coupling capacitor. The
peak-to-peak value of external clock signal is required between 0.3 and 0.7 V.
[2]. It involves: (1) initial tolerance, (2) crystal loading, (3) aging, and (4) temperature changing. The acceptable crystal
frequency tolerance is subject to the bandwidth of the receiver and the RF tolerance between the receiver and its paired
transmitter.
[3]. This parameter is to a large degree crystal dependent.
1.9 Low-frequency Oscillator
Table 9.Low-frequency Oscillator Specifications
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Calibration frequency[1]
FLPOSC
32
kHz
Frequency accuracy
After calibration
±1
%
Temperature coefficient[2]
-0.02
%/°C
Supply voltage coefficient[3]
+0.5
%/V
Initial calibration time
tLPOSC-CAL
4
ms
Notes:
[1].The low-frequency oscillator is automatically calibrated to the crystal oscillator frequency at the PUP stage.
[2].After calibration, the frequency will drift with temperature.
[3].After calibration, the frequency will drift with the change of the supply voltage.

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page11/50
www.cmostek.com
1.10 Low Battery Detection
Table 11. Low Battery Detection Specifications
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Detection accuracy
LBDRES
50
mV
1.11 Digital Interface
Table 12. Digital Interface Specifications
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Digital input high level
VIH
Vdd-0.4
VDD
Digital input low level
VIL
0.2
VDD
Digital output high level
VOH
@IOH= -0.5mA
Vdd-0.4
V
Digital output low level
VOL
@IOL= 0.5mA
0.4
V
SCLK frequency
FSCL
10
MHz
SCLK high time
TCH
50
ns
SCLK low time
TCL
50
ns
SCLK rising edge time
TCR
10
ns
SCLK falling edge time
TCF
10
ns
1.12 Typical Parameter Chart
1.12.1 Rx Current Vs. Data rate
Test condition: Freq = 434 MHz, ppm = 10.

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page12/50
www.cmostek.com
1.12.2 Rx Sensitivity Vs. Data rate
Test condition: Freq = 434 MHz, ppm = 10, BER <= 0.1%
1.12.3 Tx Power Vs. Supply Power Voltage
Test condition: Freq = 434 MHz, 20 dBm matching network, Tx power with 3.3 V and 20 dBm

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page13/50
www.cmostek.com
1.12.4 Tx Phase Noise

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page14/50
www.cmostek.com
2 Pin Descriptions
Figure 1. CMT2310A Pin Arrangement
Table 13. CMT2310A Pin Description
Pin #
Pin Name
I/O
Description
1
RXP
I
RF signal positive input
2
RXN
I
RF signal negative input
3
NC
O
Floating, not connected
4
TX
O
Tx output
5
PA_VDD
IO
PA VDD
6
VIO
IO
IO VDD
7
GPIO 4
IO
Configurable, see Table 17 CMT2310A GPIO for more details.
8
GPIO 5_RST
IO
Configurable, see Table 17 CMT2310A GPIO for more details.
9
DVDD
I
Digital VDD
10
AVDD
I
Analog VDD
11
DC_VSW
I
DCDC
12
VBAT
I
Analog VDD
13
GPIO 3
IO
Configurable, see Table 18 CMT2310A GPIO for more details.
14
GPIO 2
IO
Configurable, see Table 18 CMT2310A GPIO for more details.
15
SCLK
I
SPI clock.
16
SDO
O
SPI data output.
17
SDI
I
SPI data input.
18
CSB
I
Chip select bar
19
XI
I
32M Crystal circuit input.
20
XO
O
32M Crystal circuit output.
21
NIRQ
I
Configurable, see Table 17 CMT2310A GPIO for more details.
22
GPIO 1
IO
Configurable, see Table 17 CMT2310A GPIO for more details.
23
GPIO 0
IO
Configurable, see Table 17 CMT2310A GPIO for more details.
24
AGND
I
Analog GND.
25
GND
I
GND

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page15/50
www.cmostek.com
3 Typical Application Schematic
3.1 Direct Tie Schematic Diagram
Figure 2. Direct Tie Application Schematic Diagram (DCDC enabled)
Figure 3. Direct Tie Application Schematic Diagram (DCDC disabled)
CMT2310A_QFN24_T

