Himoinsa CEM7 User manual

INSTRUCTION MANUAL
PROFESSIONAL
DIGITAL CONTROL UNIT CEM7

GENERATOR HS355 | PAGE 2
CONTENTS
31. Introduction
62. Front of the display module
10 3. Operating modes
12 4. Operation
22 5. CEM7 control unit inputs and outputs
31 6. CEM7 control unit alarms
47 7. Maintenance
51 8. Options (expansions)
56 9. Appendix I: parameters table
66 10. Appendix II. CEM7 control unit screens
79 11. Appendix III: dimensions, wiring and mechanical parts
92 12. Appendix IV: CAN communications
95 13. Appendix V: calibration of the control unit
97 14. Appendix VI: expanding inputs
97 15. Appendix VII: communications failure

INTRODUCTION | PAGE 3
1. INTRODUCTION
The CEM7 control unit is a generator set power supervision and control device.
The control unit consists of 2 different modules:
•Display module. The display module is responsible for carrying out
the information tasks regarding the status of the device and allows
actions to be performed by the user; through the display module
the user is able to control the control unit, as well as program and
congure the functions. Through the display module, access is given
to a record of the last 10 errors registered by the control unit.
•Measurements module. The measurements module is responsible
for performing the tasks of monitoring and control of the control unit.
This module is located in the rear panel to reduce wiring and increase
the control unit's immunity against electromagnetic noise. All the
signal, sensor and actuators are connected to the measurements
module. (See illustrations in Appendix III)
NOTE
A Timer module can be added as an option to the measurements module and
allows the functions of start up, blocking and scheduled maintenance to be
performed. Also, the Timer module allows the capacity of the error records to be
increased.

INTRODUCTION | PAGE 4
3. Congurable inputs; the measurements plate has 5 inputs that can be
programmed to perform the following functions:
•Tariff change warning
•Tariff change (CEM7 + CEA7CC2)
•Start up disabling
•External start
•Test (CEM7 + CEA7CC2)
•Forced operation
•Programmable alarms
•Genset contactor conrmation
•Parameter set selection
4. Engine statistics:
•Operating hours
•Number of starts
5. The measurements module commands the following engine functions:
•Preheating
•Stopping
•Starting
•Heating resistor
•Fuel transfer pump
•Battery charging alternator excitation
The measurements module has outputs which allow the status of the control unit
to be monitored:
•Motor started
•Control unit alarm
•3 programmable outputs that monitor the status of the control unit
alarms or the engine status inputs
The measurements module commands relay outputs for activation of the genset
contactor and the electronic protection that trips the genset's general circuit
breaker.
The connection of the measurements module and display module is performed
via a CAN communications bus, enabling the interconnection between additional
modules which ensures the scalability of the control unit.
The following additional modules can be added as options via the CAN bus:
1.1 MEASUREMENTS MODULE
The measurements module provides the following electrical signal characteristics,
both those generated and those from the network itself:
•Phase-neutral voltage
•Phase-to-phase voltage
•Current phase
•Frequency
•Active, apparent and reactive power
•Power factor and cosine of FI
•Instant energy (kWh) and accumulated power (day, month, year) with
the timer option
•THD (total harmonic distortion) of voltages and currents
•Calculation of harmonics up to order 20
The measurements module provides the following engine characteristics:
1. Engine alarm inputs:
•Fuel reserve
•Oil pressure
•Water temperature
•Water level
•Emergency stop (mushroom head stop button)
2. Analogue inputs of the engine:
•Fuel level
•Pressure
•Temperature
•Congurable input (Oil temperature)
•Charge-battery alternator voltage

INTRODUCTION | PAGE 5
•Timer device
•Telesignal device
•CCJ1939 device
•Repetitive display
•Telecontrol device
•Announcement panel device
•CAN/USB
•CAN/232 + MODEM LINE
•CAN/232 + MODEM GSM
•CAN/232 + MODEM GSM/GPS POSITIONING
•CAN/232 + MODEM GPRS HG FLEET MANAGER
•CAN/232 + MODEM GPRS/GPS HG FLEET MANAGER
•CAN/485 (MODBus)
•CAN/LAN
•CAN/LAN (MODBUS IP)
•CAN/LAN HG FLEET MANAGER
•Second Zero Suppressor
•PT100 temperature probes expansion
•ATS panel with CEC7 control unit.
•Precision gauge

