IDT 89HPES34H16 User manual

®
October 2008
6024 Silver Creek Valley Road, San Jose,California 95138
Telephone: (800) 345-7015 • (408) 284-8200 • FAX: (408) 284-2775
Printed in U.S.A.
©2008 Integrated Device Technology,Inc.
IDT™89HPES34H16
PCI Express® Switch
User Manual

GENERAL DISCLAIMER
Integrated Device Technology, Inc. reserves the right to make changes to its products or specifications at any time, without notice, in order to improve design or performance
and to supply the best possible product. IDT does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described other than the circuitry embodied in an IDT product. The
Company makes no representations that circuitry described herein is free from patent infringement or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is
granted by implication or otherwise under any patent, patentrights or other rights, of Integrated Device Technology, Inc.
CODE DISCLAIMER
Code examples provided by IDT are for illustrative purposes only and should not be relied upon for developing applications. Any use of the code examples below is completely
at yourown risk. IDT MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS ORWARRANTIES OF ANY KINDCONCERNING THE NONINFRINGEMENT, QUALITY, SAFETY OR SUITABILITY
OF THE CODE, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICU-
LAR PURPOSE, ORNON-INFRINGEMENT. FURTHER, IDT MAKESNO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES ASTO THETRUTH, ACCURACYOR COMPLETENESS
OF ANY STATEMENTS, INFORMATION OR MATERIALS CONCERNING CODE EXAMPLES CONTAINED IN ANY IDT PUBLICATION OR PUBLIC DISCLOSURE OR
THAT IS CONTAINED ON ANY IDT INTERNET SITE. IN NO EVENT WILL IDT BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT, PUNITIVE OR
SPECIAL DAMAGES, HOWEVER THEY MAY ARISE, AND EVEN IF IDT HAS BEEN PREVIOUSLY ADVISED ABOUT THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. The code
examplesalsomaybe subjecttoUnitedStatesexportcontrollawsandmaybesubjecttotheexportorimportlawsof othercountriesandit isyourresponsibilitytocomplywith
any applicable laws or regulations.
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
Integrated Device Technology's products are not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems unless a specific writtenagreement pertaining to
such intended use is executed between the manufacturer and anofficer of IDT.
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems which (a) are intended for surgical implant into the body or (b) support or sustain life and whose failure to perform,
when properly used in accordance with instructions for use providedin the labeling, can be reasonably expected toresult in a significant injury to the user.
2.A criticalcomponentisanycomponentsofalifesupportdeviceorsystemwhosefailuretoperformcanbereasonablyexpected to cause the failure of the life support device
or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness.
IDT, theIDT logo, and Integrated Device Technology are trademarks or registered trademarks of Integrated Device Technology, Inc.

Notes
PES34H16 User Manual 1 October 30, 2008
®
About This Manual
Introduction
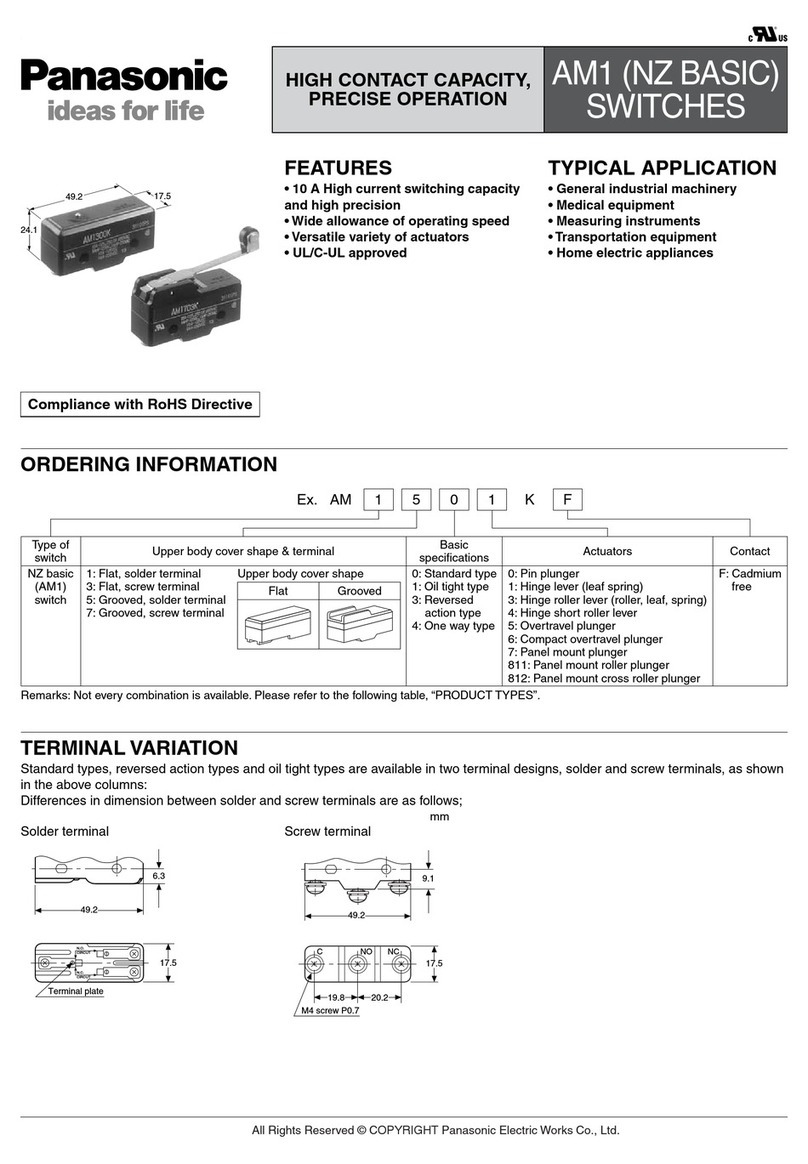
This user manual includes hardware and software information on the 89HPES34H16, a member of
IDT’s PRECISE™ family of PCI Express® switching solutions offering the next-generation I/O interconnect
standard.
Finding Additional Information
Information not included inthis manual such as mechanicals, packagepin-outs, and electrical character-
istics can be found in thedata sheet for this device, which is available from the IDT website (www.idt.com)
as well as through your local IDT sales representative.
Content Summary
Chapter 1, “PES34H16 Device Overview,” provides a complete introduction to the performance capa-
bilities of the 89HPES34H16. Included in this chapter is a summary of features for the device as well as a
system block diagram and pin description.
Chapter 2, “Upstream Port Failover,” describes upstream port failover mechanism in the PES34H16
that enables the construction of fault tolerant systems.
Chapter 3, “Clocking, Reset, and Initialization,” provides a description of the two differential refer-
ence clock inputs that are used internally to generate all of the clocks required by the internal switch logic
and the SerDes.
Chapter 4, “Link Operation,” describes the operation of the link feature including polarity inversion,
link width negotiation, and lane reversal.
Chapter 5, “General Purpose I/O,” describes how the 32 General Purpose I/O (GPIO) pins may be
individually configured as general purpose inputs, general purpose outputs, or alternate functions.
Chapter 6, “SMBus Interfaces,” describes the operation of the 2 SMBus interfaces on the PES34H16.
Chapter 7, “Power Management,” describes the power management capability structure locatedin the
configuration space of each PCI-PCI bridge in the PES34H16.
Chapter 8, “Hot-Plug and Hot-Swap,” describes the behavior of the hot-plug andhot-swap features in
the PES34H16.
Chapter 9, “Configuration Registers,” discusses the base addresses, PCI configuration space, and
registers associated with the PES34H16.
Chapter 10, “JTAG Boundary Scan,” discusses an enhanced JTAG interface, including a system logic
TAP controller, signal definitions, a test data register, an instruction register, and usage considerations.
Signal Nomenclature
To avoid confusion when dealing with a mixture of “active-low” and “active-high” signals, the terms
assertion and negation are used. The term assert or assertion is used to indicate that a signal is active or
true, independent of whether that level is representedby a high or low voltage. The term negate ornegation
is used to indicate that a signal is inactive or false.
To define the active polarity of a signal, a suffix will be used. Signals ending with an ‘N’ should be inter-
preted as being active, or asserted, when at a logic zero (low) level. All other signals (including clocks,
buses and select lines) will be interpreted as being active, or asserted when at a logic one (high) level.

