OY51 Measuring light grids (10mm beam spacing)
2
Contents
1 Preliminary notes............................................................. 3
1.1 Symbols used........................................................... 3
1.2 Warnings used.......................................................... 3
2 Safety instructions............................................................ 4
3 Intended use ................................................................ 5
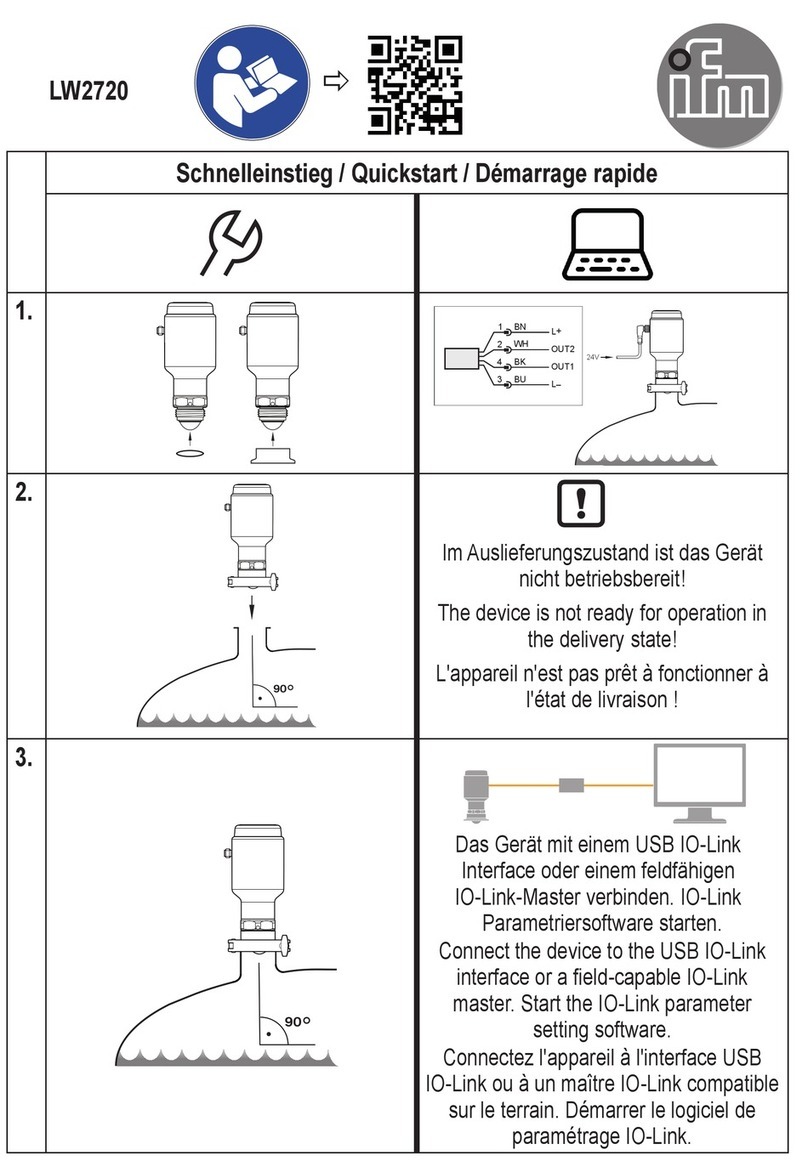
4 Getting started............................................................... 6
5 Function.................................................................... 7
5.1 IO-Link................................................................ 7
6 Installation .................................................................. 8
6.1 Installation instructions.................................................... 8
6.1.1 Fastening .......................................................... 8
6.1.2 Optical alignment..................................................... 9
6.2 Multiple systems......................................................... 9
7 Electrical connection .......................................................... 11
7.1 Transmitter wiring diagram................................................. 11
7.2 Receiver wiring diagram................................................... 11
7.3 Synchronisation of transmitter and receiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
7.3.1 Synchronisation via ifm Y cable (EY5053 and EY5054) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
7.3.2 Synchronisation via standard sockets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
7.3.3 Optical synchronisation................................................ 12
8 Operating and display elements.................................................. 14
8.1 Transmitter LED states................................................... 14
8.2 Receiver LED states...................................................... 14
9 Operation................................................................... 15
9.1 Switching mode (SIO mode) ............................................... 15
9.2 Operation with IO-Link master.............................................. 15
9.3 Process values.......................................................... 15
9.3.1 FBO – first beam occupied ............................................. 15
9.3.2 LBO – last beam occupied ............................................. 16
9.3.3 CBO – central beam occupied........................................... 16
9.3.4 NBO – number of beams occupied . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
9.3.5 NCBO – number of consecutive beams occupied . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
9.3.6 Tolerance .......................................................... 17
10 Technical data............................................................... 18
10.1 Light grid with 10 mm beam spacing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
11 Troubleshooting.............................................................. 19
11.1 Transmitter fault diagnostics ............................................... 19
11.2 Fault diagnosis receiver................................................... 19
12 Maintenance, repair and disposal ................................................ 20