E. LDO Block ............................................................................................................................18
3.3.3 Battery Charging Block ....................................................................................................18
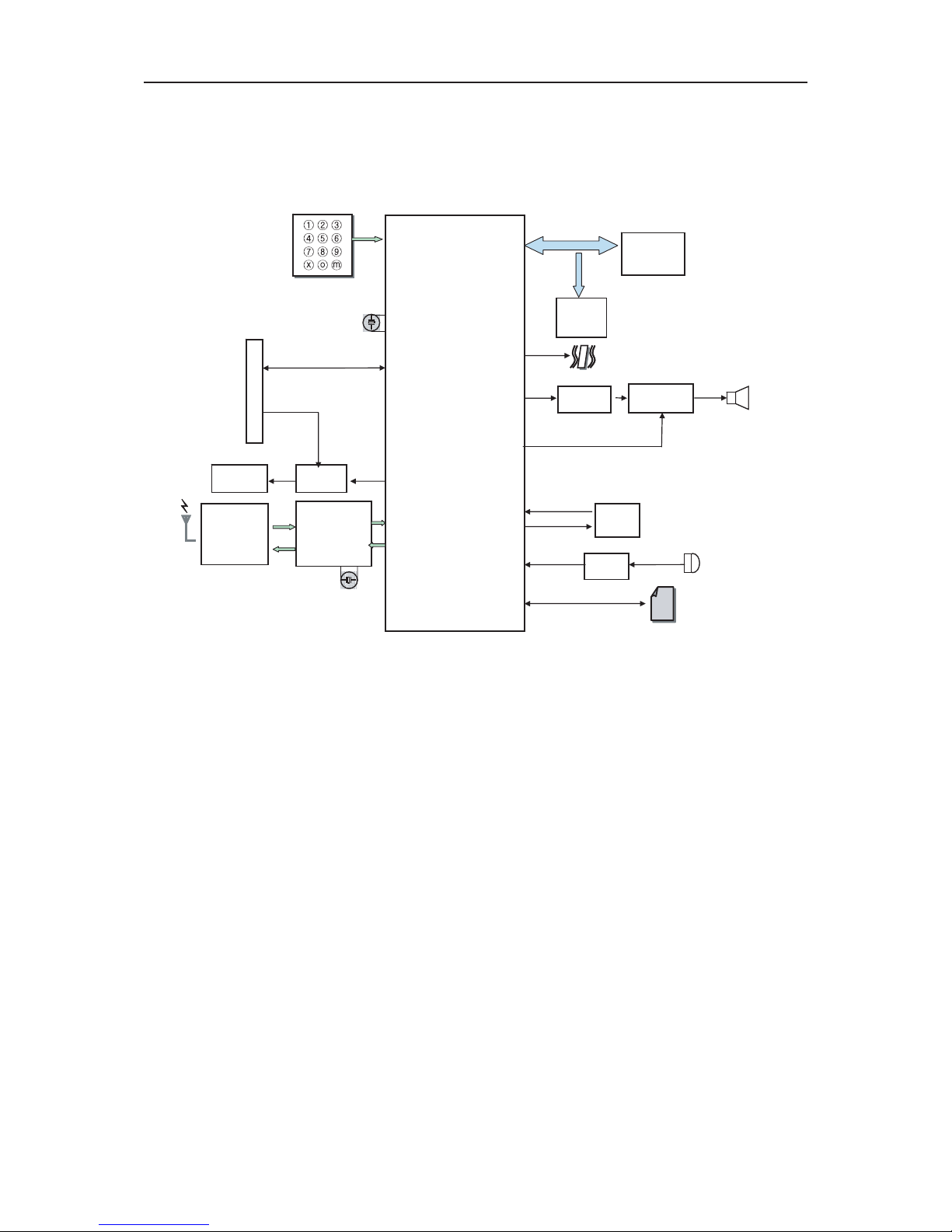
3.3.4 Display and Interface ......................................................................................................20
3.3.5 Keypad Switches and Scanning ......................................................................................21
3.3.6 Microphone...................................................................................................................... 22
3.3.7 Soft-midi and Main Speaker ............................................................................................23
3.3.8 Headset Interface ............................................................................................................24
3.3.9 Key Back-light Illumination ..............................................................................................25
3.3.10 LCD Back-light Illumination............................................................................................26
3.3.11 VIBRATOR......................................................................................................................26
4. Trouble shooting..................................................................................................................28
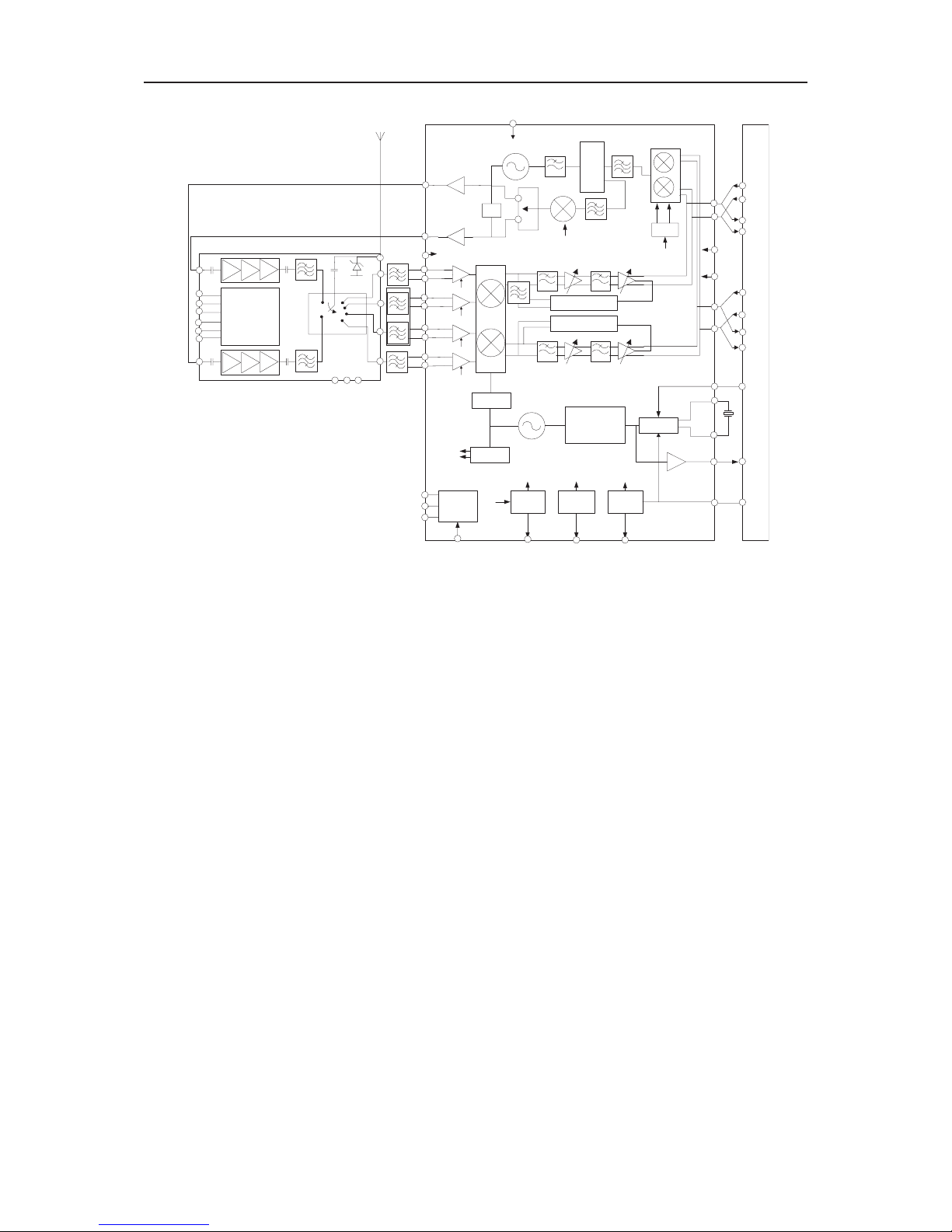
4.1 RF components ......................................................................................................................28
4.2 RX Trouble ..............................................................................................................................29
4.2.1 Check Crystal Circuit........................................................................................................30
4.2.2 Check Control Signal ......................................................................................................31
4.2.3 Check Mobile SW & ANT SW ..........................................................................................32
4.2.4 Check SAW filter..............................................................................................................34
4.2.5 Check I/Q signal ..............................................................................................................35
4.3 TX Trouble ..............................................................................................................................36
4.3.1 Check Crystal Circuit ......................................................................................................37
4.3.2 Check Control Signal ......................................................................................................38
4.3.3 Check TX I/Q signal ........................................................................................................39
4.3.4 Check PAM control signal ................................................................................................40
4.3.5 Check Mobile SW & ANT SW ..........................................................................................41
4.4 Power On Trouble ..................................................................................................................43
4.5 Charging Trouble ....................................................................................................................45
4.6 Download ..............................................................................................................................47
4.7 Calibration ..............................................................................................................................49
4.7.1 Equipment Setup..............................................................................................................49
4.7.2 Setup................................................................................................................................49
4.8 LCD Trouble............................................................................................................................56
4.8.1 LCD Blue Screen or abnormal display ............................................................................56
4.8.2 LCD Black Screen............................................................................................................57
4.9 Receiver Trouble ....................................................................................................................58
4.10 Speaker Trouble....................................................................................................................61
4.11 MIC Trouble ..........................................................................................................................63
4.12 Earphone Trouble..................................................................................................................65
4.13 KEYPAD Backlight LEDS Trouble ........................................................................................68
4.14 SIM Trouble ..........................................................................................................................69
5. Appendix ..............................................................................................................................71
1. BOM..........................................................................................................................................71
2. Exploded View ..........................................................................................................................80
3. Circuit diagram..........................................................................................................................82
4. Pcb layout..................................................................................................................................86
2