IDT
PES34H16 User Manual 2 October 30, 2008
Notes
To define buses, the most significant bit (MSB) will be on the left and least significant bit (LSB) will be on
the right. No leading zeros will be included.
Throughout this manual, when describing signal transitions, the following terminology is used. Rising
edge indicates a low-to-high (0 to1) transition. Falling edge indicates ahigh-to-low (1 to 0) transition. These
terms are illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Signal Transitions
Numeric Representations
To represent numerical values, either decimal, binary, or hexadecimal formats will be used. The binary
format is as follows: 0bDDD, where “D” represents either 0 or 1; the hexadecimal format is as follows:
0xDD, where “D” represents the hexadecimal digit(s); otherwise, it is decimal.
The compressed notation ABC[x|y|z]D refers to ABCxD, ABCyD, and ABCzD.
The compressed notation ABC[x..y]D refers to ABCxD, ABC(x+1)D, ABC(x+2)D,... ABCyD.
Data Units
The following data unit terminology is used in this document.
In quadwords, bit 63 is always the most significant bit and bit 0 is the least significant bit. In double-
words, bit 31 is always the most significant bit and bit 0 is the least significant bit. In words, bit 15 is always
the most significant bit and bit 0 is the least significant bit. In bytes, bit 7 is always the most significant bit
and bit 0 is the least significant bit.
The ordering of bytes within words is referred to as either “big endian” or “little endian.” Big endian
systems label byte zero as the most significant (leftmost) byte of a word. Little endian systems label byte
zero as the least significant (rightmost) byte of a word. See Figure 2.
Term Words Bytes Bits
Byte 1/2 1 8
Word 1 2 16
Doubleword (Dword) 2 4 32
Quadword (Qword) 4 8 64
Table 1 Data Unit Terminology
1 2 3 4
high-to-low
transition low-to-high
transition
single clock cycle

IDT
PES34H16 User Manual 3 October 30, 2008
Notes
Figure 2 Example of Byte Ordering for “Big Endian” or “Little Endian” System Definition
Register Terminology
Software in the context of this register terminology refers to modifications madeby PCIe root configura-
tion writes, writes to registers made through the slave SMBus interface, or serial EEPROM register initial-
ization. See Table 2.
Type Abbreviation Description
Hardware Initialized HWINIT Register bits are initialized by firmware or hardware mechanisms
such as pin strapping or serial EEPROM. (System firmware hard-
ware initialization is only allowed for system integrated devices.)
Bits are read-only after initialization and can only be reset (for
write-once by firmware) with reset.
Read Only and Clear RC Software can read the register/bits with this attribute. Reading the
value will automatically cause the register/bit to be reset to zero.
Writing to a RC location has no effect.
Read Clear and Write RCW Software can read the register/bits with this attribute. Reading the
value will automatically cause the register/bits to be reset to zero.
Writes cause the register/bits to be modified.
Reserved Reserved The value read from a reserved register/bit is undefined. Thus,
software must deal correctly with fields that are reserved. On
reads, softwaremust useappropriatemaskstoextractthedefined
bits and not rely on reserved bits being any particular value. On
writes, software must ensure that the values of reserved bit posi-
tions are preserved. That is, the values of reserved bit positions
must first be read, merged with the new values for other bit posi-
tions and then written back.
Read Only RO Software can only read registers/bits with this attribute. Contents
are hardwired to a constant value or are status bits that may be
set and cleared by hardware. Writing to a RO location has no
effect.
Read and Write RW Software can both read and write bits with this attribute.
Table 2 Register Terminology (Sheet 1 of 2)
0123
bit 0bit 31
Address of Bytes within Words: Big Endian
3210
bit 0bit 31
Address of Bytes within Words: Little Endian

