Micrel MIC7401 User manual

MIC7401 Evaluation Board
Configurable PMIC, Five-Channel
Buck Regulator plus One-Boost with
HyperLight Load
®
, I
2
C Control and Enable
HyperLight Load is a registered trademark of Micrel, Inc.
Micrel Inc. • 2180 Fortune Drive • San Jose, CA 95131 • USA • tel +1 (408) 944-0800 • fax + 1 (408) 474-1000 • http://www.micrel.com
July 21, 2015
Revision 1.0
General Description
The MIC7401 is a powerful, highly-integrated,
configurable, power-management IC (PMIC) featuring five
synchronous buck regulators, one boost regulator, and
high-speed I2C interface with an internal EEPROM and
micro-power shutdown. The device offers two distinct
modes of operation “standby mode” and “normal mode”.
In normal mode, the programmable switching converters
can be configured to support a variety of features,
including start-up sequencing, timing, soft-start ramp,
output voltage levels, current-limit levels, and output
discharge for each channel.
In standby mode the PMIC can configured in a low power
state by either disabling an output or by changing the
output voltage to a lower level. Independent exit from
standby mode can be achieved either by I2C
communication or the external STBY pin.
The initial settings of the evaluation board are:
Input: 2.4V to 5.5V
Output 1: 1.8V/0.8A Output 4: 1.05V/3.0A
Output 2: 1.1V/0.5A Output 5: 1.25V/1.0A
Output 3: 1.8V/0.5A Output 6: 12V/0.2A
Datasheets and support documentation are available on
Micrel’s web site at: www.micrel.com.
Requirements
The MIC7401 evaluation board requires only a single
power supply with 5A (minimum) current capability. The
output load can either be an active (electronic) or passive
(resistive) load.
Precautions
The MIC7401 evaluation board does not have reverse
polarity protection. Applying a negative voltage to the VIN
and GND terminals can damage the device. The maximum
operating rating for VIN is 5.5V. Exceeding 5.5V on the VIN
could damage the device.
Ordering Information
Part Number
Description
MIC7401EV MIC7401 Evaluation Board
MICUSB USB Dongle
Evaluation Board
A) INPUT VOLTAGE
B) OUTPUT VOLTAGES
C) USB DONGLE CONNECTOR
D) I2C SDA AND SCL
E) I2C PULL-UP TO VIN
F) STATUS AND CONTROL BIT HEADER
G) ENABLE
C
D
F
G
E
AB

Micrel, Inc.
MIC7401 Evaluation Board
July 21, 2015
2 Revision 1.0
Getting Started
1. Download GUI
To download the GUI, select “Software Package/Kit”
from the MIC7401 product page from the Micrel
website (www.micrel.com). Users can either save the
compressed installation file to hard drive or extract the
compressed file using a program such as PeaZip,
WinRAR, or WinZip. Then run MIC7401Install.msi to
install the GUI.
When the installation process is complete, click on the
Windows “Start” button, then select “All Programs” to
view the Start Menu. Find the new Micrel folder and
“click” on the Serial Programmer > MIC7401 to locate
the GUI program.
Before you launch the GUI, the USB dongle must be
connect to the PC by the USB cable, the USB dongle
plugged into the evaluation board and the board
powered up.
2. Set the USB Dongle and Switch Position
The USB dongle has a micro switch with two positions:
“I2C” and “NOM” (refer to Figure 1). To ensure the PC
is capable of communicating to the IC, confirm that the
micro switch is in the I2C (or left) position. Pin 1 on the
edge connector is the ground pin, which has a square
solder pad.
Figure 1. MIC7401 USB Dongle Micro Switch
3. Connect USB Dongle
The USB dongle is inverted and plugged into the 4-pin
socket (see Figure 2). Cutting off the extra pins is
recommended. Next, turn on the power supply and
slowly ramp up then input voltage. Now, click on the
MIC7400 ICON in the Start Menu to launch the GUI.
Figure 2. USB Dongle Connection to Evaluation Board
4. Configure the GUI for Direct Editing
When the MIC7401 GUI Interface window appears (see
Figure 3), the connection between the computer and the
USB dongle must be verified by clicking on the “Test”
button. “Target OK” will appear on the bottom of the GUI
window indicating it is operational. Before configuring the
MIC7401, the GUI needs to be set for direct editing. To do
this click on Link >Link Mode >Directing Editing. Now it is
time to program the MIC7401.
Figure 3. MIC7401 GUI Interface
Test
Button
Save
Configuration
Target
OK