FRONT OF THE DISPLAY MODULE | PAGE 6
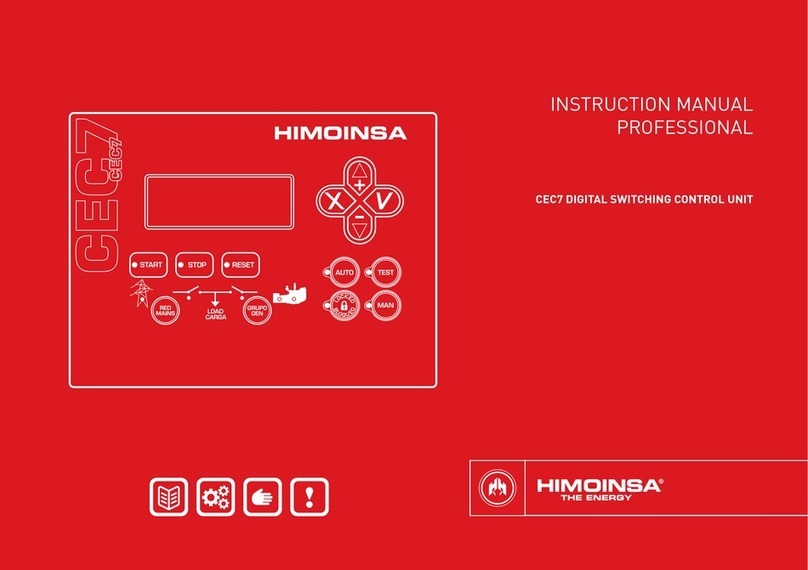
2. FRONT OF THE DISPLAY MODULE
The display module has a backlit display and various LEDs for monitoring the
status of the control unit. It also has keys that allow the user to control and
program the control unit.
Fig.1
CEM7 display module
Fig.2
CEM7P display module

FRONT OF THE DISPLAY MODULE | PAGE 7
2.1.2 CONTROL UNIT COMMAND BUTTONS
Engine start button (only in manual mode)
Controls the start up with a single push.
Lit LED: Engine started.
Engine stop button (only in manual mode)
The rst press stops the engine following a cooling cycle. The
second press stops the engine immediately.
Lit LED: Engine stopping (with or without cooling)
Alarms reset button. Allows acoustic signals to be eliminated
and the user to report the alarms.
LED flashing: Pending notication alarms.
Lit LED: Alarms active.
Fuel transfer pump button.
In manual mode, this button activates the fuel transfer pump
if the fuel level is below the programmed limit.
Lit LED: Fuel transfer pump active.
2.1.3 DISPLAY BUTTONS
Confirm (V). Enter the menus and conrm the data
entered.
Cancel (X). Leave the menus and cancel the data entered.
Up (+). Advance through the selection on display screens,
the selection in maintenance menus and increase the
programming settings.
Down (-). Go back through the selection on display screens,
the selection in maintenance menus and decrease the
programming settings.
1. Backlit display 4 lines by 20 digits.
NOTE
The display goes into low power mode (backlight off) after 10 minutes have
passed without any keystroke.
2. Control unit buttons
•Buttons for control unit operating mode
•Control unit command buttons
•Display buttons
•Genset contactor activation button (only CEM7P module)
3. Status LEDs
•ENGINE status LEDs
•ALARMS LEDs
•CONTACTORS status LEDs
2.1 CONTROL UNIT BUTTONS
2.1.1 BUTTONS FOR CONTROL UNIT OPERATING MODES
Automatic mode: The control unit
monitors the status of the genset and
manages its operation and the
programmable inputs.
Manual mode: The control unit is
commanded by the user.
Lit LED: Automatic
mode active
LED flashing:
Automatic mode
blocked
LED off: Manual
mode active