IDT
PES34H16 User Manual 4 October 30, 2008
Notes
Use of Hypertext
In Chapter 9, Tables 9.2 and 9.3 contain register names and page numbershighlighted in blue under the
Register Definition column. In pdf files, users can jump from this source table directly to the registers by
clicking on the register name in the source table. Each register name in the table is linked directly to the
appropriate register in the register section of the chapter. To return to the source table after having jumped
to the register section, click on the same register name (in blue) in the register section.
Reference Documents
PCI Express Base Specification, Revision 1.1, PCI Special Interest Group.
PCI Power Management Interface Specification, Revision 1.1, PCI Special Interest Group.
PCI to PCI Bridge Architecture Specification, Revision 1.2, PCI Special Interest Group.
SMBus Specification, Revision 2.0.
Revision History
October 17, 2007: Initial Publication.
December 14, 2007: In Chapter 1, added second virtual channel capability and changed Device ID to
0x8034.
December 26, 2007: Changed device number from 34T16 to34H16.
April 15, 2008: In Chapter 9, changed 0x0definition for bit EEPE in SWPERCTL register from“time-out”
to “end-to-end parity error”.
October 30, 2008: Updated the following Description fields: LDIS in the PCIELCTL register, INTXD in
PCICMD register, changed RO to RW forbits 10:9 in the HPCFGCTL register, SDOENERR in the AERUES
register, DLLLA in both the PCIESTS and PCIELCAP registers, and added note in Description field for
SWMODE field.
Read and Write Clear RW1C Software can read and write to registers/bits with this attribute.
However, writing a value of zero to a bit with this attribute has no
effect. A RW1C bit can only be set to a value of 1 by a hardware
event. To clear a RW1C bit (i.e., change its value to zero) a value
of one must be written to the location. An RW1C bit is never
cleared by hardware.
Read and Write when
Unlocked RWL Software can read the register/bits with this attribute. Writing to
register/bits with this attribute will only cause the value to be modi-
fied if the REGUNLOCK bit in the SWCTL register is set. When
the REGUNLOCK bit is cleared, writes are ignored and the regis-
ter/bits are effectively read-only
Write Transient WT The zero is always read from a bit/field of this type. Writing of a
one is used to quality the writing of other bits/fields in the same
register.
Zero Zero A zero register or bit must be written with a value of zero and
returns a value of zero when read.
Type Abbreviation Description
Table 2 Register Terminology (Sheet 2 of 2)

Notes
PES34H16 User Manual i October 30, 2008
Table of Contents
®
About This Manual
Introduction ....................................................................................................................................1
Content Summary ..........................................................................................................................1
Signal Nomenclature .....................................................................................................................1
Numeric Representations ..............................................................................................................2
Data Units ......................................................................................................................................2
Register Terminology .....................................................................................................................3
Use of Hypertext ............................................................................................................................4
Reference Documents ...................................................................................................................4
Revision History .............................................................................................................................4
PES34H16 Device Overview
Introduction.....................................................................................................................................1-1
List of Features...............................................................................................................................1-1
Logic Diagram.................................................................................................................................1-3
System Identification.......................................................................................................................1-4
Vendor ID................................................................................................................................1-4
Device ID................................................................................................................................1-4
Revision ID.............................................................................................................................1-4
JTAG ID..................................................................................................................................1-4
SSID/SSVID............................................................................................................................1-4
Device Serial Number Enhanced Capability...........................................................................1-4
Pin Description................................................................................................................................1-5
Pin Characteristics........................................................................................................................1-12
Port Configuration.........................................................................................................................1-15
Disabled Ports......................................................................................................................1-16
Upstream Port Failover
Introduction.....................................................................................................................................2-1
Failover...........................................................................................................................................2-2
Static Upstream Port Failover.................................................................................................2-3
Dynamic Upstream Port Failover............................................................................................2-3
Clocking, Reset, and Initialization
Introduction.....................................................................................................................................3-1
Initialization.....................................................................................................................................3-3
Reset...............................................................................................................................................3-4
Fundamental Reset................................................................................................................3-5
Hot Reset................................................................................................................................3-6
Upstream Secondary Bus Reset............................................................................................3-7
Downstream Secondary Bus Reset........................................................................................3-8
Downstream Port Reset Outputs....................................................................................................3-8
Power Enable Controlled Reset Output..................................................................................3-9
Power Good Controlled Reset Output....................................................................................3-9