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page16/50
www.cmostek.com
Table 3-1. 20 dBm Direct Tie Application BOM
No.
Descriptions
Component Values
Unit
Supplier
315 MHz
+20 dBm
433 MHz
+20 dBm
868 MHz
+20 dBm
915 MHz
+20 dBm
C1
±5%, 0402 NP0, 50 V
22
12
12
12
pF
C2
±5%, 0402 NP0, 50 V
6.8
5.6
3.3
3.3
pF
C3
±5%, 0402 NP0, 50 V
8.2
6.2
3.3
3.0
pF
C4
±5%, 0402 NP0, 50 V
8.2
NC
NC
NC
pF
C5
±5%, 0402 NP0, 50 V
NC
NC
NC
NC
pF
C6
±5%, 0402 NP0, 50 V
5.6
3.9
1.8
1.8
pF
C7
±5%, 0402 NP0, 50 V
5.6
3.9
1.8
1.8
pF
C8
±5%, 0603 NP0, 50 V
2.2
uF
C9
±5%, 0402 NP0, 50 V
1
uF
C10
±5%, 0402 NP0, 50 V
220
pF
C11
±5%, 0402 NP0, 50 V
100
nF
C12
±5%, 0603 NP0, 50 V
4.7
uF
C13
±5%, 0402 NP0, 50 V
NC
pF
C14
±5%, 0402 NP0, 50 V
NC
pF
C17
±5%, 0402 NP0, 50 V
100
nF
L1
±5%, 0603 Chip Ceramic Inductor
220
180
100
100
nH
Sunlord
L2
±5%, 0603 Chip Ceramic Inductor
68
47
15
12
nH
Sunlord
L3
±5%, 0603 Chip Ceramic Inductor
56
39
15
12
nH
Sunlord
L4
±5%, 0603 Chip Ceramic Inductor
33
33
8.2
6.2
nH
Sunlord
L5
±5%, 0603 Chip Ceramic Inductor
47
33
8.2
6.2
nH
Sunlord
L6
±5%, 0603 Chip Ceramic Inductor
47
33
15
12
nH
Sunlord
L7
±5%, 0603 Chip Ceramic Inductor
47
33
15
12
nH
Sunlord
L8
±5%, 0603 Chip Ceramic Inductor
220
68
33
33
nH
Sunlord
L9
±5%, 0603 Chip Ceramic Inductor
33
NC
NC
NC
nH
Sunlord
L10
10
uH
X1
±10 ppm, SMD
32
MHz
EPSON
U1
CMT2310A RF receiver and
transmitter
-
CMOSTEK

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page17/50
www.cmostek.com
Table 3-2. 13 dBm Direct Tie Application BOM
No.
Descriptions
Component Values
Unit
Supplier
315 MHz
+13 dBm
433 MHz
+13 dBm
868 MHz
+13 dBm
915 MHz
+13 dBm
C1
±5%, 0402 NP 0, 50 V
8.2
18
15
15
pF
C2
±5%, 0402 NP 0, 50 V
3.9
5.6
3.9
4.3
pF
C3
±5%, 0402 NP 0, 50 V
9.1
6.8
3.3
3.0
pF
C4
±5%, 0402 NP 0, 50 V
9.1
NC
NC
NC
pF
C5
±5%, 0402 NP 0, 50 V
NC
NC
NC
NC
pF
C6
±5%, 0402 NP 0, 50 V
5.6
3.9
1.8
1.8
pF
C7
±5%, 0402 NP 0, 50 V
5.6
3.9
1.8
1.8
pF
C8
±5%, 0603 NP 0, 50 V
2.2
uF
C9
±5%, 0402 NP 0, 50 V
1
uF
C10
±5%, 0402 NP 0, 50 V
220
pF
C11
±5%, 0402 NP 0, 50 V
100
nF
C12
±5%, 0603 NP 0, 50 V
4.7
uF
C13
±5%, 0402 NP 0, 50 V
NC
pF
C14
±5%, 0402 NP 0, 50 V
NC
pF
C17
±5%, 0402 NP 0, 50 V
100
nF
L1
±5%, 0603 Chip Ceramic Inductor
220
180
100
100
nH
Sunlord
L2
±5%, 0603 Chip Ceramic Inductor
56
56
15
12
nH
Sunlord
L3
±5%, 0603 Chip Ceramic Inductor
10
47
15
12
nH
Sunlord
L4
±5%, 0603 Chip Ceramic Inductor
33
15
8.2
8.2
nH
Sunlord
L5
±5%, 0603 Chip Ceramic Inductor
56
15
8.2
8.2
nH
Sunlord
L6
±5%, 0603 Chip Ceramic Inductor
47
33
15
12
nH
Sunlord
L7
±5%, 0603 Chip Ceramic Inductor
47
33
15
12
nH
Sunlord
L8
±5%, 0603 Chip Ceramic Inductor
220
68
33
33
nH
Sunlord
L9
±5%, 0603 Chip Ceramic Inductor
33
NC
NC
NC
nH
Sunlord
L10
10
uH
X1
±10 ppm, SMD
32
MHz
EPSON
U1
CMT2310A RF receiver and
transmitter
-
CMOSTEK

