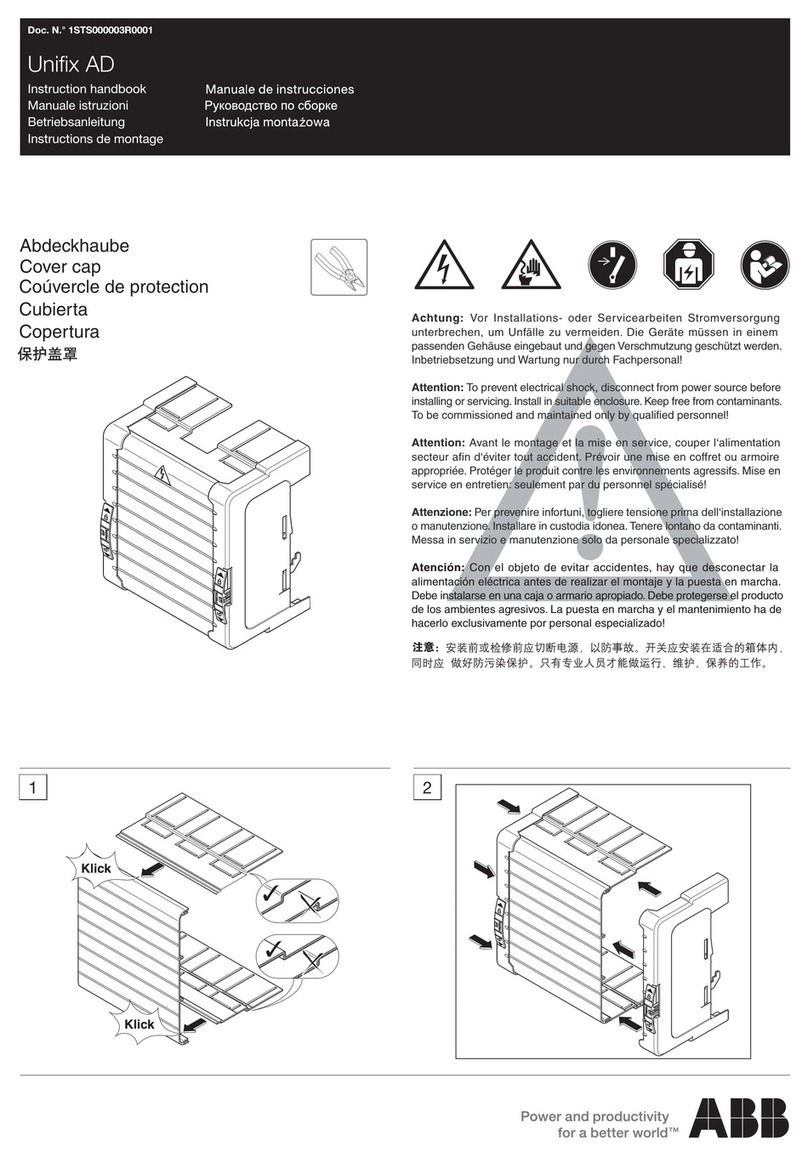
2)Turn the pump handle right or left by 1/4 (90o), push it toward to the pump.
3)Insert the new tube into the aspirating pump.
4)Pull the pump handle at a 1/2 stroke until it locks and wait for 0.5 minutes or until the completion of sampling is
confirmed with the flow indicator of the pump.
5)On completion of sampling, read the scale at the maximum point of the stained layer.
6)Then multiply the reading value by 2.
Ⅰ. The scale is calibrated at 20℃(68°F), 50 %R.H. and 1013hPa. Readings obtained in other
circumstances should be corrected.
(REFER TO ITEM 3. CORRECTION FOR AMBIENT CONDITIONS.)
Ⅱ. When the maximum point of the stained layer is unclear or oblique, read the scale at the centre
between the longest and shortest points.
3. CORRECTION FOR AMBIENT CONDITIONS:
①Temperature; The scale is calibrated based on the temperature of 20℃(68°F). Readings obtained in other temperature
circumstances should be corrected with the following temperature correction table.
Table of the coefficient for temperature correction (based on 20℃)
Procedure of temperature correction: Actual readings can be obtained by multiplying the readings of tubes by
coefficient for temperature correction shown in the above. Therefore,
Actual Hydrogen sulphide concentration (ppm)=
Reading value (ppm)×Coefficient for temperature correction
②Humidity; No correction is necessary.
③Atmospheric Pressure;
True concentration = Tube reading ×1013
Atmospheric pressure(in hPa)
4. INTERFERENCE:
Arsine changes the colour of the whole reagent to pale orange and coexistence of more than 0.25ppm of Arsine gives
higher readings. More than 0.5ppm of Hydrogen selenide produces a similar stain and coexistence of them gives higher
readings. More than 0.2ppm of Mercaptans produces a similar stain and coexistence of them gives higher readings.
Phosphine changes the colour of the whole reagent to pale pink and coexistence of more than 0.4ppm of Phosphine gives
higher readings. More than 3ppm of Hydrogen cyanide changes the colour of the whole reagent to pale orange and
coexistence of Hydrogen cyanide with Hydrogen sulphide does not affect on the readings if the maximum end point of the
pink stain is discernable. Less than 1000ppm of Sulphur dioxide does not affect on the readings. More than 50ppm of
Nitrogen dioxide changes the colour of the whole reagent to pale orange and coexistence of more than 1ppm of Nitrogen
dioxide gives lower readings. Ammonia does not change the colour of reagent itself, but coexistence of 1ppm Ammonia with
Hydrogen sulphide fade the discoloured layer from the zero end of the detecting reagent(inlet side of the tube).
5. CHEMICAL REACTION IN THE DETECTOR TUBE:
H2S + 2CH3C6H4SO3Ag →Ag2S + 2CH3C6H4SO3H
6. DISPOSAL OF TUBES:
USED TUBES SHOULD BE DISPOSED CAREFULLY ACCORDING TO RELEVANT REGULATIONS, IF ANY.
7. HAZARDOUS AND DANGEROUS PROPERTIES OF HYDROGEN SULPHIDE:
TLV-TWA◆
Explosion range in air
◆Threshold Limit Value established by the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists, 2012.
8. INSPECTION OF ASPIRATING PUMP:
Checking for leaks;
①Insert a sealed, unbroken detector tube into the pump.
②Align the guide marks on the shaft and stopper of the pump.
③Pull the handle to a full stroke and wait for 1 minute.
④Unlock the handle and allow it to return slowly into the pump by holding the cylinder and handle securely.
CAUTION HANDLE WILL TEND TO SNAP BACK INTO THE PUMP QUICKLY.
⑤If the handle returns completely to the original position, the performance is satisfactory. Otherwise,
refer to maintenance procedures shown in the instruction manual of the pump to correct the leakage.
9. USER RESPONSIBILITY:
It is the sole responsibility of the user of this equipment to ensure that the equipment is operated, maintained, and
repaired in strict accordance with these instructions and the instructions provided with each Model AP-20, AP-20S,
400B, AP-1, AP-1S or 400A aspirating pump, and that detector tubes are not used beyond their expiration date or