IDT Table of Contents
PES34H16 User Manual ii October 30, 2008
Notes
Link Operation
Introduction.....................................................................................................................................4-1
Polarity Inversion............................................................................................................................4-1
Link Width Negotiation....................................................................................................................4-1
Lane Reversal.................................................................................................................................4-1
Link Retraining................................................................................................................................4-4
Link Down.......................................................................................................................................4-5
Slot Power Limit Support................................................................................................................4-5
Upstream Port ........................................................................................................................4-5
Downstream Port....................................................................................................................4-5
Link States......................................................................................................................................4-5
Active State Power Management ...................................................................................................4-6
Link Status......................................................................................................................................4-6
General Purpose I/O
Introduction.....................................................................................................................................5-1
GPIO Configuration ........................................................................................................................5-2
GPIO Pin Configured as an Input...........................................................................................5-2
GPIO Pin Configured as an Output........................................................................................5-2
GPIO Pin Configured as an Alternate Function......................................................................5-2
SMBus Interfaces
Introduction.....................................................................................................................................6-1
Master SMBus Interface.................................................................................................................6-2
Initialization.............................................................................................................................6-2
Serial EEPROM......................................................................................................................6-2
I/O Expanders.........................................................................................................................6-6
Slave SMBus Interface.................................................................................................................6-17
Initialization...........................................................................................................................6-17
SMBus Transactions ............................................................................................................6-18
Power Management
Introduction.....................................................................................................................................7-1
PME Messages...............................................................................................................................7-2
Power Express Power Management Fence Protocol.....................................................................7-2
Power Budgeting Capability ...................................................................................................7-3
Hot-Plug and Hot-Swap
Introduction.....................................................................................................................................8-1
Hot-Plug I/O Expander ...........................................................................................................8-4
Hot-Plug Interrupts and Wake-up...........................................................................................8-4
Legacy System Hot-Plug Support ..........................................................................................8-4
Hot-Swap........................................................................................................................................8-6
Configuration Registers
Configuration Space Organization..................................................................................................9-1
Upstream Port (Port 0) ...........................................................................................................9-3
Downstream Ports (Ports 1 through 15).................................................................................9-8
Register Definitions.......................................................................................................................9-11
Type 1 Configuration Header Registers...............................................................................9-11
PCI Express Capability Structure.........................................................................................9-22

IDT Table of Contents
PES34H16 User Manual iii October 30, 2008
Notes
Power Management Capability Structure.............................................................................9-35
Message Signaled Interrupt Capability Structure.................................................................9-36
Subsystem ID and Subsystem Vendor ID............................................................................9-38
Extended Configuration Space Access Registers................................................................9-38
Advanced Error Reporting (AER) Enhanced Capability.......................................................9-39
Device Serial Number Enhanced Capability.........................................................................9-45
PCI Express Virtual Channel Capability...............................................................................9-46
Power Budgeting Enhanced Capability................................................................................9-57
Switch Control and Status Registers....................................................................................9-59
Internal Switch Error Control and Status Registers..............................................................9-76
JTAG Boundary Scan
Introduction...................................................................................................................................10-1
Test Access Point.........................................................................................................................10-1
Signal Definitions..........................................................................................................................10-1
Boundary Scan Chain...................................................................................................................10-3
Test Data Register (DR)...............................................................................................................10-5
Boundary Scan Registers.....................................................................................................10-5
Instruction Register (IR)................................................................................................................10-7
EXTEST................................................................................................................................10-8
SAMPLE/PRELOAD.............................................................................................................10-8
BYPASS...............................................................................................................................10-8
CLAMP.................................................................................................................................10-9
IDCODE................................................................................................................................10-9
VALIDATE............................................................................................................................10-9
RESERVED..........................................................................................................................10-9
Usage Considerations........................................................................................................10-10

IDT Table of Contents
PES34H16 User Manual iv October 30, 2008
Notes

Notes
PES34H16 User Manual v October 30, 2008
List of Tables
®
Table 1.1 PES34H16 Device IDs.........................................................................................................1-4
Table 1.2 PES34H16 Revision ID........................................................................................................1-4
Table 1.3 PCI Express Interface Pins..................................................................................................1-5
Table 1.4 SMBus Interface Pins..........................................................................................................1-7
Table 1.5 General Purpose I/O Pins....................................................................................................1-7
Table 1.6 System Pins.......................................................................................................................1-10
Table 1.7 Test Pins............................................................................................................................1-11
Table 1.8 Power and Ground Pins.....................................................................................................1-12
Table 1.9 Pin Characteristics.............................................................................................................1-12
Table 3.1 Reference Clock Mode Encoding........................................................................................3-1
Table 3.2 Boot Configuration Vector Signals.......................................................................................3-3
Table 5.1 General Purpose I/O Pin Alternate Function.......................................................................5-1
Table 5.2 GPIO Pin Configuration.......................................................................................................5-2
Table 6.1 Serial EEPROM SMBus Address........................................................................................6-2
Table 6.2 PES34H16 Compatible Serial EEPROMs...........................................................................6-3
Table 6.3 I/O Expander 0 Signals......................................................................................................6-10
Table 6.4 I/O Expander 1 Signals......................................................................................................6-11
Table 6.5 I/O Expander 2 Signals......................................................................................................6-11
Table 6.6 I/O Expander 3 Signals......................................................................................................6-12
Table 6.7 I/O Expander 4 Signals......................................................................................................6-13
Table 6.8 I/O Expander 5 Signals......................................................................................................6-13
Table 6.9 I/O Expander 6 Signals......................................................................................................6-14
Table 6.10 I/O Expander 7 Signals......................................................................................................6-15
Table 6.11 I/O Expander 8 Signals......................................................................................................6-15
Table 6.12 I/O Expander 9 Signals......................................................................................................6-16
Table 6.13 I/O Expander 10 Signals....................................................................................................6-17
Table 6.14 Slave SMBus Address When a Static Address is Selected...............................................6-17
Table 6.15 Slave SMBus Command Code Fields...............................................................................6-18
Table 6.16 CSR Register Read or Write Operation Byte Sequence ...................................................6-19
Table 6.17 CSR Register Read or Write CMD Field Description.........................................................6-20
Table 6.18 Serial EEPROM Read or Write Operation Byte Sequence................................................6-21
Table 6.19 Serial EEPROM Read or Write CMD Field Description.....................................................6-21
Table 7.1 PES34H16 Power Management State Transition Diagram.................................................7-2
Table 8.1 Downstream Port Hot-Plug Signals.....................................................................................8-3
Table 9.1 Base Addresses for Port Configuration Space Registers....................................................9-1
Table 9.2 Upstream Port 0 Configuration Space Registers.................................................................9-3
Table 9.3 Downstream Ports 1 through 15 Configuration Space Registers........................................9-8
Table 10.1 JTAG Pin Descriptions.......................................................................................................10-2
Table 10.2 Boundary Scan Chain........................................................................................................10-3
Table 10.3 Instructions Supported by PES34H16’s JTAG Boundary Scan.........................................10-8
Table 10.4 System Controller Device Identification Register...............................................................10-9