FRONT OF THE DISPLAY MODULE | PAGE 8
2.2.2 ALARMS LEDS
Fuel reserve
Lit: Analogue sensor alarm
Flashing: Digital sensor alarm
Off: Without alarm
Battery level
High temperature
Engine start up failure
Overspeeding
Low oil pressure
Auxiliary 1 (freely
programmable)
Auxiliary 2 (freely
programmable)
NOTE
For more details see the Alarms section
2.2.3 CONTACTORS STATUS LEDS (CEM7 + CEA7CC2).
These LEDs only appear active when the switching control unit is connected.
Start up option due to Network Voltage Failure (CEM7 + CEA7CC2)
The M and G symbols on the front of the control unit only appear activated when
the switching control unit is connected.
Network contactor status Lit: Contactor active
Flashing: Contactor in the
connection/disconnection
phase.
Off: Contactor disconnected.
Genset contactor status
2.1.4 CONTACTOR BUTTONS (ONLY CEM7P MODULE)
Genset contactor. Enable/disable genset contactor (manual
mode only).
2.2 STATUS LEDS
2.2.1 ENGINE STATUS LEDS
Motor started Lit: Engine running detected
Off: Motor stopped
Preheating Lit: Engine preheating activated
Off: Engine preheating deactivated
Start engine Lit: Engine started
Off: Engine start deactivated
Alternator status
battery charging
Lit: With engine running, voltage in the
battery charging alternator is detected
Off: Stopped engine or engine running
without voltage in the battery charging
alternator

FRONT OF THE DISPLAY MODULE | PAGE 9
2.3 PASSWORDS
The CEM7 control unit has 2 levels of 4-digit password to protect against
unauthorized access. The different levels of access are as follows:
•User (default password: 1111). User level access allows the operator
to access the main menu of the CEM7 control unit.
•Maintenance (default password: 1911). Maintenance level access
allows the operator to access the Parameters programming option
from the main menu.
The CEM7 control unit's passwords are customizable by the user from the main
menu. A user can congure both passwords for their access level and lower-level
passwords.
NOTE
To enter a password see Appendix II: password entry

OPERATING MODES | PAGE 10
3. OPERATING MODES
3.1 MANUAL MODE
In manual mode, the control unit is commanded by the user via the front panel of
the display module. The user can start and stop the engine by pressing the
START and STOP keys respectively.
Pressing the START key initiates the engine starting procedure (without
deactivating the network contactor CEM7 + CEA7CC2). Pressing the STOP key
initiates the engine stopping procedure with cooling; a second press of the STOP
key causes the engine to stop immediately without waiting for the cooling time.
x 1 click
WITH cooling
x 2 (double click)
WITHOUT cooling
NOTE
In manual mode, the control unit's protection devices remain active, being able
to produce alarms that cause the motor to stop.
In manual mode, the control unit does not take into consideration the start
conditions (programmed, by external signal) that can be programmed.
Activation of the genset contactor on the CEM7P display module is performed by
pressing the GENSET key.

OPERATING MODES | PAGE 11
3.3 MODE LOCKING FUNCTION
Pressing the Auto or Man keys for 5 seconds activates the locking of the mode.
This control unit state is indicated by the ashing of the mode key currently
active. To deactivate the mode lock and allow normal operation of the control
unit, press the key associated to the active mode for 5 seconds.
5 ’’ Locked 5 ’’ Unlocked
In order to achieve activation of the genset contactor, the engine has to be
running and provide a stabilised electrical signal.
3.2 AUTOMATIC MODE
In automatic mode supervision of the installation is managed by the control
unit. Under certain conditions which can be programmed, the control unit starts
the genset to power the installation.
Programmable conditions for genset starting and activation of the genset
contactor include:
•External start (Settings table, parameter 10)
•Start programmed by schedule
•Forced operation signal (Settings table, parameter 12 and
Regulations table, parameter 25)
•Starting via the switching panel (CEA7CC2)
Programmable conditions for genset starting without activation of the genset
contactor include:
•Tariff warning (Settings table, parameter 7)
•Engine test (Settings table, parameter 11)
Also in automatic mode it is possible to manage start ups by using external
devices (PC, modem, display modules or switching control units).