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page18/50
www.cmostek.com
4 Function Description
The CMT2310A is a high integrated mixed-signal transceiver, which employs a 32 MHz crystal to provide PLL reference
frequency and digital clock with supporting of OOK, 2-(G)FSK, 4 (G)FSK modulation/demodulation as well as Direct and Packet
Data processing modes.
Figure 4. Functional Block Diagram
In receiver part, the chip applies LNA+MXR+PGA+ADC+PLL low-IF architecture to achieve the Sub-GHz wireless receiving
function. In transmitter part, it applies PLL+PA architecture to achieve the Sub-1 GHz wireless transmitting function. The chip can
achieve high-performance RF transmission and receiving with no need of extra RF switch components,
In the receiver system, the analog circuit mixes the RF signal to IF and converts the signal from analog to digital through ADC
module, then outputs the two signal paths I/Q to the digital circuit for digital demodulation.The digital circuit is responsible for
mixing the IF signal to zero-frequency (baseband) and performing a series of filtering and decision processing, meanwhile it
applies AFC and AGC to control the analog circuit dynamically, and finally the original signal is demodulated. After demodulation,
the signal is sent to the decoder for decoding and then filled into FIFO, or output to GPIO directly.
In the transmitter system, the digital circuit encodes and packets the data then sends it to the modulator (or send data directly to
modulator without encoding). Then modulator will directly control the PLL and PA to have 2 (G)FSK, 4 (G)FSK or OOK based
modulation then transmit out the data.
The chip integrates a mini micro-controller (supporting supplier internal programming only), which controls and schedules various
functions and operations like auto-ACK, auto-frequency-hopping, DUTY-CYCLE based low-power Tx and Rx, CSMA function,
etc.
The chip provides SPI communication port. The external MCU can access registers to have various function configures, to
control the chip or access FIFO.

