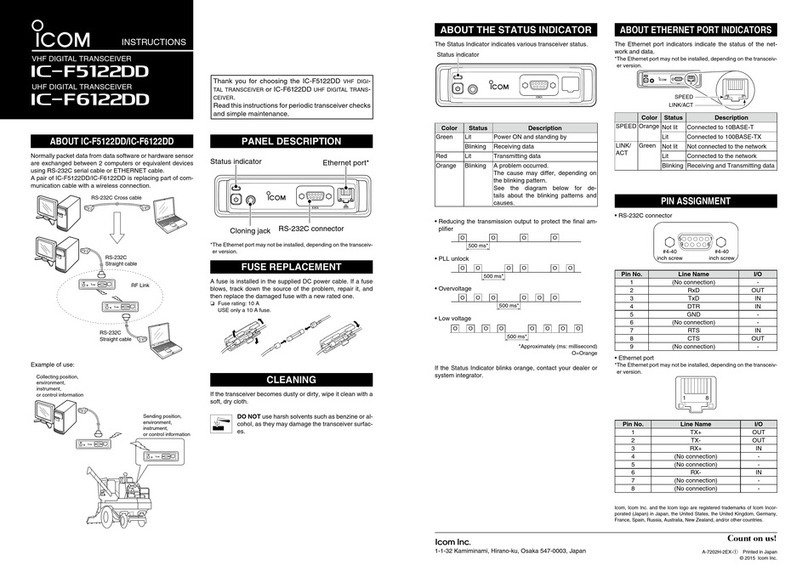
4 - 3
POWER
AMP.
APC
AMP.
DRIVE
AMP.
+
1
3
4
–
HV
to antenna
connector
T2
TMUT
RF signal
from PLL circuit
T8V
APC control circuit
FOR
REV
Q48
Q23
IC37
IC29
D40D38
YGR
AMP.
• APC CIRCUIT
4-2 TRANSMITTER CIRCUITS
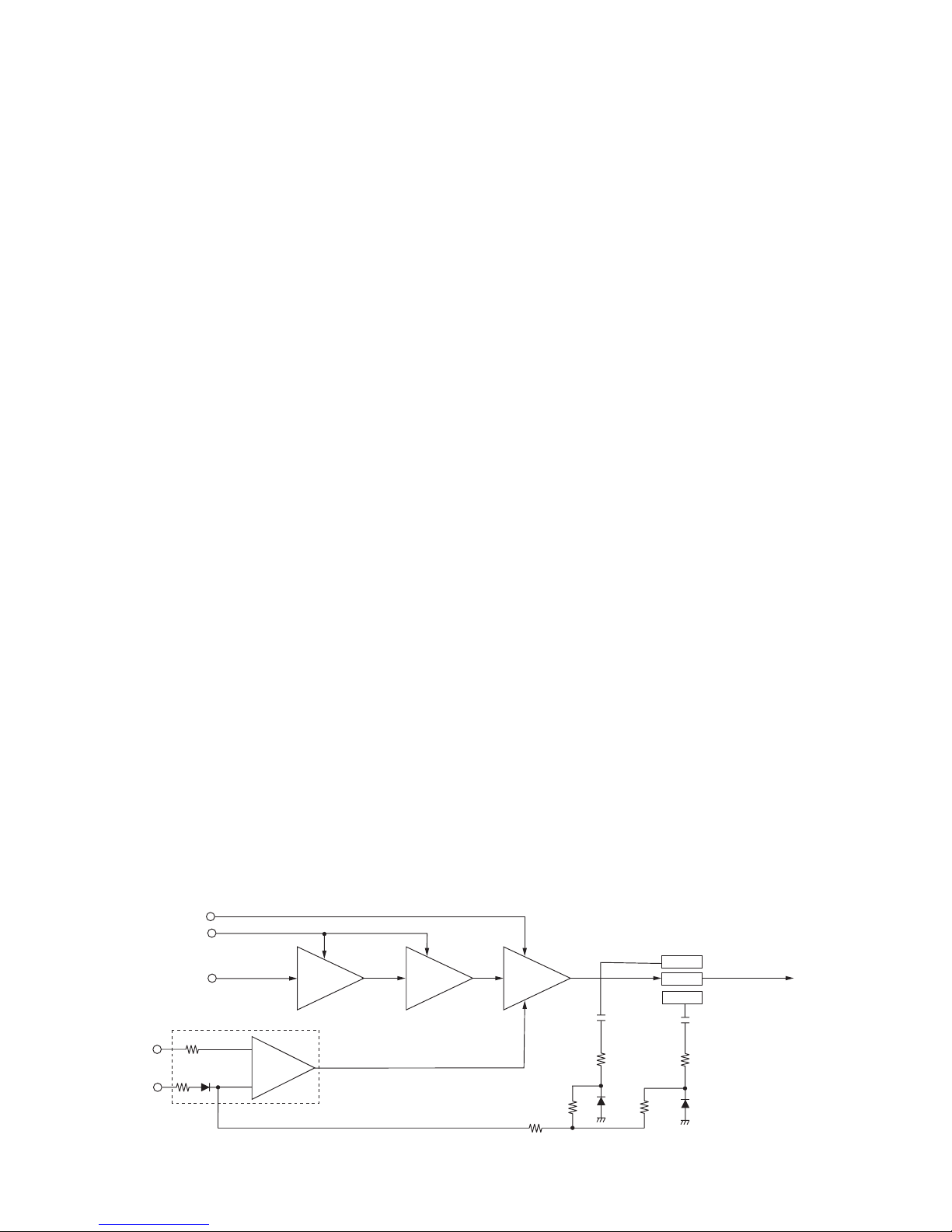
4-2-1 MICROPHONE AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
The microphone amplifier circuit amplifies audio signals
within +6 dB/octave pre-emphasis 6 characteristics from the
microphone to a level needed for the modulation circuit.
This transceiver employs the base band IC which is com-
posed of microphone amplifier, compressor, scrambler,
limiter, splatter filter, MSK modulator, etc. at the microphone
amplifier section.
The AF signals from the microphone connector (FRONT
UNIT; J2, pin 6) are passed through the microphone switch
(FRONT UNIT; IC8, pins 1, 6, 7) and are then applied to the
ALC amplifier (FRONT UNIT; IC9) during digital mode oper-
