www.nationalrailwaysupply.com
1-800-357-3572 2 38059D
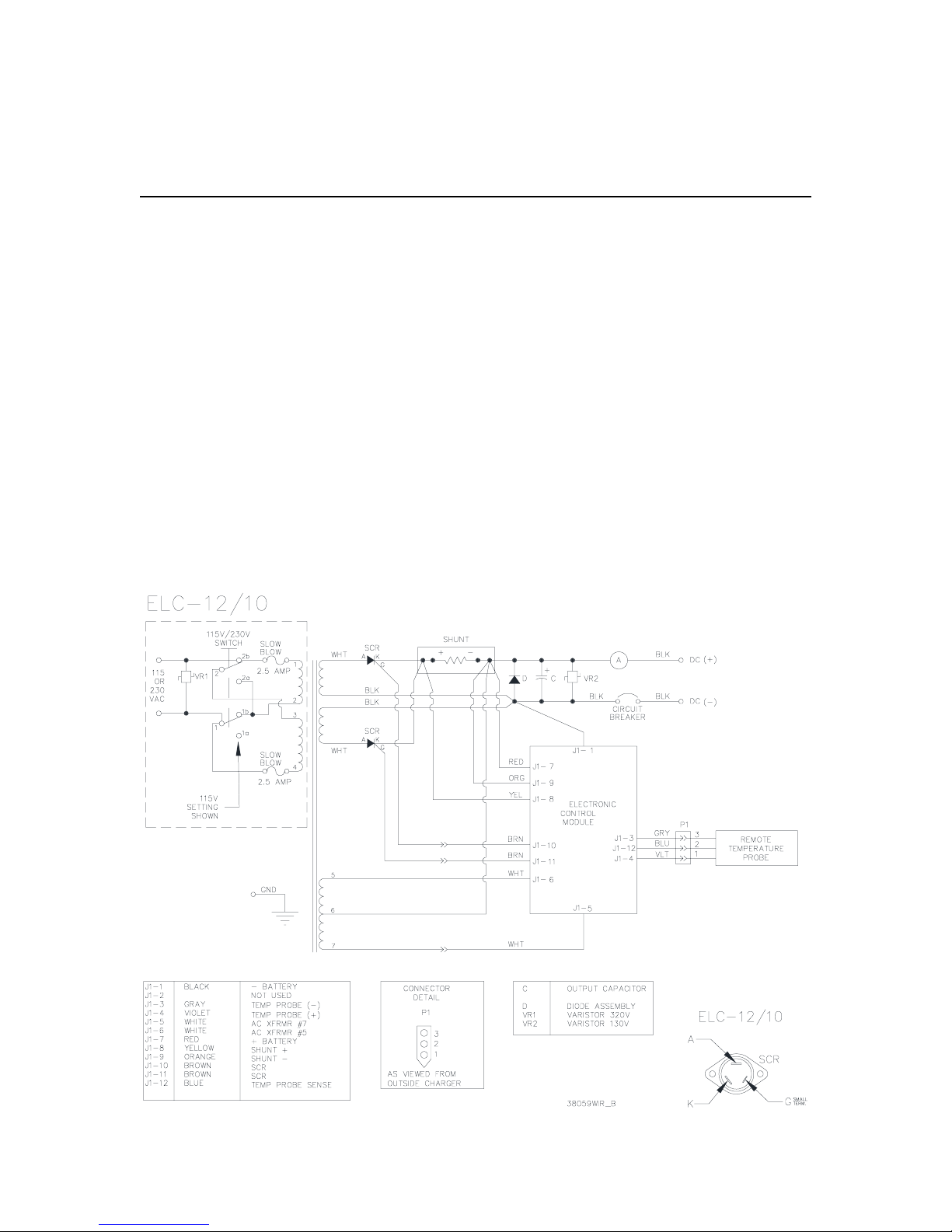
3. THEORY OF OPERATION
When the charger is connected to the desired AC
voltage source (115 or 230), the transformer creates
auxiliary voltages for the electronic control module.