Micrel, Inc.
MIC7401 Evaluation Board
July 21, 2015
3 Revision 1.0
Evaluation Board Description
Programming Options
Every regulator has its own configuration settings that
allow the output voltage, current-limit, and soft-start ramp
rate to be set (Figure 4). The global settings like power-on-
reset (POR) threshold and start-up delay are at the top of
the MIC7401 GUI Interface window (Figure 5).
Figure 4. Regulator Settings
The first dial sets the output voltage for normal mode and
the second sets standby mode. To change the voltage
setting, click on the up/down arrow or click and hold the
right mouse button on the pointer and drag the pointer to
the desired voltage level, then release the mouse button.
Note that the register associated with the output changes
on-the-fly every time the mouse is clicked. As the voltage
level in the GUI changes, the output of the MIC7401 will
also change. The “On” check box is the ON/OFF control
for the regulators. If checked, the regulator is enabled.
The soft-start ramp rate is registered in µs-per-step, with
each step being 50mV for the buck regulators and 200mV
for the boost. It controls both the rising and falling rate of
the output voltage.
The PGOOD mask is used to control the global power
good output (PG). If this box is checked, then the output
will not contribute to the overall power good output. This
allows the output to go from normal mode to standby mode
without triggering a power good fault. Also the global
power good flag will not be affected by an over-current
fault.
The PG status box is checked when the output is within
91% of its regulated value. The OC status box indicates an
overcurrent condition.
In Figure 5, the POR threshold monitors AVIN and sets the
lower and upper limit of the POR comparator. The POR
delay time starts as soon as AVIN voltage rises above the
upper threshold. The POR output goes low without delay
as soon as AVIN fall below the lower threshold limit.
Figure 5. Global Settings
The startup delay sets the delay between the internal
power good signal and the enable of the next regulator in
the sequence. The sequence setting allows the outputs to
come up in any order. There are six time slots. Each time
slot can be programmed for up to six regulators to be
turned on at once or none at all.
The MIC7401 can be powered up into either standby or
normal mode. The IC will start-up in standby mode if the
standby-mode check box is checked.
The soft-start speed check box when checked set the soft
start ramp to the 8µs to 1024µs speed range. The OT
check box is a status indicator when checked indicates an
overtemperature fault.
Evaluation Board
The MIC7401 evaluation board provides numerous two-pin
headers to monitor various system parameters such as
input voltage, output voltage, standby mode, and power
good. A standard test clip can be used, but for a more
elegant solution, use a test cable from Joy Signal PN: 9-
905305.
Micrel, Inc.
MIC7401 Evaluation Board
July 21, 2015
4 Revision 1.0
Functional Description
The MIC7401 is one of the industry’s most-advanced
PMIC devices designed for solid state drives (SSD) on the
market today. It is a multi-channel solution which offers
software configurable soft-start, sequencing, and digital
voltage control (DVC) that minimizes PC board area.
These features usually require a pin for programming.
However, this approach makes the IC larger by increasing
pin count, and also increases BOM cost due to the
external components.
The following is a complete list of the programmable
features of the MIC7401:
•Buck output voltage (0.8V – 3.3V/50mV steps)
•Boost output voltage (7.0V – 14V/ 200mV steps)
•Power-on-reset (2.25V – 4.25V/50mV steps)
•Power-on-reset delay (5ms – 160ms/5ms steps)
•Power-up sequencing (6 time slots)
•Power-up sequencing delay (0ms – 7ms/1ms steps)
•Soft-start (4µs – 1024µs per step)
•Buck current-limit threshold
−(1.1A to 6.1A/0.5A steps)
•Boost current-limit threshold
−(1.76A to 2.6A/0.12A steps)
•Boost pull-down (37mA to 148mA/37mA steps)
•Buck pull-down (90Ω)
•Buck standby output voltage programmable
•Boost standby output voltage programmable
•Global power-good masking
These features give the system designer the flexibility to
customize the MIC7401 for their application. For example,
VOUT1 current limit can be programmed to 4.1A and VOUT2
can be set to 1.1A. These outputs can be programmed to
come up at the same time or 2.0ms apart. In addition, in
power-saving standby mode, the outputs can either be
turned off or programmed to a lower voltage. With this
programmability the MIC7401 can be used in multiple
platforms.
The MIC7401 buck regulators are adaptive on-time
synchronous step-down DC-to-DC regulators. They are
designed to operate over a wide input voltage range from
2.4V to 5.5V and provide a regulated output voltage at up
to 3.0A of output current. An adaptive on-time control
scheme is employed to obtain a constant switching
frequency and to simplify the control compensation. The
device includes an internal soft-start function which
reduces the power supply input surge current at start-up
by controlling the output voltage rise time.
The MIC7401 has a current-mode boost regulator that can
deliver up to 200mA of output current and only consumes
70µA of quiescent current. The 2.0MHz switching
frequency allows small chip inductors to be used.
Programmable overcurrent sensing protects the boost
from overloads and an output disconnect switch opens to
protect against a short-circuit condition. Soft-start is also
programmable and controls both the rising and falling
output.
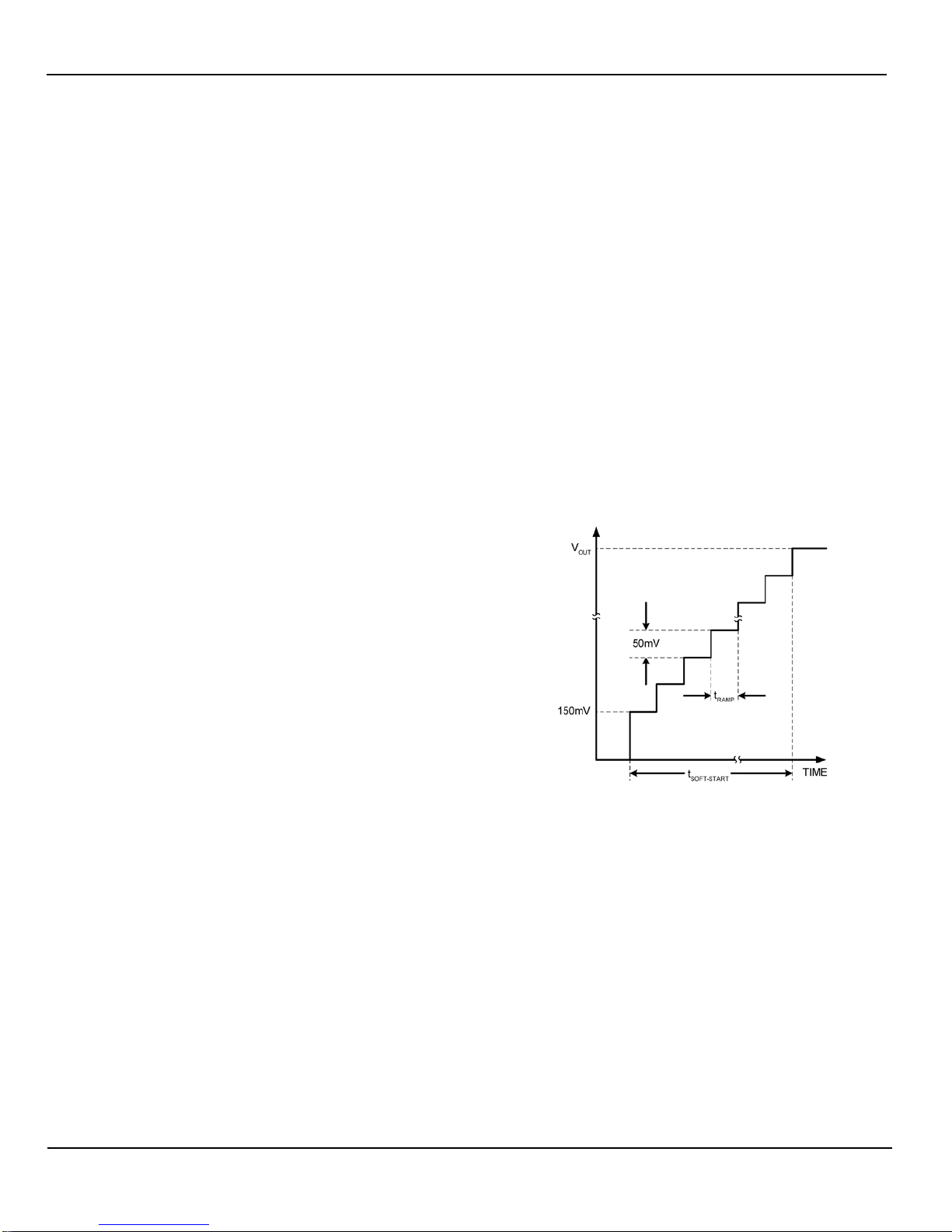
Programmable Buck Soft-Start Control
The MIC7401 soft-start feature forces the output voltage to
rise gradually, which limits the inrush current during start-
up. A slower output rise time will draw a lower input surge
current. The soft-start time is based on the least significant
bit (LSB) of an internal DAC and the speed of the ramp
rate, as shown in Figure 6. Figure 6 illustrates the soft-start
waveform for all five synchronous buck converters. The
initial step starts at 150mV and each subsequent step is
50mV.
Figure 6. Buck Soft-Start
The output ramp rate (tRAMP) is set by the soft-start
registers. Each output ramp rate can be individually set
from 4µs to 1024µs, see Table 1 for details.

