Type LR125
7
CAUTION
3. The standard pilot mounting position is as
shown in Figure 1. Other mounting positions
are available.
4. Apply a good grade of pipe compound to the
external pipeline threads for a threaded body,
or use suitable line gaskets for a anged body.
Use approved piping procedures when installing
the regulator.
A regulator may leak toxic chemical to
the environment. In toxic or hazardous
liquid service, leaked chemical may
accumulate and cause personal injury,
death or property damage due to
escaping uid.
To prevent such injury or damage,
provide piping or tubing to vent the
hazardous liquid to a remote, safe
location away from air intakes or any
hazard-prone location. The exhaust
piping must be designed and installed to
guard against excessive ow restriction.
Protect the vent line or stack opening
against condensation or clogging.
5. If system operation during maintenance is
required, install isolating and vent valves
as needed.
6. A clogged pilot spring case vent may cause
the regulator to function improperly. To prevent
plugging (and to keep the spring case from
collecting moisture, corrosive chemicals or other
foreign material) point the vent down, orient it to
the lowest possible point on the spring case or
otherwise protect it. Protect the vent assembly
from icing, moisture or debris that may cause
blockage, as required. Inspect the vent regularly
to make sure it has not been plugged. To remotely
vent a spring case, remove the vent and install
obstruction-free tubing or piping into the 1/4 NPT
vent tapping. Provide protection on a remote vent
by installing a screened vent cap onto the remote
end of the vent pipe.
7. As shown in Figure 3, run a supply pressure line
from the upstream pipeline to the restrictor inlet
(use 3/8 NPT outer diameter tubing or larger).
Install a lter or strainer upstream of the restrictor,
if needed, to keep the supply source from clogging
the restrictor or pilot. Inspect and clean this lter
regularly to make sure it has not been plugged
which can prevent proper regulator operation.
8. Install a downstream pressure control line with
a minimum size of 1/2 in. / 13 mm (as shown
in Figure 3) to the pilot control line or outlet
connection. Connect the other end of the control
line at a minimum of 8 to 10 pipe diameters
downstream of the regulator in a straight run of
pipe. Do not place a control line connection in a
turbulent area, such as in or directly downstream
of a swage or elbow. Signicant restrictions in
the control line can prevent proper pressure
registration. When using a hand valve, it should be
a full ow valve, such as a full port ball valve.
9. Good piping practices usually require swaging up
to larger downstream piping to obtain reasonable
downstream uid velocity.
Startup and Adjustment
Note
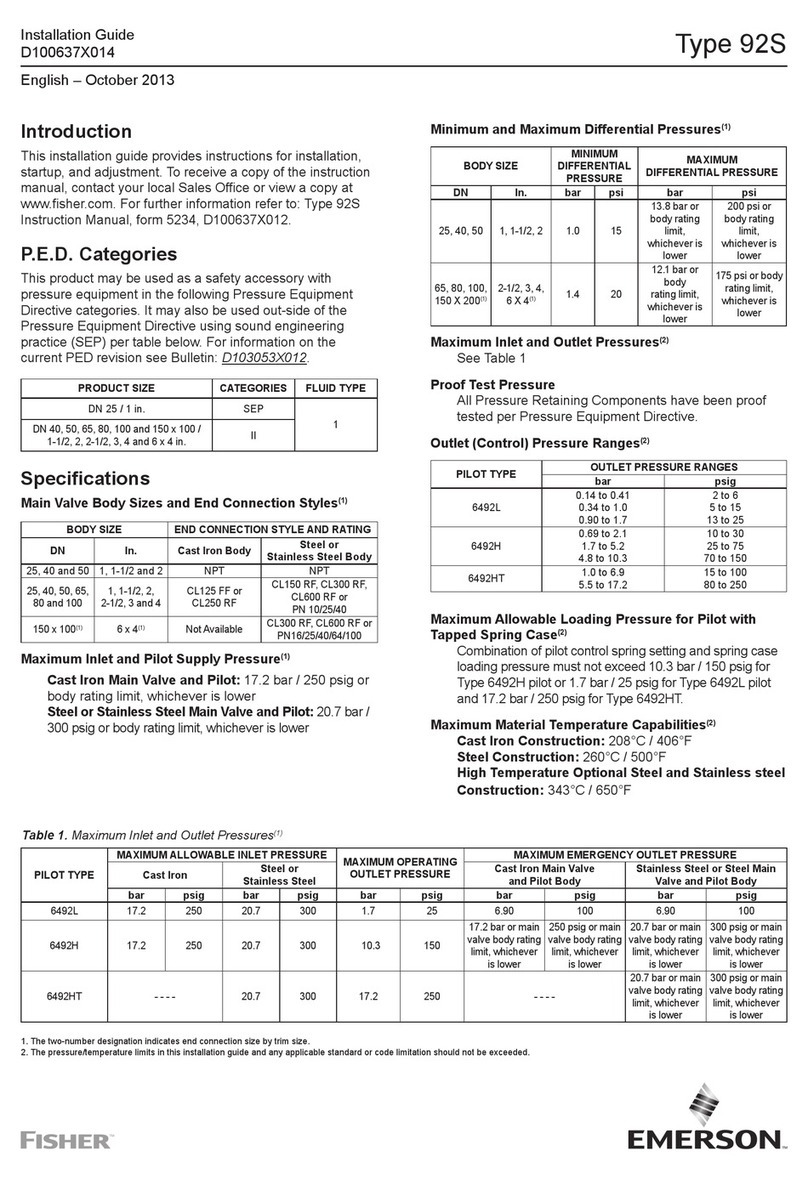
Tables 1 and 2 show the maximum inlet
pressures for specic constructions.