IDT List of Tables
PES34H16 User Manual vi October 30, 2008
Notes

Notes
PES34H16 User Manual vii October 30, 2008
List of Figures
®
Figure 1.1 PES34H16 Architectural Block Diagram ............................................................................1-2
Figure 1.2 PES34H16 Logic Diagram .................................................................................................1-3
Figure 1.3 All Ports Unmerged Configuration ...................................................................................1-15
Figure 1.4 Three Ports Merged Configuration ...................................................................................1-16
Figure 2.1 Upstream Port Failover Architecture ..................................................................................2-1
Figure 2.2 Upstream Failover Mode Data Configurations ...................................................................2-2
Figure 3.1 Common Clock on Upstream and Downstream (option to enable or disable Spread
Spectrum Clock) ................................................................................................................3-1
Figure 3.2 Non-Common Clock on Upstream; Common Clock on Downstream (mustdisable
Spread Spectrum Clock) ....................................................................................................3-2
Figure 3.3 Common Clock on Upstream; Non-Common Clock on Downstream (must disable
Spread Spectrum Clock) ....................................................................................................3-2
Figure 3.4 Non-Common Clock on Upstream and Downstream (must disable Spread Spectrum
Clock) .................................................................................................................................3-3
Figure 3.5 Fundamental Reset in Transparent Mode with Serial EEPROM Initialization ....................3-6
Figure 3.6 Power Enable Controlled Reset Output Mode Operation ..................................................3-9
Figure 3.7 Power Good Controlled Reset Output Mode Operation .....................................................3-9
Figure 4.1 Unmerged Port Lane Reversal for Maximum Link Width of x4
(MAXLNKWDTH[5:0]=0x4) ................................................................................................4-2
Figure 4.2 Unmerged Port Lane Reversal for Maximum Link Width of x2
(MAXLNKWDTH[5:0]=0x2) ................................................................................................4-2
Figure 4.3 Merged Port Lane Reversal for Maximum Link Width of x2 (MAXLNKWDTH[5:0]=0x2) ...4-3
Figure 4.4 Merged Port Lane Reversal for Maximum Link Width of x4 (MAXLNKWDTH[5:0]=0x4) ...4-3
Figure 4.5 Merged Port Lane Reversal for Maximum Link Width of x8 (MAXLNKWDTH[5:0]=0x8) ...4-4
Figure 4.6 PES34H16 ASPM Link Sate Transitions ...........................................................................4-6
Figure 6.1 SMBus Interface Configuration Examples .........................................................................6-1
Figure 6.2 Sequential Double Word Initialization Sequence Format ...................................................6-4
Figure 6.3 Configuration Done Sequence Format ..............................................................................6-4
Figure 6.4 Serial EEPROM Initialization Errors ...................................................................................6-5
Figure 6.5 I/O Expander Function Allocation ......................................................................................6-6
Figure 6.6 I/O Expander Default Output Signal Value ........................................................................6-7
Figure 6.7 Slave SMBus Command Code Format ............................................................................6-18
Figure 6.8 CSR Register Read or Write CMD Field Format ..............................................................6-20
Figure 6.9 Serial EEPROM Read or Write CMD Field Format ..........................................................6-21
Figure 6.10 CSR Register Read Using SMBus Block Write/Read Transactions with PEC
Disabled ...........................................................................................................................6-22
Figure 6.11 Serial EEPROM Read Using SMBus Block Write/Read Transactions with PEC
Disabled ...........................................................................................................................6-23
Figure 6.12 CSR Register Write Using SMBus Block Write Transactions with PEC Disabled ...........6-23
Figure 6.13 Serial EEPROM Write Using SMBus Block Write Transactions with PEC Disabled ........6-23
Figure 6.14 Serial EEPROM Write Using SMBus Block Write Transactions with PEC Enabled ........6-23
Figure 6.15 CSR Register Read Using SMBus Read and Write Transactions with PEC Disabled ....6-24
Figure 7.1 PES34H16 Power Management State Transition Diagram ...............................................7-1
Figure 8.1 Hot-Plug on Switch Downstream Slots Application ............................................................8-1
Figure 8.2 Hot-Plug with Switch on Add-In Card Application ..............................................................8-2
Figure 8.3 Hot-Plug with Carrier Card Application ..............................................................................8-2
Figure 8.4 PES34H16 Hot-Plug Event Signalling ...............................................................................8-5
Figure 9.1 Port Configuration Space Organization .............................................................................9-2

IDT List of Figures
PES34H16 User Manual viii October 30, 2008
Notes
Figure 10.1 Diagram of the JTAG Logic ..............................................................................................10-1
Figure 10.2 State Diagram of PES34H16’s TAP Controller ................................................................10-2
Figure 10.3 Diagram of Observe-only Input Cell .................................................................................10-6
Figure 10.4 Diagram of Output Cell ....................................................................................................10-6
Figure 10.5 Diagram of Output Enable Cell ........................................................................................10-7
Figure 10.6 Device ID Register Format ...............................................................................................10-9