ation (bypassed during FM mode operation.) The signals are
amplified at the microphone amplifier (FRONT UNIT; IC5,
pins 3, 4) and then applied to MAIN UNIT via J1 (pin 10).
The amplified signals are applied to the microphone ampli-
fier section of the base band IC (IC2, pin 3). The amplified
signals are passed through (or bypass) the compressor,
scrambler sections of IC2, and are then passed through the
high-pass, limiter amplifier, splatter filter sections of IC2.
The output signals from the base band IC (IC2, pin 7) are
applied to the FM/PM switch (IC43, pins 12–14) after pass
through the microphone switch (IC42, pins 12, 14). The sig-
nal are passed through the low-pass filter (IC1, pins 4, 13)
and then applied to the D/A converter (IC8, pins 3, 4). The
output signal from D/A converter (IC8, pin 3) are applied to
the modulation circuit (D12).
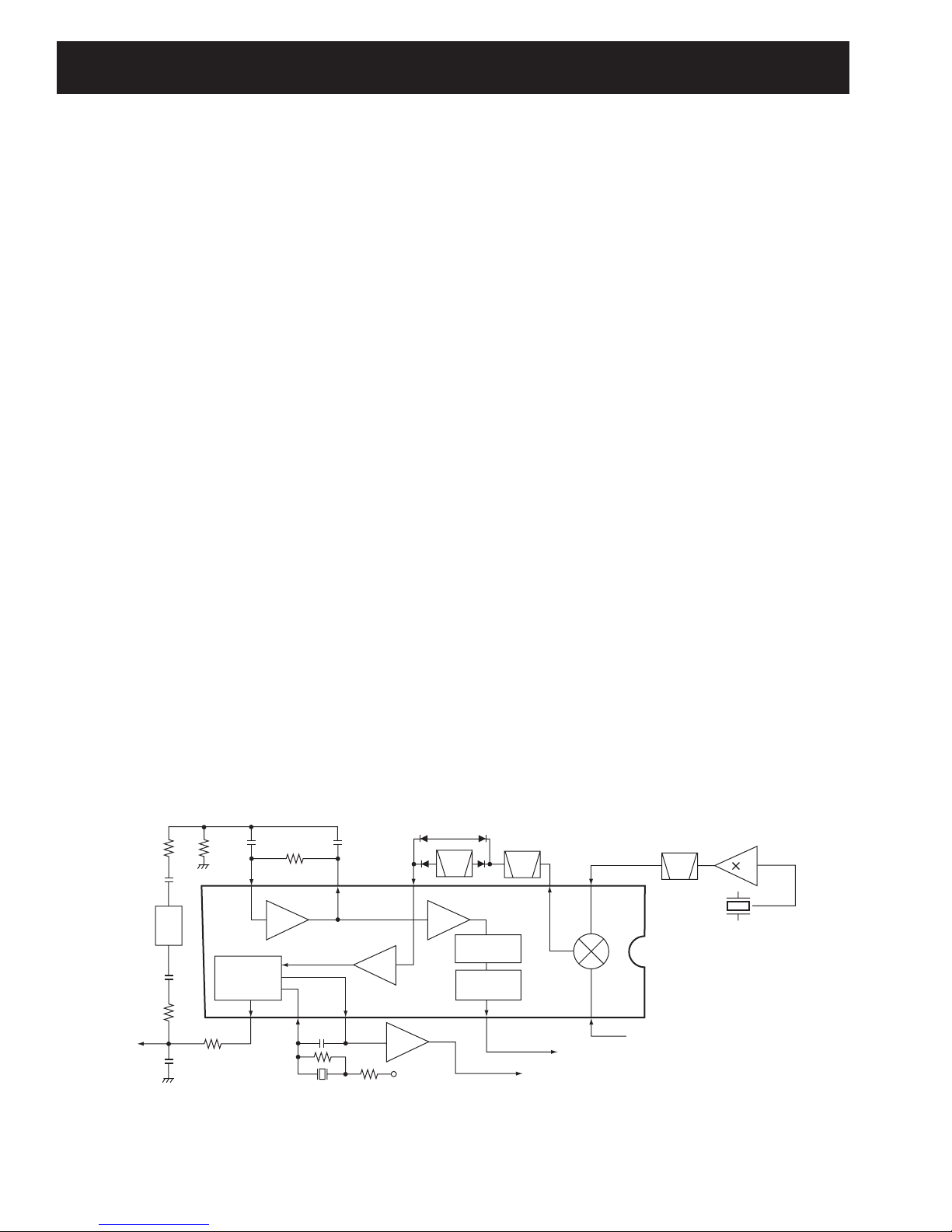
4-2-2 MODULATION CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
The modulation circuit modulates the VCO oscillating signal
(RF signal) using the microphone audio signals.
The AF signals from the D/A converter (IC8, pin 3) change
the reactance of varactor diode (D12) to modulate the oscil-
lated signal at the TX VCO circuit (Q16, D70 D71). The
modulated VCO signal is amplified at the buffer amplifiers
(Q20, Q22) and is then applied to the YGR (Q23) amplifier
via the T/R switch (D19).
The CTCSS/DTCS signals (“CENC0”, “CENC1”, ”CENC2”)
from the Main CPU (IC23, pins 89–91) are combined at
resistors (R158, R159, R162) and are then pass through the
low-pass filter (IC9, pins 12, 14).
The filtered signals are applied to the D/A converter (IC8,
pins 9, 10), and are then mixed with the filtered microphone
audio signals. The mixed signals are applied to the D/A con-
verter (IC8, pin 3, 4) after pass through the low-pass filter
(IC1, pins 8, 9). The output signal from D/A converter (IC8,
pin 3) are applied to the D12 in the TX VCO circuit.
