6
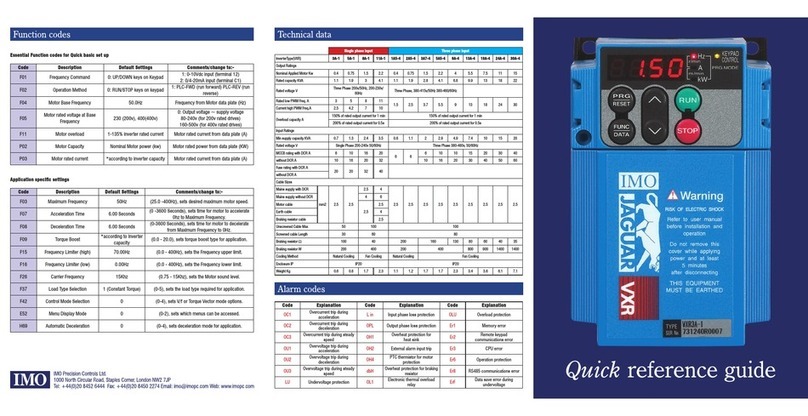
JAGUAR CUB CMCOMMON SPECIFICATIONS
Item Explanation
Output Maximum frequency 50 to 120Hz (in 1Hz steps)
frequency Base frequency 50 to 120Hz (in 1Hz steps)
Starting frequency 1 to 6Hz (in 1Hz steps)
Carrier frequency 0.75 to 15kHz
Accuracy (Stability) • Analog setting : ±1.0% of maximum frequency (at 25 ±10˚C)
• Digital setting : ±0.01% of maximum frequency (at -10 to +50˚C)
Setting resolution • Analog setting : 1/256 of maximum frequency ex.) 0.25Hz at 60Hz, 0.5Hz at 120Hz
• Digital setting : 0.01Hz at maximum frequency of up to 99.9Hz (1Hz at maximum frequency of 100Hz and above)
Control Control method •
Sinusoidal PWM control
Voltage/freq. (V/f) characteristic
Maximum output voltage proportional to line input voltage (without AVR control)
Torque boost Manual: Code selection (0 to 31), including the save energy pattern for variable torque load
Starting torque 150% (at 6Hz) (Torque boost code (F09) is 20 and above.)
Operation method • KEYPAD operation : key, key
• Digital input signal operation : FWD or REV command
• LINK operation : RS485 (Option)
Frequency setting • KEYPAD operation : or key
• Built-in potentiometer: Potentiometer is standard equipment
• Analog input: 0 to +10VDC (0 to +5VDC)
v to 20mADC
• Multistep frequency: 4 different frequencies can be selected by terminal (SS1) and (SS2).
• LINK operation: RS485 (Option)
Running status signal Relay output: Alarm output for any fault. (1SPDT)
Analog output: Output frequency, output current, PID feedback value, DC link circuit voltage
Acceleration time 0.0 to 60s (0.0 = 0.01s)
Deceleration time 0.1 to 60s
Frequency limiter High and low limiter can be preset.
Bias frequency Bias frequency can be preset (-120 to 120Hz)
Gain for frequency setting
100% (For 0 to +10VDC) or 200% (For 0 to +5VDC)
Jump frequency control Jump frequency (3 points) and its common jump hysteresis width (0 to 30Hz0 can be preset
Auto-restart after Automatic restart is available after a momentary power failure (retry method)
momentary power failure
PID control This function can control flow rate pressure, etc. (with an analog feedback signal.)
• Reference signal (F01): • KEYPAD operation ( or key)
• Voltage input (Terminal 12)
• Current input (Terminal C1)
• Analog input (Built-in Potentiometer)
• Feedback signal (H21) • Terminal 12 (0 to +10V DC or 1 to 5V DC)
• Terminal C1 (4 to 20mA DC)
Indication Operation mode • Output frequency, output current, PID reference value, PID feedback value
(running or stopping • Setting frequency
Program mode Function code, data code
Trip mode Displays trip fault code as follows
• OC1 (Overcurrent during acceleration)
• OC2 (Overcurrent during deceleration)
• OC3 (Overcurrent running at constant speed)
• OU1 (Overvoltage during acceleration)
• OU2 (Overvoltage during deceleration)
• OU3 (Overcurrent running at constant speed)
• LU (Low voltage)
• OH1 (Overheating at heatsink)
• OH2 (External thermal relay tripped)
• OL (Motor overload)
• OLU (Inverter unit overload)
• Er1 (Memory error)
• Er3 (CPU error)
• Er8 (RS485 error)
Operation and Trip mode Trip history (passed/4 times
Charge lamp (Red) When the DC link circuit voltage is higher than 50V,. the charge lamp is ON
Protection Overload Protects the inverter by electronic thermal overload relay and detection of inverter temperature
Overvoltage detection Detects DC link circuit voltage (400V), and stops the inverter
Undervoltage Detects DC link circuit undervoltage (200V) and stops the inverter
Overheating Protects the inverter by detection of inverter temperature
Short-circuit Short-circuit protection for inverter output circuit
Ground fault Ground fault protection for inverter output circuit (detection at starting)
Motor overload • Protects the motor after the inverter trips
(running or stopping • Electronic thermal overload relay can be selected for standard motor or IMO inverter motor
Stall prevention
• Controls the output frequency to prevent (overcurrent) trip when the output current exceeds the limit value during acceleration
• Lowers the output frequency to hold almost constant torque when the output current exceeds the limit value during operation at constant speed
• Controls the output frequency to prevent (overvoltage) trip when the DC link circuit voltage exceeds the limit value during deceleration
Auto reset When the inverter is tripped, it resets automatically and restart. 5-times auto reset can be selected
Condition Installation location Free from a dusty location, corrosive gases, oil mist and direct sunlight. Indoor use only
(Installation Altitude 1000m or less. (Applicable to 3000m with power derating: -10%/1000m)
and
Ambient temperature -10˚ to +50˚C
operation)
Ambient humidity 5 to 95% RH (non-condensing)
Vibration 3mm at 2 to 9Hz, 1m/s2at 9 to 200Hz
Storage conditions • Temperature: -25˚ to +65˚C • Humidity: 5 to 95% RH
Setting