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page19/50
www.cmostek.com
4.1 Transmitter
The transmitter of CMT2310A is based on direct frequency synthesis technology. Its carrier is generated by a low-noise
fractional-N frequency synthesizer. The modulated data is transmitted by an efficient single-ended power amplifier(PA).The output
power can be read and written via the register, with configurable value ranging from -10 dBm to +20 dBm by a step of 1 dB.
In OOK mode, when PA switches on and off quickly according to data transmitted, it will easily produce spectral spurs and
glitches near the target carrier. Through the PA Ramping mechanism, it can help to minimize the spurs and glitches. In FSK
mode, the transmitter supports to have Gaussian filtering on signals before transmission, namely GFSK, thus to make the
transmitting spectrum more concentrated.
Users can design a PA matching network based on specific application requirements to optimize the transmission efficiency at
the required output power. Typical application schematics and required BOMs are detailed in Section 3 Typical Application
Schematic.
The transmitter can work in direct mode and packet mode respectively. In direct mode, data is sent to the chip directly through the
DIN pin of the chip then transmitted directly. In packet mode, data can be pre-loaded into the FIFO in STBY status and then
transmitted along with other packet elements. In 4FSK mode, it only supports data transmitting from FIFO.
4.2 Receiver
An ultra-low-power, high-performance low-IF OOK/ FSK receiver is built in the CMT2310A. Its processing steps are as follows: 1)
the RF signal sensed by the antenna is amplified by the low-noise amplifier; 2) the signal is down-converted to the intermediate
frequency by the quadrature mixer; 3) the signal is further amplified by the programmable amplifier; 4) The signal is sent to the
digital domain through A/D convertor for digital demodulation processing. During power on reset (POR), each analog module is
calibrated to the internal reference voltage. This allows the chip to keep its best performance at different temperatures and
voltages. Baseband filtering and demodulation is accomplished by the digital demodulator. The AGC loop adjusts the system
gain to optimize the performance parameters such as system linearity, selectivity and sensitivity.
Leveraging CMOSTEK's low-power design technology, the receiver in always-on mode consumes only a very low power.The
periodic operating mode and wake-up function can further reduce the average power consumption of the system to satisfy
applications with strict power consumption requirements.
Similar to the transmitter, the CMT2310A receiver can operate in direct mode and packet mode as well.In direct mode, the
demodulator output data can be directly output through the DOUT pin of the chip. DOUT can be assigned to GPIO by
configuration. In packet mode, the demodulator data output is sent to the data packet handler, get decoded then is filled into the
FIFO, then MCU can read the FIFO through SPI interface.
4.3 Additional Functions
4.3.1 Power-On Reset (POR)
The power-on reset circuit detects the change of the VDD power supply and generate reset signal to reset the entire CMT2310A
system. After the POR, the MCU must go through initialization process and re-configure the CMT2310A. There are two situations
that will lead to the generation of POR.
The first situation is a very short and sudden decrease of VDD. The corresponding POR triggering condition is that VDD
dramatically decreases by 0.9 V +/- 20% (namely 0.72 V – 1.08 V) within less than 2 us. To be noticed, it detects a decreasing
amplitude of the VDD but not the absolute value of VDD as shown in the figure below.

CMT2310A
Rev 1.0E | Page20/50
www.cmostek.com
Figure 5. Sudden Decrease of VDD Leading to Generation of POR
The second situation is a slow decrease of the VDD. The corresponding POR triggering condition is that VDD decreases to 1.45
V +/- 20% (namely 1.16 ~ 1.74 V) within a time more than or equal to 2 us. To be noticed, it detects an absolute value of VDD but
not the decreased amplitude as shown in the figure below.
Figure 6. Slow Decrease of VDD Leading to Generation of POR
4.3.2 Crystal Oscillator
The crystal oscillator provides the reference clock for PLL as well as the system clock for digital module.The value of load
capacitance depends on the CLparameter according crystal specification.The total load capacitance between XI and XO should
be equal to CL, in order to make the crystal accurately oscillate at 32 MHz.
Con chip is the on-chip load capacitor connected at both ends of the crystal with a adjustable value range of 23 - 29 pF by a step of
about 190 fF. Coff chip is the external load capacitor connected at both ends of the crystal to ground, which is optional, i.e. it's up to
user whether to apply it. Cpar is the parasitic capacitor connected at both ends of the crystal to ground with a value of about 2 ~6pF.
A crystal oscillator of 15 pF is recommended to collaborate with CMT2310A. Besides, the less the ppm value of the crystal, the
better the performance of the receiver.
Table of contents
Other CMOSTEK Transceiver manuals

CMOSTEK
CMOSTEK CMT2380F17 User manual
CMOSTEK
CMOSTEK CMT216 Series User manual

CMOSTEK
CMOSTEK CMT2300A User manual

CMOSTEK
CMOSTEK CMT2300A-EQR User manual
CMOSTEK
CMOSTEK CMT2300A User manual
CMOSTEK
CMOSTEK CMT2300A Operating manual

CMOSTEK
CMOSTEK CMT2380F64 User manual
CMOSTEK
CMOSTEK CMT2300A User manual

CMOSTEK
CMOSTEK CMT2300AW Instruction Manual