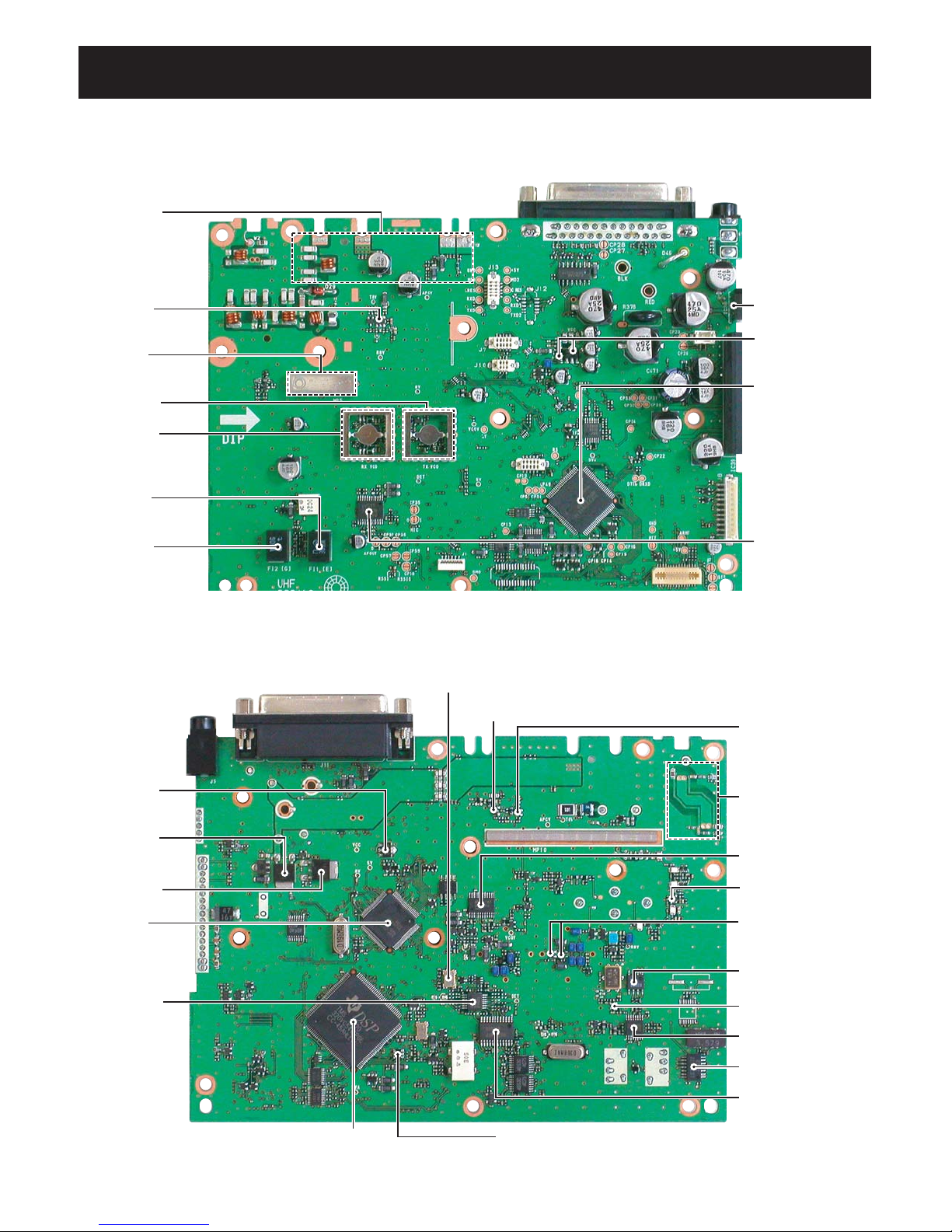
4-2-3 POWER AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS (MAIN UNIT)
The power amplifier circuits amplify the VCO oscillating sig-
nal to an output power level.
The signal from the T/R switch (D19) is amplified at the YGR
(Q23), drive (Q48) and power (IC29) amplifiers to obtain 45
W (IC-F2721/D/F2821/D; 25 W for IC-F2710/F2810) of RF
power.
The amplified signal is passed through the low-pass filter
(L35, C345, C346, C348, C349), antenna switch (D29, D30),
low-pass filters (L42–L44, C376, C388, C389, C391, C551,
C552), power detector (D38, D40) and low-pass filter (L49,
C432, C461), and is then applied to the antenna connector
(CHASSIS unit; J1).
The bias voltage of the power amplifier (IC29) is controlled
by the APC circuit.
4-2-4 APC CIRCUIT (MAIN UNIT)
The APC circuit protects the power amplifier from a mis-
matched output load and stabilizes the output power.
The power detector circuit (D38, D40) detects the forward
signals and reflection signals and converts it into DC volt-
age. The output voltage is at a minimum level when the
antenna impedance is matched with 50 Ωand is increased
when it is mismatched.
The detected voltage is applied to the differential amplifier
(IC37; pins 3, 4), and the “T2” signal from the D/A converter
(IC30, pin 2), controlled by the main CPU (IC23), is applied
to the other input for reference (IC37, pin 1). When antenna
impedance is mismatched, the detected voltage exceeds the
power setting voltage. Then the output voltage of the differ-
ential amplifier (IC37, pin 4) controls the bias voltage of the
power amplifier (IC29) to reduce the output power.