OPERATION | PAGE 12
4. OPERATION
4.1 STARTING THE ENGINE
Under the conditions for activating the control unit, proceed to perform the
following engine start procedure:
4.1.1 DIESEL ENGINE
1. Start delay. Once activation conditions are detected, it is possible to program
a time delay (Times table, parameter 3) before continuing the engine start up
procedure only in automatic (CEM7 + CEA7CC2 or CEM7 + AE)
2. Preheating of the motor (PR). The control unit activates preheating output
(PR) for the programmed time (Times table, parameter 4). The control unit allows
programming of a temperature threshold (Thresholds table, parameter 48) of the
coolant sensor that interrupts the preheating process, before proceeding with
the engine start up.
3. Enabling the starting of the motor (positive contact activation). Enabling the
starting of the motor (positive contact activation) is performed via the
measurements module PC output. The output supports a Stop by De-energisation
conguration (output activation during engine operation) or Stop by Excitation
(engine stop pulse -Table times, - parameter 12). The operating mode of the
enabled output can be set (Times table, parameter 18).

OPERATION | PAGE 13
4.1.2 GAS ENGINE
1. Checking the engine gas train (PR). The process of checking the gas train
begins with the activation of the PR output and lasts for a programmable
maximum time (Times table, parameter 4). If the control unit has a programmable
input (Settings table, parameter 25) assigned to the verication of the gas train,
the process checking the gas train shall end when activation of the gas train
verication input is detected; if gas train activation time ends without having
detected gas train verication, the control unit shall attempt the start again. If
the control unit has no input assigned to gas train verication (Settings table,
parameter 25, value 0), the control unit shall carry out the engine start after the
time set for checking the gas train. The gas train output PR will remain active
from the engine's start and running process until the engine stop is carried out.
2. Starting the motor (ARR). For a maximum time (Times table, parameter 5),
the start output of the measurements module is activated while waiting to detect
at least one of the programmed start conditions (Regulations table, parameters
19 to 22).
3. Gas Ignition (PC). Some time after (Times table, parameter 30) activating the
start signal, the PC output is activated to enable engine ignition once the residual
gas has been purged.
4. Gas valve. Some time after (Times table, parameter 31) activating the Gas
Ignition signal, the output congured as gas valve is activated (Settings table,
parameters 1 to 3, value 25).
5. If during the set time no motor starting is detected, the control unit waits for a
period of time (Times table, parameter 2) before retrying the start. Once a certain
number of starts has been exceeded without detecting any start condition (Times
table, parameter 1), the control unit activates the Starting Failure alarm.
6. During motor starting, the excitation of the battery charging alternator is
carried out through the D+ output for a period of time (Times table, parameter 8).
Once the excitation of the alternator has been completed, the measurement
module monitors the correct functioning of the battery charging alternator. In the
event a battery charging alternator failure is detected, the Alternator Failure
alarm is activated (Alarms table, parameter 10).
4. Starting the motor (ARR). For a maximum time (Times table, parameter 5),
the start output of the measurements module is activated while waiting to detect
at least one of the programmed start conditions. The possible engine starting
conditions are:
•Generator voltage (Regulations table, parameter 19). The motor is
considered started when a certain generator voltage is exceeded
(Threshold table, parameter 20).
•Alternator voltage (Regulations table, parameter 20). The motor is
considered started when a certain battery charging alternator voltage
is exceeded (Threshold table, parameter 21).
•Pickup frequency (Regulations table, parameter 21). The motor is
considered started when a certain pickup frequency is exceeded
(Threshold table, parameter 22). To activate the pickup calculation
via the engine ring gear, it is necessary to enter the number of teeth
on the engine's ywheel ring gear (Threshold table, parameter 24);
if the number of teeth for the ywheel ring gear is zero, the pickup
frequency is calculated via the generator frequency according to the
ratio 50 Hz / 1500 rpm, 50 Hz / 3000 rpm or 60 Hz /1800 rpm
(Regulations table, parameter 26).
•Low Oil Pressure Signal (Regulations table, parameter 22). Due to
its characteristics, it is not advisable to use the low oil pressure
signal to detect if the engine is running, but its use is recommended
as protection against a restart, as the engine is already running.
Exceptions to this engine start detection are SCANIA engines and
sensors that have their own power source.

