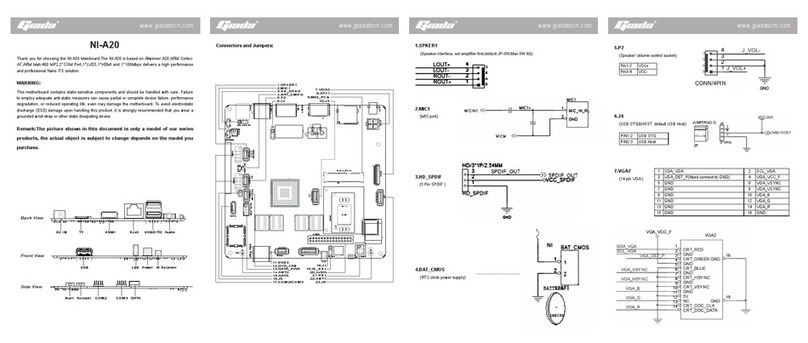
3. BIOS Function
1. Supports PNP, APM and ATAPI;
2. Supports ACPI and DMI;
3. Automatic detection and supporting hard disk whose LBA mode is over 160G;
4. End-users can easily upgrade the motherboard with BIOS.
4. BIOS Setting
Note
The descriptions relating to BIOS in this Manual can only be used for reference as the BIOS version of the
motherboard is upgraded continuously. Giada provides no guarantee that the contents in this Manual be
consistent with the information you acquire.
BIOS is a basic I/O control program saved in the Flash Memory. Bridging the motherboard and the operating
system, BIOS is used for managing the setup of the related parameters between them. When the computer is
activated, the system is first controlled by the BIOS program. First, a self-detection called POST is performed
to check all hard devices and confirm the parameters of the synchronous hardware. Once all detections are
completed, BIOS will hand over the controlling to the operating system (OS). As BIOS serves as the only
channel that connects the hardware and software, whether your computer can run stably and work in optimized
state will hinge on how to properly set the parameters in BIOS. Therefore, the correct setup of BIOS plays a
key role in stably running the system and optimizing its performance.
The CMOS Setup will save the set parameters in the built-in CMOS SRAM on the motherboard. When the
power is shut off, the lithium battery on the motherboard will provide continuously power for CMOS SRAM.
The BIOS setup program will allow you to configure the following items:
1. HD drive, floppy drive and peripheral devices;
2. Video display type and display items;
3. Password protection;
4. Power management characteristics.
A. State of BIOS Setup
When the computer is started up, BIOS will run the self-detection (Post) program. This program includes series
of diagnosis fixed in BIOS. When this program is executed, the following information will appear if any error is
found:
Press F1 to Run Setup
Press F 2 to Load default values and continue
To enter BIOS, you can press F1; to load the default values and enter the system, you can press F2. After the
self-detection process is completed, you can press DEL to enter the BIOS interface if no error is found. If the
indicative information disappears before you can act, you can shut off the computer and turn on it again, or you
can press the key RESET on the machine case. To restart your computer, you can also simultaneously press
<Ctrl>+<Alt>+<Delete>.
B. Function Keys definitions