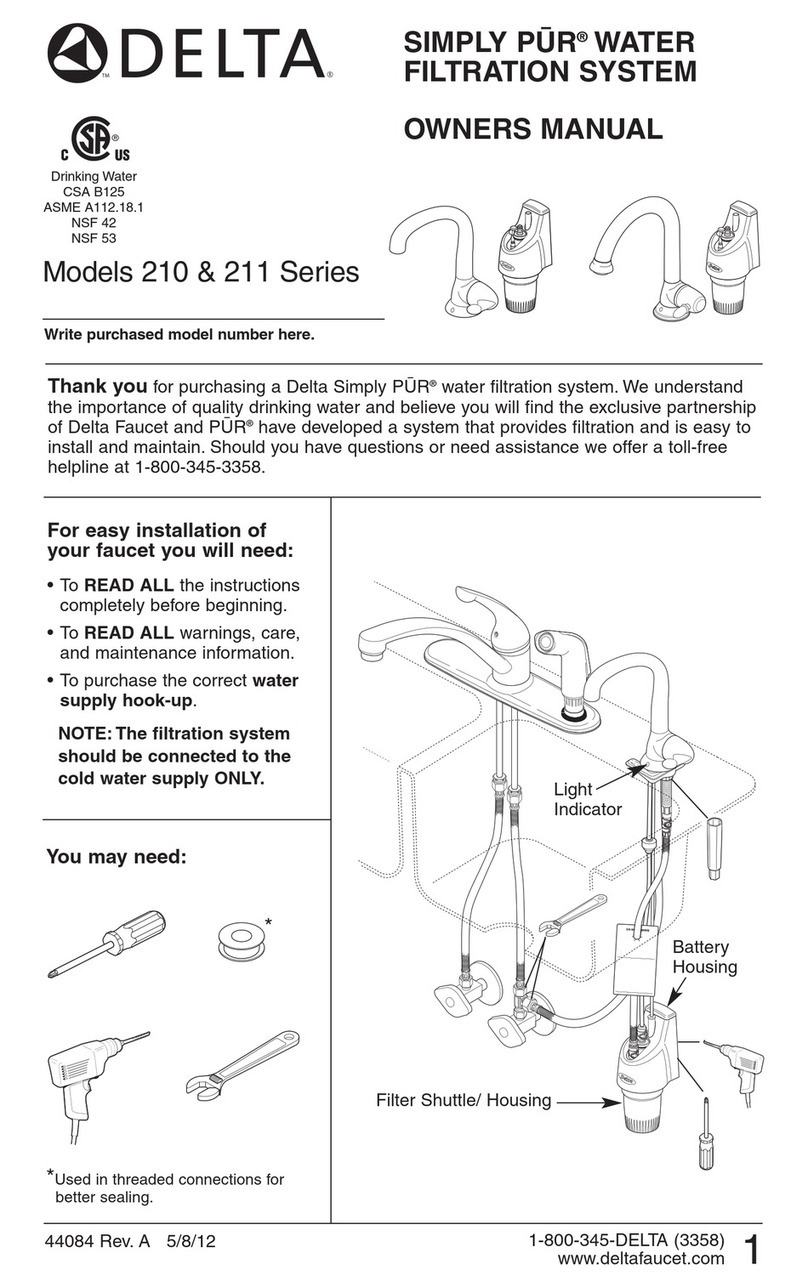
8
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
1. Prepare an excavation with an opening approximately one
foot larger than the dose tank and a depth that will allow
water to freely flow from the treatment plant into the dose
tank. Backfill with a 6 inch layer of sand or gravel if otherwise
unable to provide a smooth, level, compact base. Install the
pump access pipe into the dose tank through the top of the
tank and seal. Provide a sufficient length of pipe to extend
into the pump access riser about 4 inches. We recommend
that the hole be roped off in some fashion to prevent injury to
passers by.
2. Fill the dose tank with clean water before back filling. Backfill
around the tank approximately 12 inches below ground level.