PRACTICAL EXAMPLE OF A START OPERATION
NOTE
Before starting the start cycle it is advisable to ensure the genset's main circuit
breaker is in the off position (OFF).
OPERATION
By pressing the START button the start cycle is initiated and is indicated by the
START button's LED switching on. At the same time if the motor has a preheating
plug the PR output is activated, with the corresponding LED switching on ( ),
for the programmed time. (1)
Fig.1
Once this time has elapsed the PR output is deactivated, and the corresponding
LED turns off ( ) and immediately the positive contact of the PC output is
activated and 0.5 seconds later the ARR output with the switching on of the LED
( ), this output remains activated until any engine running condition is
detected. (2)
7. Generator stabilisation. Once any start condition is detected, the control unit
waits for a xed time for stabilization of the generator signal before monitoring
the quality of the generator signal.
8. Nominal condition. After achieving engine stabilisation, verication of the
generator signal is performed. In this state, the quality of the signal produced by
the genset is evaluated (voltage levels, frequency,...).
OPERATION | PAGE 14

Fig.2
Once it has been detected that the engine is running the LED switches on ( ),
this indicates the end of the start cycle and the START button turns off. (3)
Fig.3
The LED corresponding to the battery charging alternator voltage ( ) switches
on when the voltage provided by the alternator exceeds the voltage threshold set
by default. (4)
Fig.4
If during the start cycle, the engine started condition is not detected after 5
seconds, the ARR output deactivates and the corresponding LED turns off
( ). Subsequently the control unit automatically attempts a new start, repeating
a new cycle without the need to press START (4 cycles by default). After
exhausting the attempts to start the engine without success, the control unit
display shows the alarm (START FAILURE). (5)
To interrupt the start cycle just press the STOP button.
x4
Fig.5
OPERATION | PAGE 15

OPERATION | PAGE 16
NOTE
The display shows the engine status screen, where the engine status is displayed
during the start up operation. This sequence is:
Genset: Stopped
Genset: Starting
Genset: Started
Genset: Stabilised
Genset: Charging
NOTE
The start an automatic system using a timer, external signal, etc. is carried out
following the same process as when starting manually.
4.2 ENGINE STOP
The engine stopping process in automatic mode is carried out as follows:
4.2.1 DIESEL ENGINE
1. Cooling the motor. Once free of charging, the engine will continue running for
a cooling time (Times table, parameter 11). In certain situations, it is possible to
set the alarms (Alarms table, parameters 3, 6, 9...) of the control unit to perform
a stop without engine cooling
2. Engine stop. After the engine cooling time has elapsed, the PC output of the
measurements module is enabled or disabled according to the programmed
conguration (Regulations table, parameter 18). As an engine stop condition it is
possible to select:
•Generator voltage (Regulations table, parameter 19). The engine is
considered stopped when the generator voltage is below the start up
threshold (Threshold table, parameter 20).
•Alternator voltage (Regulations table, parameter 20). The engine is
considered stopped when the battery charging alternator voltage is
below the start up threshold (Threshold table, parameter 21).
•Pickup frequency (Regulations table, parameter 21). The engine is
considered stopped when the pickup frequency is below the start
up threshold (Threshold table, parameter 22). To activate the pickup
calculation via the engine ring gear, it is necessary to enter the
number of teeth on the engine's ywheel ring gear (Threshold table,
parameter 24); if the number of teeth for the ywheel ring gear is
zero, the pickup frequency is calculated via the generator frequency
according to the ratio 50 Hz / 1500 rpm, 50 Hz / 3000 rpm or 60 Hz
/1800 rpm (Regulations table, parameter 26).
•Low Oil Pressure Signal (Regulations table, parameter 22). The
low oil pressure condition is used for detecting a stop, by which the
engine is considered stopped when it is detected that the sensor is
closed. Exceptions to this engine stop detection are SCANIA engines
and sensors that have their own power source.
4.2.2 GAS ENGINE
1. Checking the engine gas train (PR) and gas valve. The control unit
deactivates the gas supply outputs to the engine.
2. Gas Ignition (PC). Some time after (Times table, parameter 32) closing the
gas supply, the Gas Ignition output is deactivated to stop the engine. If the
engine stop is triggered by an emergency stop alarm, the Gas Ignition output is
deactivated simultaneously to cutting the gas supply.
To conrm the engine has stopped, all the programmed stop conditions must be
detected for a set period of time (Alarms table, parameter 71). If after 90
seconds an engine running condition continues to be detected, the Stop Failure
alarm is triggered.

