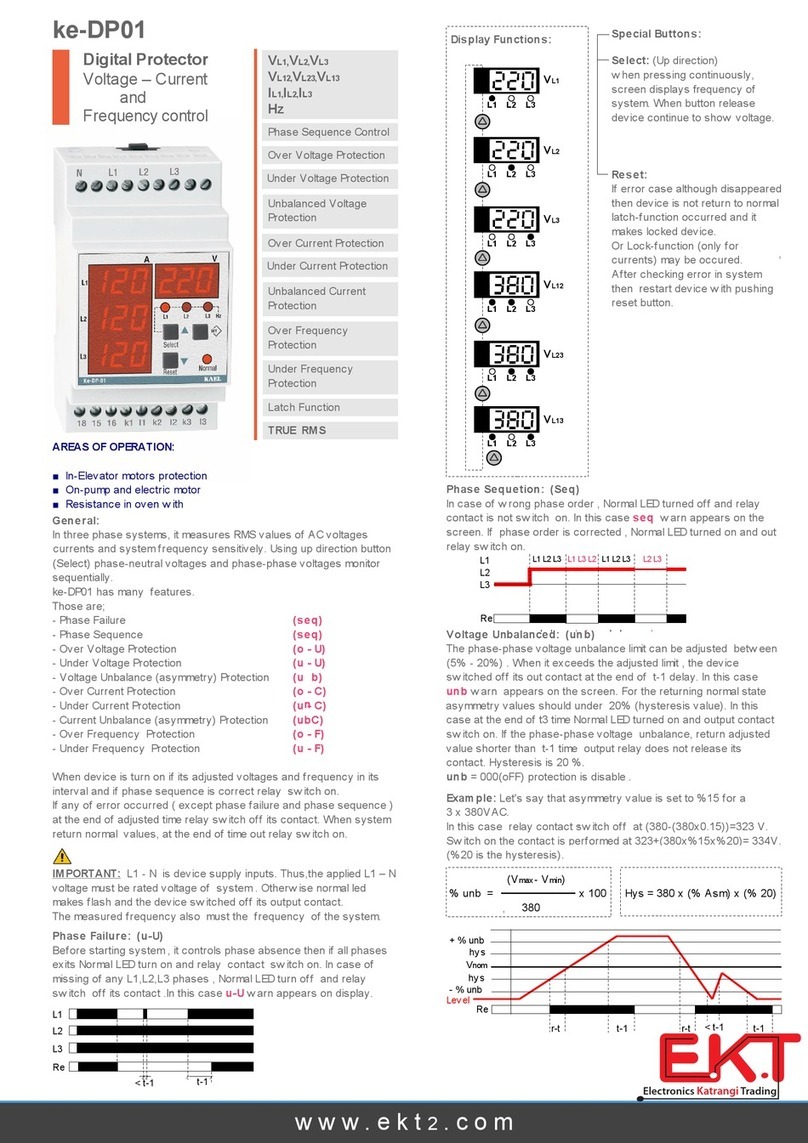
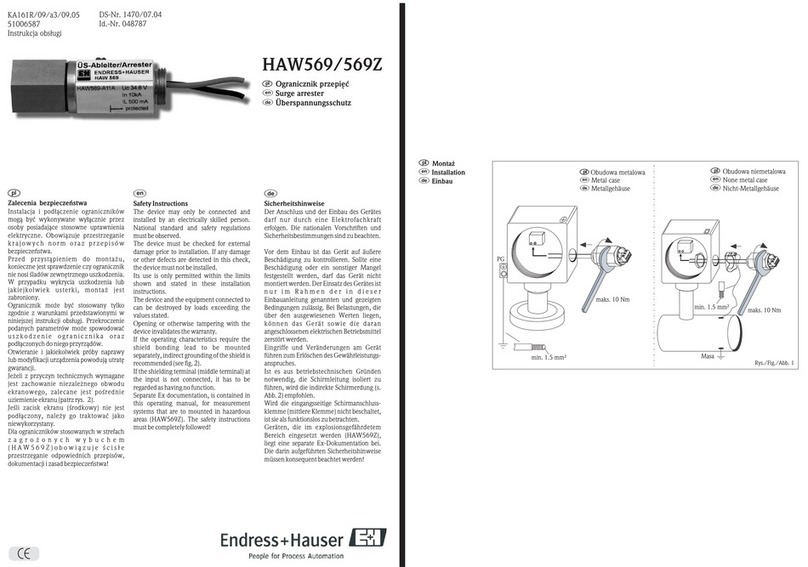
3. ELECTRICAL INFORMATION AND INTRINSICALLY
SAFE CIRCUIT SAFETY PARAMETERS
a. A wide choice of coils is available for a variety of rated current
requirements. The torque motor coil leads are attached to the connector
so external connections can provide series, parallel or single coil
operation. The valves are equipped either with an MS type connector or
with pigtail leads for electrical wiring. Refer to installation drawings of the
specific model for details. Servovalve coils should be driven with current
to provide consistency throughout the temperature range.
b. The (G)761K valves are approved for intrinsically safe protection per EN IEC
60079-0 : 2018, EN 60079-7 : 2015, and EN 60079-11 : 2012 for ATEX, and
IEC 60079-0 : 2017, IEC 60079-7 : 2017, and IEC 60079-11 : 2011 for IECEx.
The approved safety parameters are listed in the following table for all the
coils used by (G)761K series. Coil number is marked on the valve nameplate.
