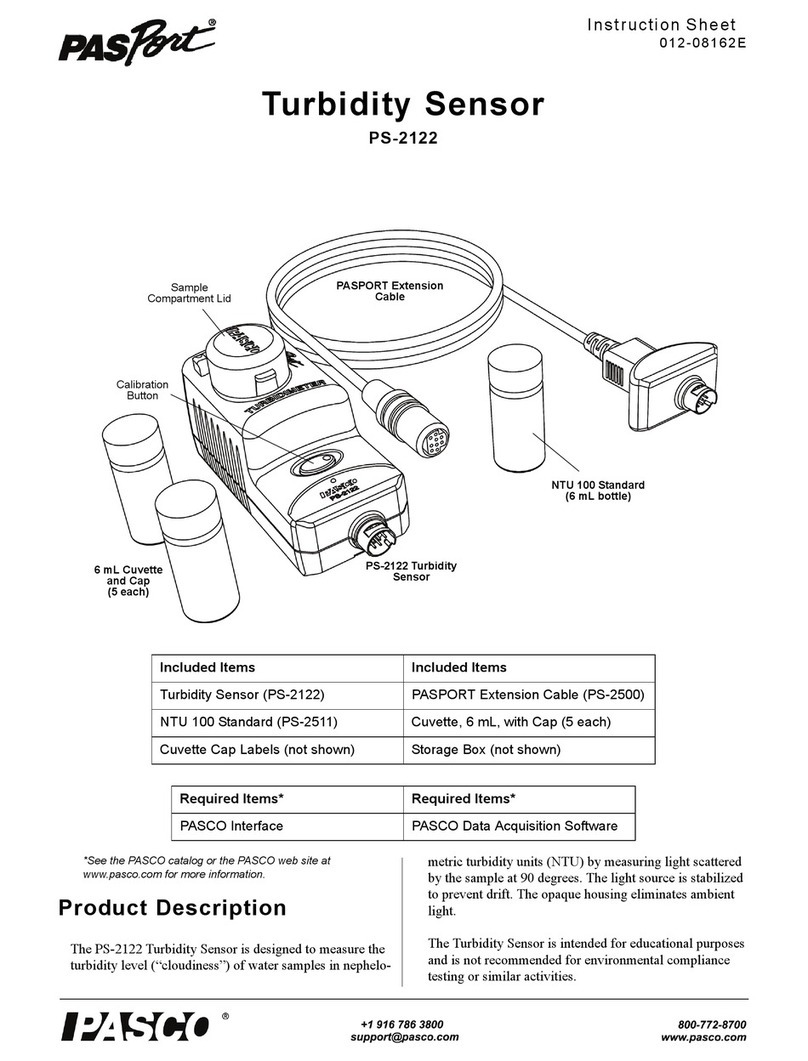
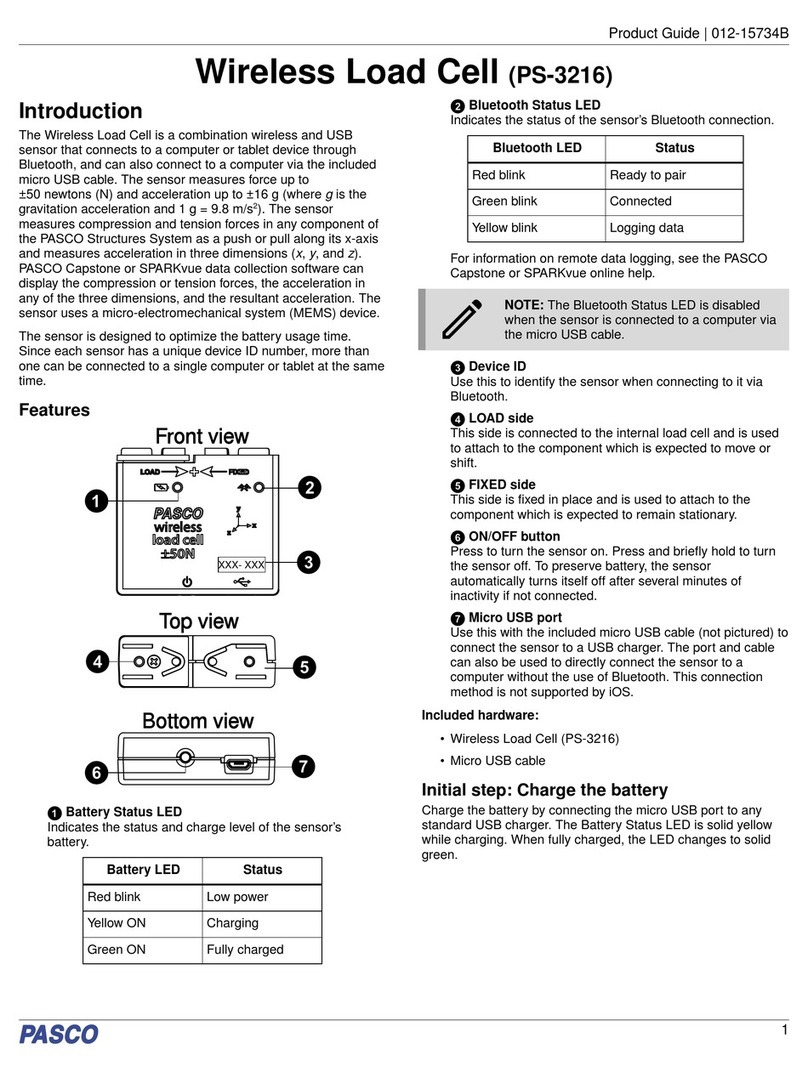
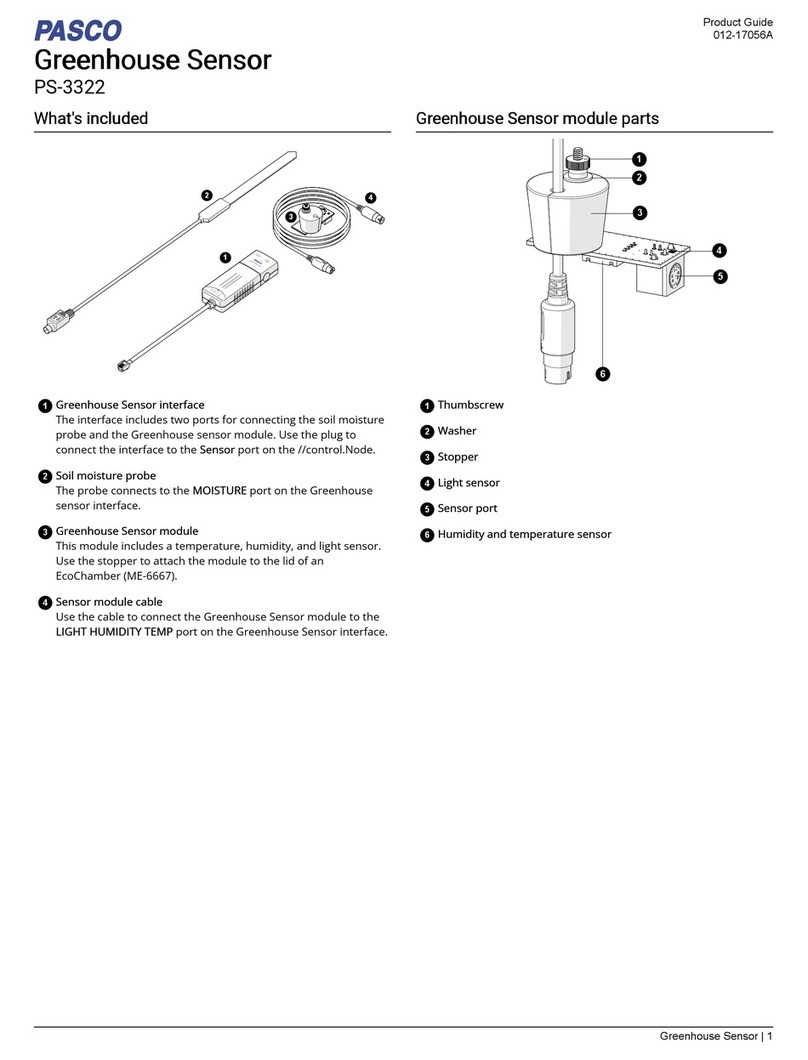
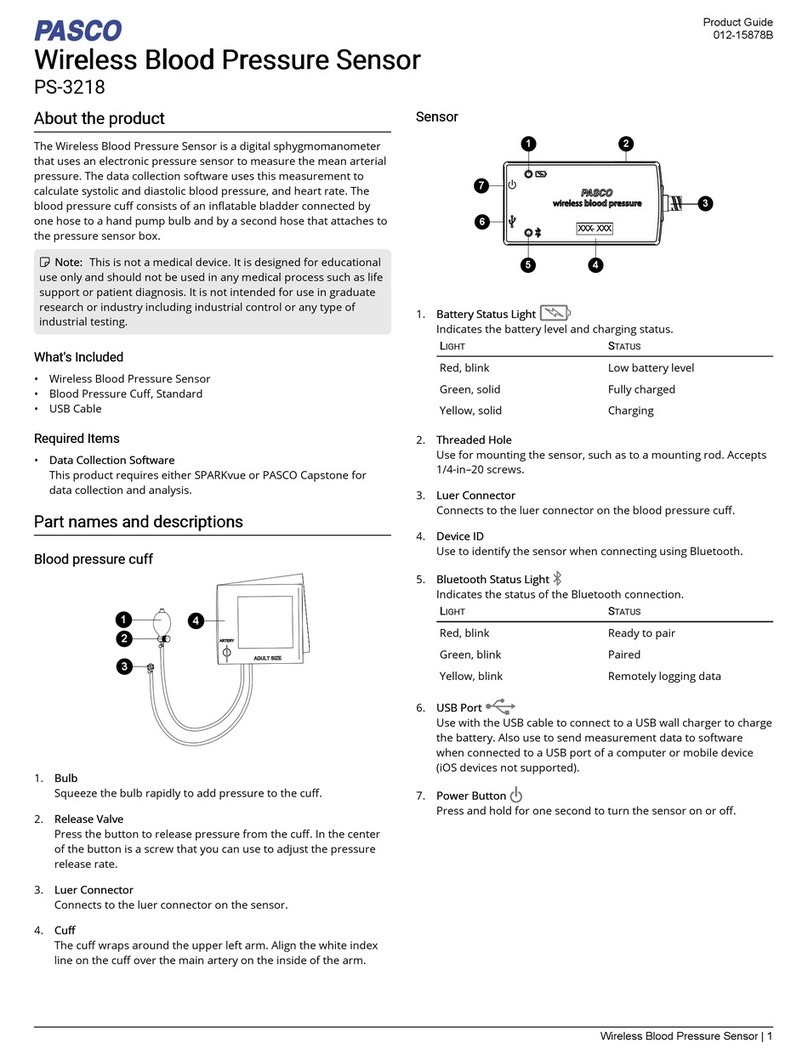
PASCO Capstone:
1. Select Calibration from the Tools palette.
2. Select Concentration from the list of measurements, then
click Next.
3. Ensure that Two Standards (2 point) is selected from the
list of calibration types, then click Next.
4. Remove approximately 10 mL of your low standard solution
from its volumetric flask and set it aside until Step 6. Add
1 mL of ISA to the flask and invert repeatedly to mix.
5. Use lab pH paper to check the pH of the standard. The
value must be between 4.0 and 4.5; if it is not, add ISA in
1 mL increments and continue mixing until the value is
within this range.
6. Fill your flask to the 100 mL mark with the low standard
solution that you removed in Step 4. (If you do not have