PRACTICAL EXAMPLE OF A STOP OPERATION
NOTE
Before starting the stop cycle it is advisable to ensure the genset's main circuit
breaker is in the off position (OFF).
The genset stop can be performed in various ways:
1. Manual: Pressing the STOP button once. To perform a stop with cooling cycle.
2. Manual: Pressing the STOP button twice. To perform a stop without cooling
cycle.
3. Turning the panel's activation key to the “O” position. To perform a stop
without cooling cycle.
4. Automatic: After cancelling the order which leads to the automatic start and
in this way performing a stop with cooling.
Sequence: We press the STOP button once and begin the stop cycle with engine
cooling. This is indicated with the STOP1 button lighting up.
Fig.1
After concluding the cooling time (120 seconds by default), the PC output is
disabled or enabled according to the type of engine to carry out the stop, the
STOP button and the LED ( ) for the started engine switch off (2).
Fig.2
If after a period of time any engine running condition is detected, the control unit
shows on the display the STOP FAILURE alarm and the LED of the STOP button
remains lit (3).
Fig.3
The LED corresponding to the battery charging alternator voltage ( ) switches
off when the voltage provided by the alternator falls below the programmed
voltage threshold (4).
OPERATION | PAGE 17

OPERATION | PAGE 18
4.3 FUEL TRANSFER PUMP
It is possible to activate the fuel transfer pump of the CEM7 control unit by
associating its operation with the BT relay of the measurements module
(Regulations table, parameter 4). Once the fuel transfer pump option is enabled,
the operating mode is then set (Regulations table, parameter 1):
1. Inhibited mode. The fuel transfer pump is not managed.
2. Manual mode. The fuel transfer pump is activated by pressing the DIESEL
TRANSF key provided that the fuel level is below the maximum deactivation
threshold (Threshold table, parameter 19)
3. Automatic mode. Managing the fuel transfer pump works by monitoring the
minimum activation threshold (Threshold table, parameter 18) below which the
BT relay is connected and a maximum deactivation threshold (Threshold table,
parameter 19) above which the BT relay disconnects.
4. Combined mode. The combined mode of the fuel transfer pump manages the
fuel transfer pump according to the Automatic mode, but also allows activation of
the BT relay by pressing the diesel Transf. key. Manual activation of the BT relay
is limited by the maximum deactivation threshold (Threshold table, parameter
19). The combined mode of the fuel transfer pump is available for control units
with rmware versions 2.56 and above.
5. Control unit mode. Managing the fuel transfer pump is performed as follows:
•When the control unit is in automatic mode or test mode, the
operation of the fuel transfer pump is managed in automatic mode.
•When the control unit is in manual mode, the operation of the fuel
transfer pump is managed manually.
•When the control unit is in locked mode, the operation of the fuel
transfer pump is inhibited (CEM7 + CEA7CC2).
The control unit mode of the fuel transfer pump is available for control units with
rmware versions 2.54 and below.
NOTE
The display shows the engine status screen, where the engine status is displayed
during the stop operation. This sequence is:
Genset: Stabilised
Genset: Cooling
Genset: Stopping
Genset: Stopped.

OPERATION | PAGE 19
4.5 BATTERY CHARGING ALTERNATOR
The battery charging alternator is connected to the CEM7 control unit via the
digital output D + and the DI analogue input of the measurements module.
The CEM7 control unit can be congured to produce an Alternator Voltage alarm
(Alarms table, parameters 10 to 12) if a low voltage supplied by the battery
charging alternator is detected through the DI analogue input of the
measurements module.
It is possible to select (Regulations table, parameter 3) between 2 modes of
operation of the battery charging alternator:
4.5.1 ALTERNATOR MODE
Operation of the CEM7 control unit's battery charging alternator congured to
alternator mode, excites the alternator via a pulse with a congurable duration
(Times table, parameter 8) during engine start process through the D+ output of
the measurements module. At the end of the pulse, the control unit tests the
voltage generated by the battery charging alternator.
The voltage generated by the battery charging alternator can be used as an
engine running condition (Regulations table, parameter 20). For this purpose, the
control unit waits to measure voltage, via the DI analogue input, which is above
an alternator voltage detection threshold (Threshold table, parameter 21).
The CEM7 control unit can be congured to produce an Alternator Voltage alarm
(Alarms table, parameters 10 to 12) if a low voltage supplied by the battery
charging alternator is detected through the DI analogue input of the
measurements module if it is set to alternator mode.
Calibration of the gauge: For correct fuel level measurements (required for
managing the fuel transfer pump and fuel level alarm) a calibration of the tank
gauge should be performed. This requires access to the minimum and maximum
gauge level parameters (Measurements table, parameters 12 and 13). To adjust
the minimum level of fuel in the tank validation of parameter 12 of the
Measurements table should be performed with the gauge in the minimum
position. To adjust the maximum level of fuel in the tank validation of parameter
13 of the Measurements table should be performed with the gauge in the
maximum position.
In the event the gauge response is not linear, it is possible to program a gauge
response curve with up to 8 points from the option MenuParametersSensors.
4.4 HEATING
Management of engine heating allows 2 modes of activation:
•Assigning the heating function to BT relay of the measurements
module (Regulations table, parameter 4).
•Assigning the heating function to one of the 3 programmable outputs
of the measurements module (Settings table, parameters 1-3)
provided that the BT relay of the measurements module is assigned
to the management of the fuel transfer pump (Regulations table,
parameter 4).
Management of engine heating provides the following function:
•Below a certain engine temperature threshold (Threshold table,
parameter 29), the heating resistor is activated.
•Below a certain engine temperature threshold (Threshold table,
parameter 28), activation of the genset contactor is controlled
and the Low Engine Temperature Alarm is managed (Alarms table,
parameters 73 to 74) .
•Above a certain engine temperature threshold (Threshold table,
parameter 30), the heating resistor is deactivated.