Notes
PES34H16 User Manual ix October 30, 2008
Register List
®
AERCAP - AER Capabilities (0x100) ..................................................................................................... 9-39
AERCEM - AER Correctable Error Mask (0x114).................................................................................. 9-44
AERCES - AER Correctable Error Status (0x110)................................................................................. 9-43
AERCTL - AER Control (0x118)............................................................................................................. 9-44
AERHL1DW - AER Header Log 1st Doubleword (0x11C) ..................................................................... 9-45
AERHL2DW - AER Header Log 2nd Doubleword (0x120)..................................................................... 9-45
AERHL3DW - AER Header Log 3rd Doubleword (0x124)...................................................................... 9-45
AERHL4DW - AER Header Log 4th Doubleword (0x128)...................................................................... 9-45
AERUEM - AER Uncorrectable Error Mask (0x108).............................................................................. 9-40
AERUES - AER Uncorrectable Error Status (0x104)............................................................................. 9-40
AERUESV - AER Uncorrectable Error Severity (0x10C)........................................................................ 9-42
BAR0 - Base Address Register 0 (0x010).............................................................................................. 9-15
BAR1 - Base Address Register 1 (0x014).............................................................................................. 9-15
BCTL - Bridge Control Register (0x03E)................................................................................................ 9-21
BIST - Built-in Self Test Register (0x00F).............................................................................................. 9-15
CAPPTR - Capabilities Pointer Register (0x034)................................................................................... 9-20
CCODE - Class Code Register (0x009)................................................................................................. 9-14
CLS - Cache Line Size Register (0x00C)............................................................................................... 9-14
DID - Device Identification Register (0x002).......................................................................................... 9-12
ECFGADDR - Extended Configuration Space Access Address (0x0F8)............................................... 9-38
ECFGDATA - Extended Configuration Space Access Data (0x0FC)..................................................... 9-39
EEPROMINTF - Serial EEPROM Interface (0x42C).............................................................................. 9-66
EROMBASE - Expansion ROM Base Address Register (0x038)........................................................... 9-20
GPECTL - General Purpose Event Control (0x450)............................................................................... 9-70
GPESTS - General Purpose Event Status (0x454)................................................................................ 9-72
GPIOCFG - General Purpose I/O Configuration (0x41C)....................................................................... 9-63
GPIOD - General Purpose I/O Data (0x420).......................................................................................... 9-64
GPIOFUNC - General Purpose I/O Control Function (0x418)................................................................ 9-63
GPR - General Purpose Register (0x40C)............................................................................................. 9-63
HDR - Header Type Register (0x00E).................................................................................................... 9-15
HPCFGCTL - Hot-Plug Configuration Control (0x408)........................................................................... 9-62
INTRLINE - Interrupt Line Register (0x03C)........................................................................................... 9-20
INTRPIN - Interrupt PIN Register (0x03D)............................................................................................. 9-21
IOBASE - I/O Base Register (0x01C)..................................................................................................... 9-16
IOBASEU - I/O Base Upper Register (0x030)........................................................................................ 9-19
IOEXPADDR0 - SMBus I/O Expander Address 0 (0x434)..................................................................... 9-68
IOEXPADDR1 - SMBus I/O Expander Address 1 (0x438)..................................................................... 9-69
IOEXPADDR2 - SMBus I/O Expander Address 2 (0x43C).................................................................... 9-69
IOEXPINTF - I/O Expander Interface (0x430)........................................................................................ 9-67
IOLIMIT - I/O Limit Register (0x01D)...................................................................................................... 9-17
IOLIMITU - I/O Limit Upper Register (0x032)......................................................................................... 9-20
MBASE - Memory Base Register (0x020).............................................................................................. 9-18
MLIMIT - Memory Limit Register (0x022)............................................................................................... 9-18
MSIADDR - Message Signaled Interrupt Address (0x0D4).................................................................... 9-37
MSICAP - Message Signaled Interrupt Capability and Control (0x0D0)................................................ 9-36
MSIMDATA - Message Signaled Interrupt Message Data (0x0DC)....................................................... 9-38
MSIUADDR - Message Signaled Interrupt Upper Address (0x0D8)...................................................... 9-37
PBUSN - Primary Bus Number Register (0x018)................................................................................... 9-15
PCICMD - PCI Command Register (0x004)...........................................................................................9-12