Micrel, Inc.
MIC7401 Evaluation Board
July 21, 2015
5 Revision 1.0
Table 1. Buck Outputs Default Soft-Start Time (DEFAULT)
VOUT
(V) tRAMP
(µs) tSS
(µs)
VOUT1 1.8 8 264
VOUT2 1.1 8 152
VOUT3 1.8 8 264
VOUT4 1.05 8 144
VOUT5 1.25 8 176
The soft-start time tSS can be calculated by Equation 1:
RAMP
OUT
SS
t
mV50 V15.0V
t×
−
=
Eq. 1
Where:
tSS = Output rise time
VOUT = Output voltage
tRAMP = Output dwell time
For example:
s264t
s8
mV50 V15.0V8.1
t
SS
SS
µ=
µ×
−
=
Eq. 2
Where:
VOUT = 1.8V
tRAMP = 8.0µs
Figure 7 shows the output of Buck 1 ramping up cleanly,
starting from 0.15V to its final 1.1V value.
Figure 7. Buck Soft-Start
Buck Digital Voltage Control (DVC)
The output voltage has a 6-bit control DAC that can be
programmed from 0.8V to 3.3V in 50mV increments. If the
output is programmed to a higher voltage, then the output
ramps up, as shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8. Buck DVC Control Ramp