OPERATION | PAGE 20
PROGRAMMING
The generator set will start operating, acquiring this load, when network power
consumption is detected which more than the limit set by parameter (Threshold
table, parameter 34). The genset will continue to operate until the genset power
consumption measured falls below a limit set by parameter (Thresholds table,
parameter 35). Both with the start and stop of the genset due to load demand,
the conditions must be validated for a programmable time (Times table,
parameter 27). The function of start up due to load demand is only enabled in
Automatic mode of the CEM7 control unit associated to a switching control unit
CEA7CC2.
NOTE
From the rmware versions of control units: Display 3.20 / Measurements 2.50
4.8 ELECTRONIC PROTECTION
DESCRIPTION
The electronic protection is a feature that permits a control unit output to be
activated in the event of an overload and short circuit alarm. This function allows
the genset's main circuit breaker to be disabled via the trip coil. While any of
these alarms that causes the engine to stop (immediate or cooling) remains
active or pending notication, the output assigned to electronic protection
remains active.
PROGRAMMING
The possible outputs that can be assigned to this function are:
•The SC relay is assigned by default to this function. Furthermore, the
SC relay is also activated when any alarm is generated which causes
the engine to stop.
•The BT relay of the measurements module (Regulations table,
parameter 4).
•Any of the programmable outputs of the measurements module
(Settings table, parameters 1 to 3).
4.5.2 DYNAMO MODE
Operation of the CEM7 control unit's battery charging alternator congured in
dynamo mode, excites the alternator via a continuous pulse through the D+
output of the measurements module while the engine is in start up phase or is
running.
The control unit congured in dynamo mode cannot use the voltage measured via
the DI analogue input for detecting an engine running condition.
The CEM7 control unit can be congured to produce an Alternator Voltage alarm
(Alarms table, parameters 10 to 12) if a low voltage supplied by the battery
charging alternator is detected through the DI analogue input of the
measurements module if it is set to alternator mode.
4.6 START/STOP KEY
The start/stop key in the ON position causes power to be supplied to the CEM7
control unit's electronic devices (measurements module and display module).
The start/stop key in the OFF position causes a controlled stop if it is running;
once the engine has stopped, power to the CEM7 control unit is disconnected.
4.7 START DUE TO LOAD DEMAND (ONLY CEA7CC2 EXPANSION)
DESCRIPTION
This function enables automatic start up and activation of generator set charging
depending on the power consumption of the network.
The start up is performed according to the programming, considering the
maximum power (Threshold table, parameter 34) the network can consume for a
period of time (Times table, parameter 27). Once the generator set is started,
the system changes genset power leaving the network free of load.
When the load in the installation is below the programmed threshold (Threshold
table, parameter 35) for deactivation and the programmed period of time (Times
table, parameter 27) has elapsed, the system returns to charging the installation
via the network and the genset begins its stopping cycle.
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents
Other Himoinsa Control Unit manuals