Backfill material should be placed in 12 inch layers and
tamped to insure maximum skin friction between dose tank
and surrounding ground.
3. Position the electrical conduit in the ground between the
pump access riser and the filter box. Drill a 1- 3/4" hole in the
pump access riser for the pump outlet pipe and a 7/8" hole
for the electrical conduit. Install round pump access riser and
rectangular filter system access box so that they are flush
with ground level, and high enough to prevent surface water
from entering them.
4. Install a schedule 40 PVC pipe of sufficient length to extend
from the pump into the round pump access pipe and have
enough room to attach the vacuum release valve and union.
Install the vacuum release valve and union using appropriate
fittings.
5. Attach the float switches to the discharge pipe using clamps
furnished by Delta. Adjust the position of the clamps as
shown on the drawings or as required to insure that the pump
stops at the minimum operating water level and turns on at
about 1'-0" above this level, and that the alarm sounds at
high level position. Set the other floats where shown.
6. Install the entire pump assembly through the pump access
riser. Install the electrical cables and connect the union
from the pump outlet to the filter system. Use silicon to seal
around exiting piping.
7. Connect the filter system outlet pipe to the drip line pressure
regulator that attaches to the supply manifold. Connect the
drip line return manifold to field flush valve, located in the
filter assembly. Connect the outlet of the field flush valve to
the inlet of the treatment system.
8. Attach control panel to suitable mounting surface using all
four mounting holes on back of box. Use proper screws of
sufficient length to insure a secure and permanent mounting.
9. Control panel is rated for outdoor service, however do not
place it where it can be immersed in rising water or where
run-off water such as from a roof will fall on it. Also do not
mount it where it is subject to wetting from sprinklers, hoses,
etc. Mount control panel where there is a minimum working
space 30” wide and 6’ high.
10. The control panel must never be connected to a circuit that is
not properly grounded. Never plug the unit into a receptacle
that has a 2 pole to 3 pole grounding adapter attached. If
there is any doubt, have a qualified electrician check for
proper grounding. The control panel must be connected
to an electric source equipped with a ground fault current
interrupter (GFCI) circuit breaker or GFCI receptacle. A
standard receptacle can be replaced with a GFCI receptacle.
GFCI breakers and receptacles can be obtained from most
stores that sell electrical supplies.
11. The wire from the filter system to the control panel if direct
buried MUST BE TYPE UF rated for underground service.
It must be buried a minimum of 2 feet below the final grade
and must be protected by conduit where it exits the ground
as shown on installation drawings. Conduit must extend a
minimum of 1'-6" below ground where the wires rise from
the ground to the control panel. These requirements are per
the National Electric Code. Check with local authorities to
see if they have more stringent requirements. Schedule 40
PVC is shown, note this is conduit not water pipe. However,
if the conduit is subject to physical damage, you must use
schedule 80 PVC conduit and appropriate fittings.