Micrel, Inc.
MIC7401 Evaluation Board
July 21, 2015
6 Revision 1.0
The ramp time is determined by Equation 2:
RAMP
INIT_OUTOUT t
mV50
VV
t×
−
=∆
Eq. 2
Where:
VOUT_INIT = Initial output voltage
VOUT = Final output voltage
tRAMP = Output dwell time
When the regulator is set in standby mode or programmed
to a lower voltage, then the output voltage ramps down at
a rate determined by the output ramp rate (tRAMP), the
output capacitance and the external load. Small loads
result in slow output voltage decay and heavy loads cause
the decay to be controlled by the DAC ramp rate.
In Figure 9, VOUT1 is switched to standby mode with an I²C
command and then switched back to normal mode either
by an I²C command or a low-to-high transition of the STBY
pin. In this case, the rise and fall times are the same due
to a 1A load on VOUT1.
Figure 9. Buck DVC Control Ramp
Programmable Boost Soft-Start Control
The boost soft-start time is divided into two parts as shown
in Figure 10. T1 is a fixed 367µs delay starting from when
the internal enable goes high. This delay gives enough
time for the disconnect switch to turn on and bring the
inductor voltage to VIN before the boost is turned on. There
is a 50µs delay which is controlled by the parasitic
capacitance (Cgd) of the disconnect switch before the
output starts to rise.
After the T1 period, the DAC output ramp starts, T2. The
total soft-start time, tSS, is the sum of both periods. Figure
11 displays the actual boost soft-start waveform.
Figure 10. Boost Soft-Start Ramp
Figure 11. Boost Soft-Start