IDT Register List
PES34H16 User Manual x October 30, 2008
Notes
PCIECAP - PCI Express Capability (0x040) ...........................................................................................9-22
PCIEDCAP - PCI Express Device Capabilities (0x044)..........................................................................9-23
PCIEDCAP2 - PCI Express Device Capabilities 2 (0x064).....................................................................9-33
PCIEDCTL - PCI Express Device Control (0x048)..................................................................................9-24
PCIEDCTL2 - PCI Express Device Control 2 (0x068).............................................................................9-33
PCIEDSTS - PCI Express Device Status (0x04A)..................................................................................9-25
PCIEDSTS2 - PCI Express Device Status 2 (0x06A) .............................................................................9-34
PCIELCAP - PCI Express Link Capabilities (0x04C)..............................................................................9-26
PCIELCAP2 - PCI Express Link Capabilities 2 (0x06C).........................................................................9-34
PCIELCTL - PCI Express Link Control (0x050).......................................................................................9-27
PCIELCTL2 - PCI Express Link Control 2 (0x070)..................................................................................9-34
PCIELSTS - PCI Express Link Status (0x052)........................................................................................9-28
PCIELSTS2 - PCI Express Link Status 2 (0x072)...................................................................................9-34
PCIESCAP - PCI Express Slot Capabilities (0x054)...............................................................................9-29
PCIESCAP2 - PCI Express Slot Capabilities 2 (0x074)..........................................................................9-34
PCIESCTL - PCI Express Slot Control (0x058).......................................................................................9-31
PCIESCTL2 - PCI Express Slot Control 2 (0x078)..................................................................................9-34
PCIESSTS - PCI Express Slot Status (0x05A) .......................................................................................9-32
PCIESSTS2 - PCI Express Slot Status 2 (0x07A) ..................................................................................9-35
PCIEVCECAP - PCI Express VC Enhanced Capability Header (0x200)................................................9-46
PCISTS - PCI Status Register (0x006) ...................................................................................................9-13
PLTIMER - Primary Latency Timer (0x00D)............................................................................................9-15
PMBASE - Prefetchable Memory Base Register (0x024).......................................................................9-18
PMBASEU - Prefetchable Memory Base Upper Register (0x028)..........................................................9-19
PMCAP - PCI Power Management Capabilities (0x0C0)........................................................................9-35
PMCSR - PCI Power Management Control and Status (0x0C4) ............................................................9-36
PMLIMIT - Prefetchable Memory Limit Register (0x026)........................................................................9-19
PMLIMITU - Prefetchable Memory Limit Upper Register (0x02C)..........................................................9-19
PVCCAP1- Port VC Capability 1 (0x204)................................................................................................9-46
PVCCAP2- Port VC Capability 2 (0x208)................................................................................................9-47
PVCCTL - Port VC Control (0x20C)........................................................................................................9-47
PVCSTS - Port VC Status (0x20E) .........................................................................................................9-48
PWRBCAP - Power Budgeting Capabilities (0x280)...............................................................................9-57
PWRBD - Power Budgeting Data (0x288)...............................................................................................9-57
PWRBDSEL - Power Budgeting Data Select (0x284).............................................................................9-57
PWRBDV[7:0] - Power Budgeting Data Value [7:0] (0x300)...................................................................9-58
PWRBPBC - Power Budgeting Power Budget Capability (0x28C) .........................................................9-58
RID - Revision Identification Register (0x008) ........................................................................................9-14
SBUSN - Secondary Bus Number Register (0x019)...............................................................................9-16
SECSTS - Secondary Status Register (0x01E) ......................................................................................9-17
SLTIMER - Secondary Latency Timer Register (0x01B).........................................................................9-16
SMBUSCTL - SMBus Control (0x428)....................................................................................................9-65
SMBUSSTS - SMBus Status (0x424) .....................................................................................................9-64
SNUMCAP - Serial Number Capabilities (0x180) ...................................................................................9-45
SNUMLDW - Serial Number Lower Doubleword (0x184) .......................................................................9-46
SNUMUDW - Serial Number Upper Doubleword (0x188).......................................................................9-46
SSIDSSVID - Subsystem ID and Subsystem Vendor ID (0x0F4)...........................................................9-38
SSIDSSVIDCAP - Subsystem ID and Subsystem Vendor ID Capability (0x0F0)...................................9-38
SUBUSN - Subordinate Bus Number Register (0x01A)..........................................................................9-16
SWCTL - Switch Control (0x404)............................................................................................................9-61
SWPECNT - Switch Parity Error Count (0x74C).....................................................................................9-77
SWPECTL - Switch Parity Error Control (0x740)....................................................................................9-76
SWPERCTL - Switch Parity Error Reporting Control (0x748).................................................................9-77
SWPESTS - Switch Parity Error Status (0x744) .....................................................................................9-76
SWSTS - Switch Status (0x400) .............................................................................................................9-59

IDT Register List
PES34H16 User Manual xi October 30, 2008
Notes
SWTOCNT - Switch Time-Out Count (0x75C)........................................................................................9-79
SWTORCTL - Switch Time-Out Reporting Control (0x758)....................................................................9-78
SWTOSTS - Switch Time-Out Status (0x754) ........................................................................................9-77
USPFCTL - Upstream Port Failover Control (0x474)..............................................................................9-75
USPFSTS - Upstream Port Failover Status (0x470)...............................................................................9-74
USPFTIMER - Upstream Port Failover Watchdog Timer (0x478)...........................................................9-75
VCR0CAP- VC Resource 0 Capability (0x210).......................................................................................9-48
VCR0CTL- VC Resource 0 Control (0x214)............................................................................................9-49
VCR0STS - VC Resource 0 Status (0x218)............................................................................................9-50
VCR0TBL0 - VC Resource 0 Arbitration Table Entry 0 (0x230)..............................................................9-52
VCR0TBL1 - VC Resource 0 Arbitration Table Entry 1 (0x234)..............................................................9-53
VCR0TBL2 - VC Resource 0 Arbitration Table Entry 2 (0x238)..............................................................9-53
VCR0TBL3 - VC Resource 0 Arbitration Table Entry 3 (0x23C).............................................................9-54
VCR1CAP- VC Resource 1 Capability (0x21C)......................................................................................9-50
VCR1CTL- VC Resource 1 Control (0x220)............................................................................................9-51
VCR1STS - VC Resource 1 Status (0x224)............................................................................................9-51
VCR1TBL0 - VC Resource 1 Arbitration Table Entry 0 (0x240)..............................................................9-54
VCR1TBL1 - VC Resource 1 Arbitration Table Entry 1 (0x244)..............................................................9-55
VCR1TBL2 - VC Resource 1 Arbitration Table Entry 2 (0x248)..............................................................9-55
VCR1TBL3 - VC Resource 1 Arbitration Table Entry 3 (0x24C).............................................................9-56
VID - Vendor Identification Register (0x000)...........................................................................................9-11