Use pressure gauges to monitor inlet
pressure, outlet pressure and any
intermediate pressure during startup.
Startup
1. Make sure all block and vent valves are closed.
2. Back out the pilot adjusting screw.
3. Set the restrictor to the “4” position.
4. SLOWLY OPEN the valves in the following order:
a. Pilot supply and control line valve(s), if used
b. Inlet block valve
c. Outlet block valve
5. Set the pilot to the desired outlet (control) pressure
according to the pilot adjustment procedure.
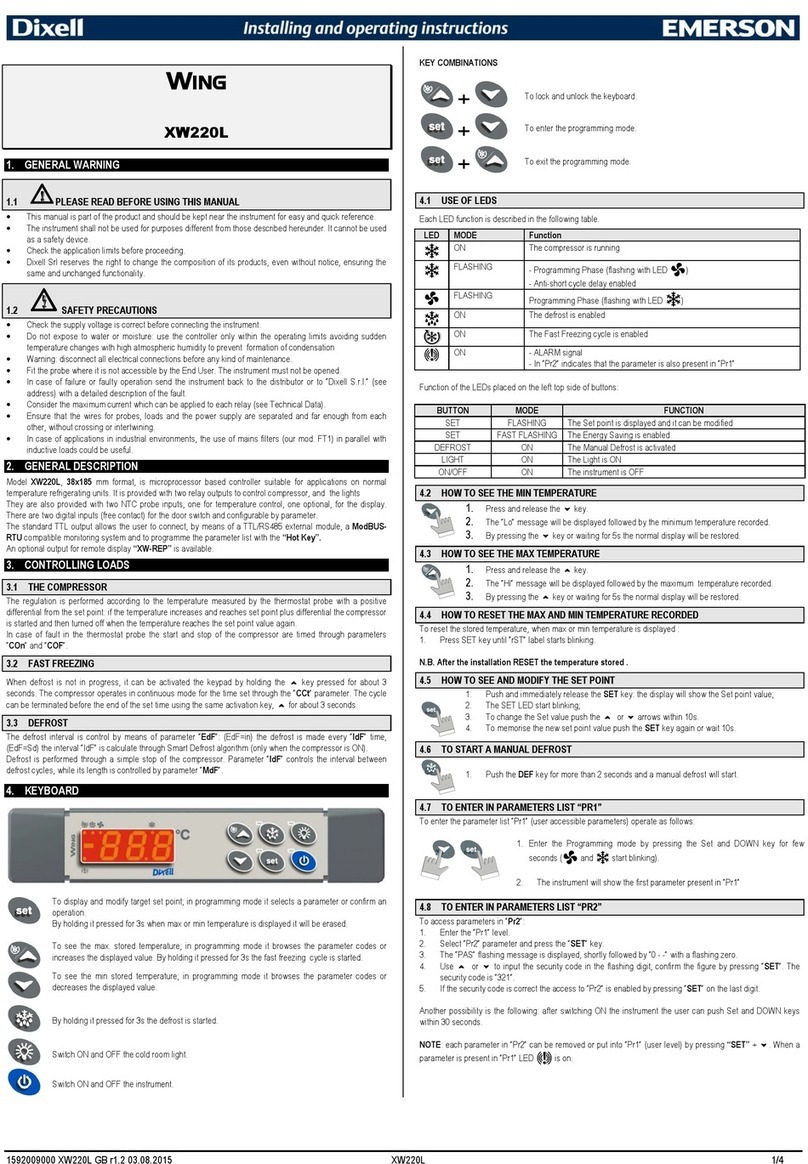
Pilot Adjustment
The factory setting of the regulator can be varied
within the pressure range stamped on the nameplate.
To change the outlet pressure, loosen the jam nut
(key 17, Figure 15) and turn the adjusting screw
(key 15) clockwise to increase outlet pressure or
counterclockwise to decrease it. Monitor the outlet
pressure with a test gauge during the adjustment.
Tighten the locknut to maintain the desired setting.
All regulator springs can be backed o to provide zero
outlet. Recommended outlet pressure ranges available
and color codes of the respective springs are shown in
Table 3.