Micrel, Inc.
MIC7401 Evaluation Board
July 21, 2015
7 Revision 1.0
( )
( )
s16
V2.0 V4.1V12
2T
t
V2.0 V4.1V
2T
2T1Tt
RAMP
OUT
SS
µ×
−
=
×
−
=
+=
Eq. 3
Where:
T1 = 367µs
T2 = 848µs
tSS = 367µs + 848µs = 1.215ms
VOUT = Output voltage
tRAMP = Output dwell time = 16µs
Boost Digital Voltage Control (DVC)
The boost output control works the same way as the buck,
except that the voltage steps are 200mV (see Figure 12).
When the boost is programmed to a lower voltage the
output ramps down at a rate determined by the output
ramp rate (tRAMP), the output capacitance and the external
load. During both the ramp up and down time, the power-
good output is blanked and will not imitate a fault flag.
Figure 12. Boost DVC Control Ramp
The ramp time can be computed using Equation 4:
RAMP
INIT_OUTOUT
t
V2.0VV
t×
−
=∆
Eq. 4
Where:
VOUT_INIT = Initial output voltage
Table 2. Boost Output Default Soft-Start Time
VOUT
(V) tRAMP
(µs) tSS
(ms)
VOUT6 12 16 1.215
Buck Current Limit
The MIC7401 buck regulators have high-side current
limiting that can be varied by a 4-bit code. If the regulator
remains in current limit for more than seven consecutive
PWM cycles, the output is latched off, the overcurrent
status register bit is set to 1, the power-good status
register bit is set to 0 and the global power-good (PG)
output pin is pulled low. An overcurrent fault on one output
will not disable the remaining outputs. Table 3 shows the
current-limit register settings vs. output current. The
current-limit register setting is set at twice the maximum
output current.
Table 3. Buck Current-Limit Register Settings
IOUT(MAX) IPROG BINARY HEX
0.5A 1.1A 1111 F’h
1.0A 2.1A 1101 D’h
1.5A 3.1A 1011 B'h
2.0A 4.1A 1001 9'h
2.5A 5.1A 0111 7'h
3.0A 6.1A 0101 5'h
The output can be turned back on by recycling the input
power or by software control. To clear the overcurrent fault
by software control, set the enable register bit to “0” then
clear the overcurrent fault by setting the fault register bit to
“0”. This will clear the over-current and power-good status
registers. Now the output can be re-enabled by setting the
enable register bit to “1”.

Micrel, Inc.
MIC7401 Evaluation Board
July 21, 2015
8 Revision 1.0
During start-up sequencing if Output 1 is still shorted,
Outputs 2 through 4 will come up normally. Once an
overcurrent condition is sensed, then the fault register is
set to “1” and the start-up sequence will stop and no
further outputs will be enabled.
The programmable current-limit setting sets the peak
switch current threshold, not the average outputs current.
The peak current is higher than the average due to the
inductor ripple current. Figure 13 illustrates how the
current limit threshold varies with input voltage.
Figure 13. Current-Limit Threshold vs. Input Voltage
Boost Current Limit
The boost current limit features cycle-by-cycle protection.
The duty cycle is cut immediately once the current limit is
hit. When the boost current limit is hit for five consecutive
cycles, the FAULT signal is asserted and remains asserted
with the boost converter keeping on running until the boost
is powered off.
This protects the boost in normal overload conditions, but
not in a short-to-ground case. For a short circuit to ground,
the boost current limit will not be able to limit the inductor
current. This short-circuit condition is sensed by the
current in the disconnect switch. When the disconnect
switch current limit is hit for four consecutive master clock
cycles (2MHz), regardless if the boost is switching or not,
both the disconnect switch and boost are latched off
automatically and the FAULT signal is asserted.
The output can be turned back on by recycling the input
power or by software control. To clear the overcurrent fault
by software control, set the enable register bit to “0” then
clear the overcurrent fault by setting the fault register bit to
“0”.
Global Power-Good Pin
The global power-good output indicates that all the outputs
are above the 91% limit after the power-up sequence is
completed. Once the power-up sequence is complete, the
global power good output stays high unless an output falls
below its power-good limit, a thermal fault occurs, the input
voltage drops below the lower UVLO threshold or an
output is turned OFF by setting the enable register bit to
“0” unless the PGOOD_MASK[x] bit is set to “1” (Default).
A power-good mask bit can be used to control the global
power-good output. The power-good mask feature is
programmed through the PGOOD_MASK[x] registers and
is used to ignore an individual power-good fault. When
masked, PGOOD_MASK[x] bit is set to “1”, an individual
power good fault will not cause the global power good
output to de-assert.
If all the PGOOD_MASK[x] bits are set to “1”, then the
power good output de-asserts as soon as the first output
starts to rise. The PGOOD_MASK[x] bit of the last output
must be set to “0” to have the PG output stay low until the
last output reaches 91% of its final value.
The global power-good output is an open-drain output. A
pull-up resistor can be connected to VIN or VOUT. Do not
connect the pull-up resistor to a voltage higher than AVIN.
Standard Delay
There is a programmable timer that is used to set the
standard delay time between each time slot. The timer
starts as soon as the previous time slot’s output power
good goes high. When the delay completes, the regulators
assigned to that time slot are enabled, see Figure 14.
Figure 14. Standard Delay Time