The electronic control module controls and monitors
the charger so it will perform properly. The
transformer also supplies the power output used for
charging the batteries and provides electrical
isolation between the charger's output and the AC
source.
The charger's output current flows through a shunt
and is sensed by the electronic control module along
with the charger's output voltage. These values are
converted into drive pulses for the SCRs by the
control module. This pulsating charge current (a
pulse occurs each time an SCR is on) is then filtered
by a large capacitor and the batteries to provide a
smooth output.
The charger has an "IE" profile which is: (a) High
rate constant current, and (b) Constant voltage.
When the charger is first started, the SCRs will
conduct for a certain portion of the sinusoidal anode
voltage to provide the required charging current at
the low level of battery voltage. In this start region, a
constant current is applied to the battery. The SCR
conduction will then increase as the battery voltage
increases in order to provide a higher output voltage
while maintaining a constant charging current.
When the battery voltage reaches the float voltage,
the SCRs will start to decrease their output. This
causes the charger to automatically change from a
constant current charge region to a constant voltage
charge region. As the batteries become fully
charged, the output current decreases. A
continuous constant float voltage will be supplied to
the batteries to maintain their charge.
Another feature of the charger is temperature
compensation, which keeps the batteries from
getting under- or over-charged. TEMPERATURE
COMPENSATION ONLY OCCURS WHEN USING
A TEMPERATURE PROBE. The red LED on the
front of the charger will be off when using a
functional temperature probe. If the LED is on,
either a temperature probe is not being used, or the
temperature probe is working improperly.
Temperature compensation uses a temperature
reference of 77°F (25°C), a voltage reference of 2.23
volts (the voltage of a standard gel-cell battery at
77°F), and a compensation value of 3.0 mV per °F).
The equivalent equation for the compensated
voltage is:
Vcomp = V – k (t - 77°F)
Where V is the voltage of the battery at 77°F, t is
the temperature in °F, and k = V (.003 / 2.23).
The control module has a temperature
compensation range between 32°F and 95°F ( 0°C
and 35°C) that does not allow charger voltage to
increase or decrease beyond the calculated values.
Example 1:
If a 13.62 volt battery is charging and the
temperature increases to 95°F, then the output
voltage decreases to 13.29 volts.
13.62 - .0183 (95°F - 77°F) = 13.29
Example 2:
If a 14.50 volt battery is charging and the
temperature increases to 95°F, then the output
voltage decreases to 14.15 volts.
14.50 - .0195 (95°F - 77°F) = 14.15
Example 3:
If 15.61 volt batteries are charging and the
temperature decreases to 32°F, the output voltage
increases to 16.56 volts.
15.61 - .021 (32°F - 77°F) = 16.56
4. RECEIVING AND INSTALLING THE
CHARGER
Proper installation of the charger is important in
order to achieve good charger performance and to
prevent damage to the charger and batteries. When
a charger is received, a check for possible in-transit
damage should be made. If any damage is found, it
should be reported as a claim to the carrier. To
permit free air flow for convention cooling, allow
three inches (3") minimum between the charger
sides and other equipment and four inches (4")
minimum on top of the charger.
WARNING: NEVER PLACE ANYTHING ON
TOP OF THE CHARGER WHILE OPERATING.
DAMAGE TO THE CHARGER OR BATTERIES
COULD OCCUR.
WARNING: THE CHARGER MUST BE SET
UP FOR THE PROPER USER SPECIFICATIONS
BEFORE STARTING THE INITIAL CHARGE.
5. AC ELECTRICAL SUPPLY
The charger must be connected to a single-phase,
50/60/100 Hertz AC power source, which can be
either 115 or 230 VAC depending on the charger
input voltage selection switch setting. Use an
appropriate size wire for the conditions and for the
AC amperage shown on the ratings information on
the charger. The AC power and AC ground wires
should be stripped 0.375 inches (9.5mm). Insert the
AC power and AC ground wires into the proper