GE MiCOM P40 Agile User manual
Other GE Control Unit manuals

GE
GE IC3645SR4W746N5 User manual

GE
GE Intellix BMT 330 User manual
GE
GE Mini COM Express 10 Quick user guide

GE
GE IC695ETM001 User manual

GE
GE CompactPCI VMIACC-7055 Series User manual

GE
GE AV-300i User manual

GE
GE 12000 Parts list manual

GE
GE VersaSafe VersaPoint IC220SDL840 User manual

GE
GE CAM-14 User manual
GE
GE IC3645SR4T405E1 User manual

GE
GE TLE Scalable 150 User manual

GE
GE Multilin MM300 User manual
GE
GE ATS7310 Assembly instructions

GE
GE Masoneilan 77-6 User manual

GE
GE Masoneilan 48000 Series User manual

GE
GE ARITECH ATS7300 User manual

GE
GE EX2100 User manual
GE
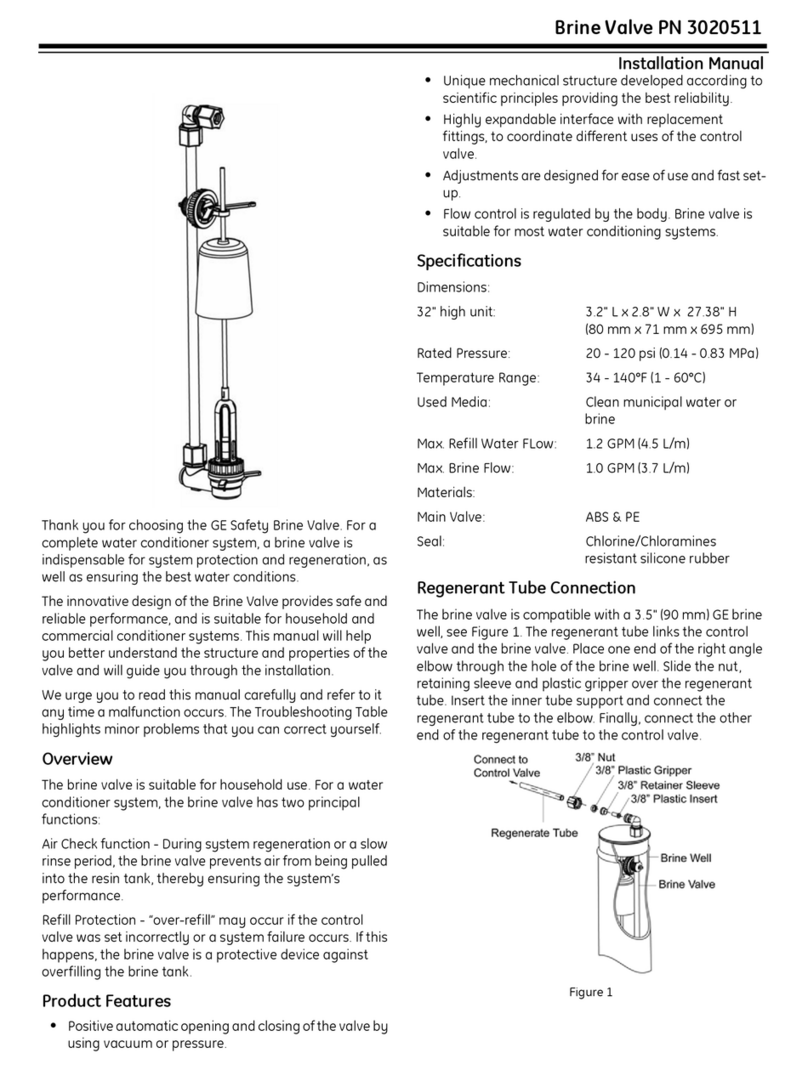
GE 3020511 User manual

GE
GE NX-591E Installation manual

GE
GE NX-1710E - Single Door Control Module Installation and operation manual
Popular Control Unit manuals by other brands

Festo
Festo Compact Performance CP-FB6-E Brief description

Elo TouchSystems
Elo TouchSystems DMS-SA19P-EXTME Quick installation guide

JS Automation
JS Automation MPC3034A user manual

JAUDT
JAUDT SW GII 6406 Series Translation of the original operating instructions

Spektrum
Spektrum Air Module System manual

BOC Edwards
BOC Edwards Q Series instruction manual

KHADAS
KHADAS BT Magic quick start

Etherma
Etherma eNEXHO-IL Assembly and operating instructions

PMFoundations
PMFoundations Attenuverter Assembly guide

GEA
GEA VARIVENT Operating instruction

Walther Systemtechnik
Walther Systemtechnik VMS-05 Assembly instructions

Altronix
Altronix LINQ8PD Installation and programming manual



