Micrel, Inc.
MIC7401 Evaluation Board
July 21, 2015
9 Revision 1.0
Power-Up Sequencing
When power is first applied to the MIC7401, all I²C
registers are loaded with their default values from the
EEPROM. There is about a 1.5ms delay before the first
regulator is enabled while the MIC7401 goes through the
initialization process. The DELAY register’s STDEL bits set
the delay between powering up each regulator at initial
power up.
The sequencing registers allow the outputs to come up in
any order. There are six time slots that an output can be
configured to power up in. Each time slot can be
programmed for up to six regulators to be turned on at
once or none at all.
Figure 15 shows an example of this feature. VOUT4 is
enabled in time slot 1. After a 1ms delay, VOUT2 and VOUT3
are enable at the same time in time slot 2. The 1ms is the
standard delay for all of the outputs and can be
programmed from 0ms to 7ms in 1ms. Next, VOUT1 is
powered up in time slot 3 and VOUT5 in time slot 4. There
are no regulators programmed for time slot 5. Finally,
VOUT6 is powered up in time slot 6. The global power-good
output, VPG, goes high as soon as the last output reaches
91% of its final value.
Figure 15. Hot Plug – VIN Rising
Global Enable Pin
When the enable pin rises above the enable threshold
voltage, the MIC7401 enters its start-up sequence.
Programmable Power-on-Reset (POR) Delay
The POR output pin provides the user with a way to let the
SOC know that the input power is failing. If the input
voltage falls below the power-on reset lower threshold
level, the POR output immediately goes low. The lower
threshold is set in the PORDN register and the upper
threshold uses PORUP register.
The low-to-high POR transition can be delayed from 5ms
to 160ms in 5ms increments. This feature can be used to
signal the SOC that the power supplies are stable. The
PORDEL register sets the delay of the POR pin. The POR
delay starts as soon as the AVIN pin voltage rises above
the power-on-reset upper threshold limit. Figure 16 shows
the POR operation.
Figure 16. Power-on-Reset (POR)

Micrel, Inc.
MIC7401 Evaluation Board
July 21, 2015
10 Revision 1.0
Timing Diagrams
Normal Power-Up Sequence for Outputs
The STDEL register sets the delay between powering up
of each regulator at initial power-up (see power-up
sequencing in Figure 17). Once all the internal power-good
registers PGOOD[1-6] are all 1, then the global PG pin
goes high without delay if the PGOOD_MASK[6] bit is set
to “0”.
The PORDEL register sets the delay for the POR flag pin.
The POR delay time starts as soon as AVIN pin voltage
rises above the system UVLO upper threshold set by the
PORUP register. The POR output goes low without delay if
AVIN falls below the lower UVLO threshold set by the
PORDN register.
Figure 17. MIC7401 Power-Up/Down

Micrel, Inc.
MIC7401 Evaluation Board
July 21, 2015
11 Revision 1.0
Standby (STBY) Pin (Wake-Up)
An I²C write command to the STBY_CTRL_REG register
or the STBY pin can be used to set the MIC7401 into
stand-by mode. The standby (STBY) pin provides a
hardware-specific manner in which to wake-up from stand-
by mode and go into normal mode. Figure 18 shows the
STBY pin operation. A low-to-high transition on the STBY
pin switches the output from stand-by mode to normal
mode.
There is a 100µs STBY deglitch time that eliminates
nuisance tripping, allowing all regulators to enable at the
same time and ramp up with their programmed ramp rates.
Figure 18. MIC7401 STBY Function (DEFAULT)