IDT Register List
PES34H16 User Manual xii October 30, 2008
Notes

Notes
PES34H16 User Manual 1 - 1 October 30, 2008
®
Chapter 1
PES34H16 Device Overview
Introduction
The 89HPES34H16 is a member of the IDT PRECISE™ family of PCI Express® switching solutions.
The PES34H16 is a 34-lane, 16-port peripheral chip that performs PCI Express packet switching with a
feature set optimized for high-performance applications such as servers, storage, and communications/
networking. It provides connectivity and switching functions between a PCI Express upstream port and up
to fifteen downstream ports and supports switching between downstream ports.
List of Features
– Sixteen maximum switch ports
•Up to three x8 ports that bifurcate up to six x4 ports
•Ten x1 ports
– Thirty-four 2.5 Gbps embedded SerDes
•Supports pre-emphasis and receive equalization on per-port basis
– Low-latency cut-through switch architecture
– Support for Max Payload Size up to 2048 bytes
– Supports two virtual channels and eight traffic classes
– PCI Express Base Specification Revision 1.1 compliant
Flexible Architecture with Numerous Configuration Options
– Port arbitration schemes utilizing round robin algorithms
– Automatic per port link width negotiation from x8 to x4 to x2 or x1
– Automatic lane reversal on all ports
– Automatic polarity inversion on all lanes
– Supports locked transactions, allowing use with legacy software
– Ability to load device configuration from serial EEPROM
– Ability to control device via SMBus
Highly Integrated Solution
– Requires no external components
– Incorporates on-chip internal memory for packet buffering and queueing
– Integrates thirty-four 2.5Gbps embedded full duplex SerDes, 8B/10B encoder/decoder (nosepa-
rate transceivers needed)
Reliability, Availability, and Serviceability (RAS) Features
– Redundant upstream port failover capability
– Supports optional PCI Express end-to-end CRC checking

IDT PES34H16 Device Overview
PES34H16 User Manual 1 - 2 October 30, 2008
– Internal end-to-end parity protection on all TLPs ensures data integrity even in systems that do not implement end-to-end CRC (ECRC)
– Supports optional PCI Express Advanced Error Reporting
– Supports PCI Express Hot-Plug
•Compatible with Hot-Plug I/O expanders used on PC
motherboards
– Supports Hot-Swap
Power Management
– Supports PCI Power Management Interface specification, Revision 1.1 (PCI-PM)
•Supports powerdown modes at the link level (L0, L0s, L1, L2/L3 Ready and L3) and at the device level (D0, D3hot)
– Unused SerDes disabled
Testability and Debug Features
– Built in SerDes Pseudo-Random Bit Stream (PRBS) generator
– Ability to read and write any internal register via the SMBus
– Ability to bypass link training and force any link into any mode
– Provides statistics and performance counters
Thirty-two General Purpose Input/Output pins
– Each pin may be individually configured as an input or output
– Each pin may be individually configured as an interrupt input
– Some pins have selectable alternate functions
Packaged in a 35mm x 35mm 1156-ball Flip Chip BGA with 1mm ball spacing
Figure 1.1 PES34H16 Architectural Block Diagram
Reset
Controller
Bifurcating PCI Express
Stack 0 Ingress
Port 0
Port 1
Bifurcating PCI Express
Stack 1 Ingress
Port 2
Port 3
Bifurcating PCI Express
Stack 2 Ingress
Port 4
Port 5
Bifurcating PCI Express
Stack 3 Ingress
Port 6
Port 7
Bifurcating PCI Express
Stack 4 Ingress
Port 8
Port 9
Bifurcating PCI Express
Stack 5 Ingress
Port 10
Port 11
Bifurcating PCI Express
Stack 6 Ingress
Port 12
Port 13
Bifurcating PCI Express
Stack 7 Ingress
Port 14
Port 15
Credit Based Queue (CBQ)
...
Credit Based Queue (CBQ)
...
Credit Based Queue (CBQ)
...
Credit Based Queue (CBQ)
...
Credit Based Queue (CBQ)
...
Credit Based Queue (CBQ)
...
Credit Based Queue (CBQ)
...
Credit Based Queue (CBQ)
...
Shared Memory Queue (SMQ)
Memory and Scheduler (MAS)
Destination
Scheduler
Destination
Scheduler
Shared Memory Queue (SMQ)
Shared Memory Queue (SMQ)
Shared Memory Queue (SMQ)
Bifurcating PCI Express
Stack 0 Egress
Port 0
Bifurcating PCI Express
Stack 1 Egress
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
Shared Memory Queue (SMQ)
Memory and Scheduler (MAS)
Destination
Scheduler
Destination
Scheduler
Shared Memory Queue (SMQ)
Shared Memory Queue (SMQ)
Shared Memory Queue (SMQ)
Bifurcating PCI Express
Stack 2 Egress
Port 4
Bifurcating PCI Express
Stack 3 Egress
Port 5
Port 6
Port 7
Shared Memory Queue (SMQ)
Memory and Scheduler (MAS)
Destination
Scheduler
Destination
Scheduler
Shared Memory Queue (SMQ)
Shared Memory Queue (SMQ)
Shared Memory Queue (SMQ)
Bifurcating PCI Express
Stack 4 Egress
Port 8
Bifurcating PCI Express
Stack 5 Egress
Port 9
Port 10
Port 11
Shared Memory Queue (SMQ)
Memory and Scheduler (MAS)
Destination
Scheduler
Destination
Scheduler
Shared Memory Queue (SMQ)
Shared Memory Queue (SMQ)
Shared Memory Queue (SMQ)
Bifurcating PCI Express
Stack 6 Egress
Port 12
Bifurcating PCI Express
Stack 7 Egress
Port 13
Port 14
Port 15
Switch Core
Master
SMBus
Interface
Slave
SMBus
Interface
GPIO
Controller
Table of contents
Other IDT Switch manuals
Popular Switch manuals by other brands

Briggs & Stratton
Briggs & Stratton 6421 installation instructions
3Com
3Com OfficeConnect 5 installation guide

Jaycar
Jaycar AC-1708 user manual

Atlona
Atlona AT-PROHD88M-SR user manual

Racal Instruments
Racal Instruments 1260-X121 user manual

HP
HP ProCurve 6600-48G Product End-of-Life Disassembly Instructions