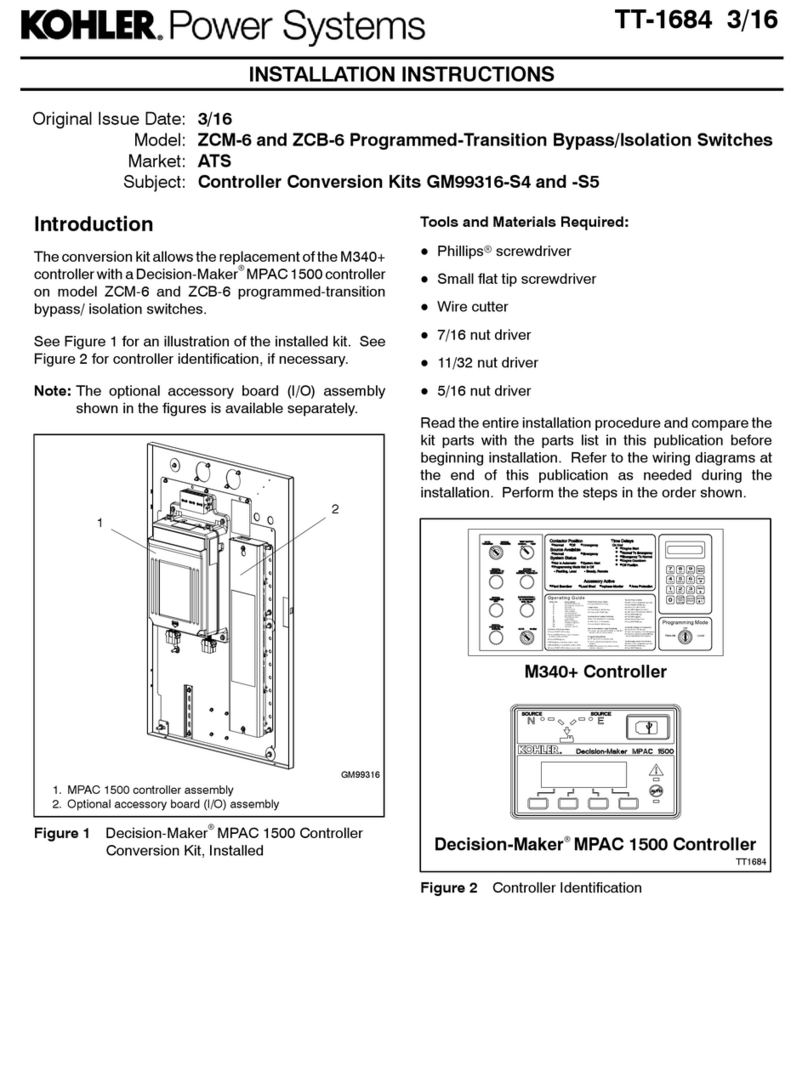
TP-6322 9/04 ISafety Precautions and Instructions
Safety Precautions and Instructions
IMPORTANT SAFETY
INSTRUCTIONS. Electromechanical
equipment, including generator sets,
transfer switches, switchgear, and
accessories, can cause bodily harm
and pose life-threatening danger when
improperly installed, operated, or
maintained. To prevent accidents be
aware of potential dangers and act
safely. Read and follow all safety
precautions and instructions. SAVE
THESE INSTRUCTIONS.
This manual has several types of safety
precautions and instructions: Danger,
Warning, Caution, and Notice.
DANGER
Danger indicates the presence of a
hazard that will cause severe
personal injury, death,orsubstantial
property damage.
WARNING
Warning indicates the presence of a
hazard that can cause severe
personal injury, death, or substantial
property damage.
CAUTION
Caution indicates the presence of a
hazard that will or can cause minor
personal injury or property damage.
NOTICE
Notice communicates installation,
operation, or maintenance information
that is safety related but not hazard
related.
Safety decals affixed to the equipment
in prominent places alert the operator
or service technician to potential
hazards and explain how to act safely.
The decals are shown throughout this
publication to improve operator
recognition. Replace missing or
damaged decals.
Accidental Starting
Accidental starting.
Can cause severe injury or death.
Disconnect the battery cables before
working on the generator set.
Remove the negative (--) lead first
when disconnecting the battery.
Reconnect the negative (--) lead last
when reconnecting the battery.
WARNING
Disabling the generator set.
Accidental starting can cause
severe injury or death. Before
working on the generator set or
connected equipment, disable the
generator set as follows: (1) Move the
generator set master switch to the OFF
position. (2) Disconnect the power to
the battery charger. (3) Remove the
battery cables, negative (--) lead first.
Reconnect the negative (--) lead last
when reconnecting the battery. Follow
these precautions to prevent starting of
the generator set by an automatic
transfer switch, remote start/stop
switch, or engine start command from a
remote computer.
Battery
Sulfuric acid in batteries.
Can cause severe injury or death.
Wear protective goggles and
clothing. Battery acid may cause
blindness and burn skin.
WARNING
Battery electrolyte is a diluted
sulfuric acid. Battery acid can cause
severe injury or death. Battery acid
can cause blindness and burn skin.
Always wear splashproof safety
goggles, rubber gloves, and boots
when servicing the battery. Do not
open a sealed battery or mutilate the
battery case. If battery acid splashes in
the eyes or on the skin, immediately
flush the affected area for 15 minutes
with large quantities of clean water.
Seek immediate medical aid in the case
of eye contact. Never add acid to a
battery after placing the battery in
service, as this may result in hazardous
spattering of battery acid.
Explosion.
Can cause severe injury or death.
Relays in the battery charger
cause arcs or sparks.
Locate the battery in a well-ventilated
area. Isolate the battery charger from
explosive fumes.
WARNING
Battery gases. Explosion can cause
severe injury or death. Battery gases
can cause an explosion. Do not smoke
or permit flames or sparks to occur near
a battery at any time, particularly when
it is charging. Do not dispose of a
battery in a fire. To prevent burns and
sparks that could cause an explosion,
avoid touching the battery terminals
with tools or other metal objects.
Remove all jewelry before servicing the
equipment. Discharge static electricity
from your body before touching
batteries by first touching a grounded
metal surface away from the battery. To
avoid sparks, do not disturb the battery
charger connections while the battery
is charging. Always turn the battery
charger off before disconnecting the
battery connections. Ventilate the
compartments containing batteries to
prevent accumulation of explosive
gases.