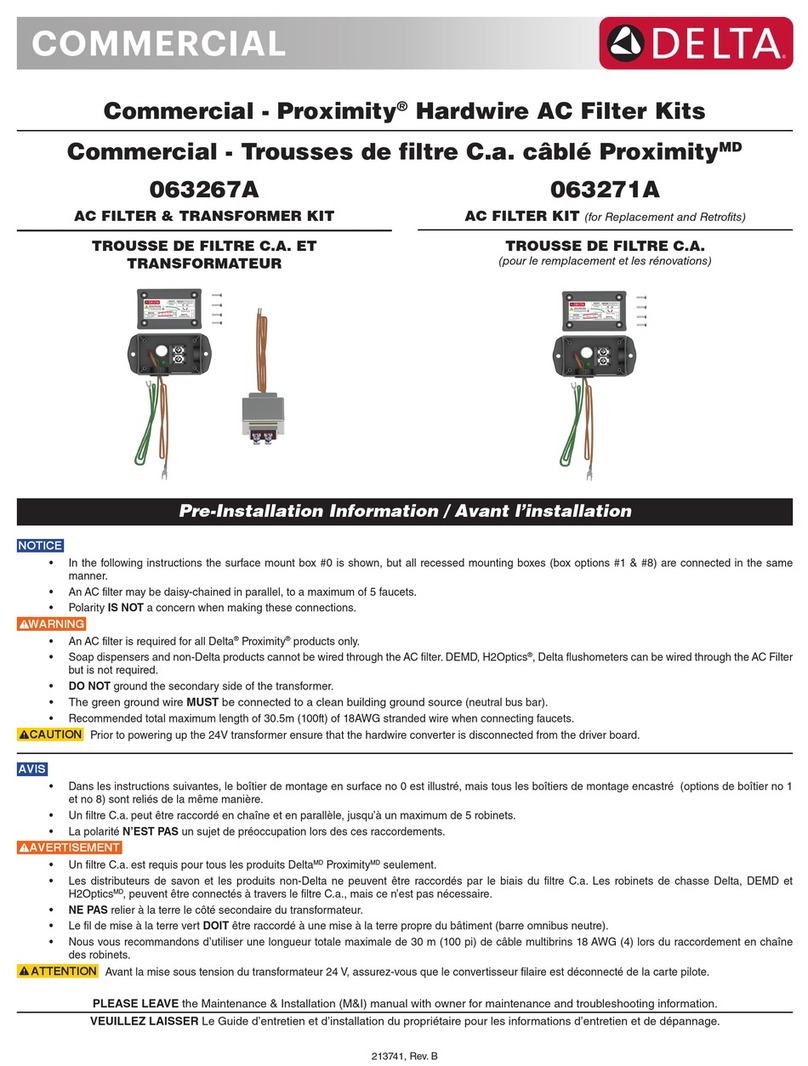
12. Wire the solenoid valves as shown on the drawings.
13. Verify that all electrical systems are connected and secure.
14. Close cover on control panel and connect control panel to a
ground fault current interrupter (GFCI) circuit.
15. Verify proper pump operation by observing pump while
manually operating pump float switch. Pump must not be run
unless immersed in water. Verify alarm system by manually
operating alarm float switch. Pump and dispose of all clean
water in the tank. Verify that 1'-2" of water remains inside
the tank when pump stop float switch turns pump off. Verify
operation of the floats by observing PLC input screen.
16. Install a 2-inch layer of gravel in the access boxes and
complete back filling the site.
17. Install drip line 6 to 8 inches deep, but not to exceed 18"
below ground. The drip line should not be stretched during
installation or damage may occur.
18. Install the system header first: Typical layout will be Filter
Unit, Zone Valve (if required) and pressure regulator at each
individual Drip Zone. Then install the PVC schedule 40 supply
lines. These should be buried at a depth of 12 to 18 inches,
4 to 12" below the depth of the WASTEFLOW®lines. If there
is a risk of freezing, bury mainlines below the frost line. At all
times avoid getting debris into the system. Flush main lines,
test for leaks and leave them full of water. Larger diameter
pipes left full of air in a trench that has not been compacted
may "float". System must be installed per drip line layout
drawings.
19. Open trenches for the sub-main manifold and flush line
manifold. These trenches should be 8 to 10 inches deep. At
the beginning of the drip line trench construct an earth damp
above drip line elevation and lay drip line over earth damp to
manifold. This will prevent water from draining from drip line.
20. Clean sub-main and flush line manifold trenches, moisten
and compact the bottom of the trench. (If this is not done,
the manifolds may "settle down" and slowly pull out the
couplings). Assemble the submain manifold outside the
trench if practical. Connect to main PVC lines and to the
system header. Flush these lines. A high water velocity is
required to carry away debris that may have entered the
pipes before or during installation. Place the sub-main and
flush manifolds into the trench.
21. Install drip lines on contour, not perpendicular or up and
down, etc. to the slope. No two drip laterals in the same zone
should have more than an 8 feet elevation difference, when
using Goeflow Classic.