Coil Configuration Marking Ui(MAX) Ii(MAX)
G4220-031 (single, series, parallel) Ex ia IIB T4 12 V 120 mA
G4220-051/098 (single, series, parallel) Ex ia IIB T4 12 V 240 mA
G4221-001 G4220-042 (single) Ex ia IIC T4 16 V 160 mA
G4221-001 G4220-042 (single) Ex ia IIC T4 24.4 V 85 mA
G4220-031 (single, parallel) Ex ia IIC T4 30 V 26 mA
G4220-031 (series) Ex ia IIC T4 30 V 18 mA
G4220-051/098 (single, parallel) Ex ia IIC T4 30 V 19 mA
G4220-051/098 (series) Ex ia IIC T4 30 V 12.7 mA
G4220-042 (single) Ex ia IIC T4 30 V 37 mA
G4220-042 (parallel) Ex ia IIC T4 30 V 20 mA
G4220-042 (series) Ex ia IIC T4 30 V 10 mA
G4221-001 (single) Ex ia IIC T4 30 V 28 mA
c. The (G)761K valves are approved for non-incendive operation for supply
current not to exceed 50 mA dc.
d. When making electric connections to the valve, appropriate measures
must be taken to ensure that locally different earth potential do not
result in excessive ground currents. When barriers are required
for the hazardous location, hazardous area (field) wiring must meet
the requirements of the barrier manufacturer. All barriers must be
mounted and installed in compliance with the barrier manufacturer’s
requirements. Twisted pairs of 18-20 gage wire are recommended. If
shielded wire is used, connect shield wire to earth ground only at the
barrier strip.
4. SPECIAL CONDITIONS FOR SAFE USE
Because the enclosure of the apparatus is made of aluminum, if it is
mounted in an area where the use of category 1 G apparatus is required,
it must be installed such that even in the event of rare incidents, ignition
sources due to impact and friction sparks are excluded.
When the electrohydraulic servovalve is used in an application for type
of explosion protection intrinsic safety “i”, the appropriate box on the data
label must be scored. When the electrohydraulic servovalve is used in an
application for type of explosion protection “n”, the appropriate box on the
data label must be scored.
After use in an application for type of explosion protection “n”, the
servovalve cannot abe safely used in a intrinsically safe application.
The screwed cable connector may only be disconnected when the
circuit is de-energized or when the location is known to be non-hazardous.
When used at an ambient temperature ≥70°C, heat resistant cable
must be used with a continuous operating temperature in accordance with
the application. When the electrohydraulic servovalve is used in type of
protection “n” or “ec”, the equipment shall only be used in an area of not
more than Pollution Degree 2, as defined in IEC 60664-1.
The cable gland shall be installed such that impact is not possible.
When the electrohydraulic servovalve is used in type of protection “n”
or “ec”, the user shall provide additional clamping of the cable to ensure that
pulling is not transmitted to the terminations.
5. HYDRAULIC SYSTEM PREPARATION
To prolong servovalve operational life and to reduce hydraulic system
maintenance, it is recommended that the hydraulic fluid be kept at a cleanliness
level of ISO DIS 4406 Code 16/13 maximum, 14/11 recommended. The most
effective filtration scheme incorporates the use of a kidney loop or “off-line”
filtration as one of the major filtration components. The filter for the “off-line”
filtration scheme should be a B3≥75 filter for maximum effectiveness.
Upon system startup and prior to mounting the servovalve, the entire
hydraulic system should be purged of built-in contaminating particles by an
adequate flushing. The servovalve should be replaced by a flushing manifold and
the hydraulic circuit powered up under conditions of fluid temperature and fluid
velocity, reasonably simulating normal operating conditions. New system filters
are installed during the flushing process whenever the pressure drop across the
filter element becomes excessive. The flushing processes should turn over the
fluid in the reservoir between fifty to one hundred times.
To maintain a clean hydraulic system, the filters must be replaced on
a periodic basis. It is best to monitor the pressure drop across the filter
assembly and replace the filter element when the pressure drop becomes
excessive. In addition to other filters that are installed in the hydraulic circuit,
it is recommended that a large capacity, low pressure ß3≥75 filter be installed
in the return line. This filter will increase the interval between filter element
replacement and greatly reduce the system contamination level.
6. INSTALLATION
The Moog (G)761K series industrial servovalve may be mounted in any
position, provided the servovalve pressure, control and tank ports match
respective manifold ports.
The mounting pattern and port location of the servovalve is shown on
Figure 4. The servo-valve should be mounted with 5/16-18 x 1.75 inch long,
socket head cap screws. Apply a light film of oil to the screw threads and torque
to 96 inch pounds. Wire mating connector for desired coil configuration and
polarity. Thread connector to valve.
7. MECHANICAL NULL ADJUSTMENT
It is often desirable to adjust the flow null of a servovalve independent
of other system parameters. The “mechanical null adjustment” on the Moog
(G)761K Series servovalve allows at least ±20% adjustment of flow null.
The “mechanical null adjustor” is an eccentric bushing retainer pin located
above the “tank” port designation on the valve body (see Figure 2) which, when
rotated, provides control of the bushing position. Mechanical feedback elements
position the spool relative to the valve body for a given input signal. Therefore, a
movement of the bushing relative to the body changes the flow null.
Adjustment Procedure
Using a 3/8inch offset box wrench, loosen the self-locking fitting until the
null adjustor pin can be rotated. (This should usually be less than 1/2 turn).
DO NOT remove self-locking fitting. Insert a 3/32 inch Allen wrench in null
adjustor pin. Use the 3/32 Allen wrench to rotate the mechanical null adjustor
pin to obtain desired flow null. Torque self-locking fitting to 57 inch lbs.
Note: Clockwise rotation of null adjustor pin produces flow from port P to port B.
Figure 2
Mechanical Null Adjustment