Micrel, Inc.
MIC7401 Evaluation Board
July 21, 2015
12 Revision 1.0
Evaluation Board Schematic
SW4
OUT4
MIC7401
C1
2.2µF
PVIN1
L4
1.0µH
PGND4
C14
22µF
PVIN4
C13
10µF
SW3
OUT3
L3
2.2µH
PGND3
C12
22µF
PVIN3
C11
10µF
SW2
OUT2
L2
2.2µH
PGND2
C10
22µF
PVIN2 26
C9
10µF L1
2.2µH
SW1
OUT1
PGND1
C3
22µF
C2
10µF
PVIN6 L6
2.2µH
PVIN6O
SW6
PGND6
C6
10µF
PVIN5 L5
2.2µH
SW5
OUT5
PGND5
C8
22µF
C7
10µF
31
30
AVIN
EN
15
14
13
POR
SCL
AGND
SDA
35
34
33
32
PG
NC
NC
AGND
12 STBY
16
R1
100kΩ
OUT6
C5
22µF
R6
499kΩ
D1
PMEG4002
27
29
28
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
17
18
2
1
3
36
4
5
7
6
8
9
11
10
R5
2kΩ
R3
2kΩ
R2
100kΩ
CLK
SDA
NC
4
3
2
VIN
VIN
VIN
VIN
VIN
VIN
VIN
VOUT1
1.8V/0.8A
VOUT6
12V/0.2A
VOUT5
1.25V/1.0A
VOUT4
1.05V/3.0A
VOUT3
1.8V/0.5A
VOUT2
1.1V/0.5A
R7
0Ω
C4
10µF
PGND
PGND
PGND
GND 1
PGND
VIN
PGND
PGND
PGND
R4
499kΩ
VIN
EN
VIN
STAND-BY
STAND-BY
POR
PG
EN
VIN
PG
EN
VIN VOUT3
VOUT3 C15
150µF +

Micrel, Inc.
MIC7401 Evaluation Board
July 21, 2015
13 Revision 1.0
Bill of Materials
Item Part Number Manufacturer Description Qty.
C1 CL05A225KO5NQNC Samsung
(1)
2.2µF/16V, Ceramic, X5R, 0402, 0.8mm, ±10% 1
C2, C7, C9, C11,
C13 CL10A106MO8NQNC Samsung 10µF/16V, Ceramic, X5R, 0603, 0.8mm, ±20% 5
C4, C6 CL21A106KAYNNNE Samsung 10µF/25V, Ceramic, X5R, 0805, 1.25mm, ±20% 2
C3, C5, C8, C10,
C12, C14 CL10A226MQ8NUNE Samsung 22µF/6.3V, Ceramic, X5R, 0603, 0.8mm, ±20% 6
C15 EEF-CX0J151XR Panasonic(2)150µF/6.3V, POS Capacitor, SP, ±20% 1
D1 PMEG4002EL NXP
(3)
0.2A/40V, Schottky, SOD-882 1
R1, R2 RC1005F104CS Samsung 100kΩ, Resistor, 0402, 1% 3
R3, R5 RC1005F202CS Samsung 2.0kΩ, Resistor, 0402, 1% 2
R4, R6 RC1005F4993CS Samsung 499kΩ, Resistor, 0402, 1% 1
R7 RC1005J000CS Samsung 0.00Ω, Resistor, 0402, Jumper 1
L1, L2, L3, L5, L6 CIG22H2R2MNE Samsung 2.2µH, 1.6A Inductor, 116mΩ,
2520 × 1.2mm (maximum) 5
L4 CIGW252010GM1R0MNE Samsung 1.0µH, 3.3A Inductor, 40mΩ,
2520 × 1.0mm (maximum) 1
U1 MIC7401YFL Micrel(4)Five-Channel Buck Regulator Plus One Boost
with HyperLight Load and I2C Control 1
Notes:
1. Samsung: www.samsung.com.
2. Panasonic: www.panasonic.com.
3. NXP: www.nxp.com.
4. Micrel, Inc.: www.micrel.com.

Micrel, Inc.
MIC7401 Evaluation Board
July 21, 2015
14 Revision 1.0
PCB Layout Recommendations
Evaluation Board Top Layer
−
Power Component Placement
Evaluation Board Top Layer
−
Layer 1 (Power Routing Layer)

Micrel, Inc.
MIC7401 Evaluation Board
July 21, 2015
15 Revision 1.0
PCB Layout Recommendations (Continued)
Evaluation Board Top Layer
−
Layer 1 (Power Routing Layer)
Evaluation Board Layer 2 (Ground Plane)

Micrel, Inc.
MIC7401 Evaluation Board
July 21, 2015
16 Revision 1.0
PCB Layout Recommendations (Continued)
Evaluation Board Top Layer
−
Layer 3 (Signal Routing Layer)
Evaluation Board Layer 4 (Ground Plane)

Micrel, Inc.
MIC7401 Evaluation Board
July 21, 2015
17 Revision 1.0
PCB Layout Recommendations (Continued)
Evaluation Board Layer
−
Layer 5 (VIN Plane)
Evaluation Board Bottom Later
−
Layer 6 (Ground Plane)

Micrel, Inc.
MIC7401 Evaluation Board
July 21, 2015
18 Revision 1.0
MICREL, INC. 2180 FORTUNE DRIVE SAN JOSE, CA 95131 USA
TEL +1 (408) 944-0800 FAX +1 (408) 474-1000 WEB http://www.micrel.com
Micrel, Inc. is a leading global manufacturer of IC solutions for the worldwide high
-
performance linear and power, LAN, and timing & communications
markets. The Company’s
products include advanced mixed-signal, analog & power semiconductors; high-
performance communication, clock
management,
MEMs-based clock oscillators & crystal-less clock generators, Ethernet switches, and physical layer transceiver ICs.
Company
customer
s include leading manufacturers of enterprise, consumer, industrial, mobile, telecommunications, automotive, and computer products.
Corporation headquarters and state
-of-the-art wafer fabrication facilities are located in San Jose, CA, with regional sale
s and support offices and
advanced technology design centers situated throughout the Americas, Europe, and Asia.
Additionally, the Company maintains an extensive network
of distributors and reps worldwide.
Micrel makes no representations or warranties
with respect to the accuracy or completeness of the information furnished in this data
sheet. This
information is not intended as a warranty and Micrel does not assume responsibility for its use.
Micrel reserves the right to change circuitry,
specification
s and descriptions at any time without notice.
No license, whether express, implied, arising by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual
property rights
is granted by this document. Except as provided in Micrel’s terms and conditions of sale for such pr
oducts, Micrel assumes no liability
whatsoever, and Micrel disclaims any express or implied warranty relating to the sale and/or use of Micrel products including
liability or warranties
relating to fitness for a particular purpose, merchantability, or infr
ingement of any patent, copyright, or other intellectual property right.
Micrel Products are not designed or authorized for use as components in life support appliances, devices or systems where malfunction of a product
can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems that (a) are intended for surgical
implant into the body or (b) support or sustain life, and whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to result in a
significant injury
to the user. A
Purchaser’s use or sale of Micrel Products for use in life support appliances, devices or systems is a Purchaser’s own risk and Purchaser agrees to fully
indemnify Micrel for any damages resulting from such use or sale.
© 2015 Micrel, Incorporated.

Mouser Electronics
Authorized Distributor
Click to View Pricing, Inventory, Delivery & Lifecycle Information:
Microchip:
ADM00812
Table of contents
Other Micrel Motherboard manuals

Micrel
Micrel KSZ8841-PMQL User manual

Micrel
Micrel KS8995MA User manual
Micrel
Micrel KSZ8795 Series User manual

Micrel
Micrel MIC23099 User manual

Micrel
Micrel KSZ9031MNX User manual

Micrel
Micrel MIC4724YMME User manual

Micrel
Micrel MIC24055 User manual

Micrel
Micrel KSZ8873MLL User manual

Micrel
Micrel KS8721BL/SL User manual

Micrel
Micrel KSZ8895 User manual

Micrel
Micrel MIC23031-4YMT EV User manual

Micrel
Micrel KSZ8081MNX User manual

Micrel
Micrel KSZ8851SNL User manual
Micrel
Micrel ULDO MIC5301/18 User manual

Micrel
Micrel KSZ8895ML User manual

Micrel
Micrel MIC2169A User manual

Micrel
Micrel MIC45208 User manual

Micrel
Micrel MIC2786 User manual

Micrel
Micrel SY88212L User manual

Micrel
Micrel MIC2039 User manual