enough solution to reach the 100 mL mark, simply add all
of the removed solution.) Invert repeatedly to mix, then
pour the entire solution into a 150 mL beaker.
7. Rinse the electrode with DI water, blot dry, and place it into
the beaker. Wait for a stable reading in the Current Value
box. (This may take several minutes.)
8. Enter the known value of the concentration, in mg/L, into
the Standard Value box and click Set Current Value to
Standard Value.
TIP: For solutions dissolved in DI water, 1 ppm
and 1 mg/L are approximately equivalent.
9. Remove the electrode from the low standard solution
beaker. Rinse the electrode with DI water and blot dry.
10. Remove approximately 10 mL of your high concentration
standard from its volumetric flask and set aside until the
next step. Add 1 mL of ISA to the flask and invert to mix.
11. Repeat Step 5 for the high standard solution, then fill the
flask to the 100 mL mark with the high standard solution
removed in the previous step. Invert to mix, then pour the
solution into a new 150 mL beaker.
12. Place the electrode into the high standard solution beaker
and wait for a stable reading in the Current Values boxes.
13. Enter the known concentration of the high standard
solution, in mg/L into the Standard Value box and click Set
Current Value to Standard Value.
14. Review your new calibration and click Finish.
Calibrating with millivolt reading
Follow this procedure only if you are using the PASPORT High
Precision pH/Temperature with ISE/ORP Amplifier.
1. Connect the sensor to a compatible PASPORT interface,
such as the 550 Universal Interface (UI-5001), and connect
the interface to SPARKvue or PASCO Capstone.
2. Create a Digits display measuring the potential reading, in
mV, from the sensor.
3. Remove approximately 10 mL of your low standard solution
from its volumetric flask and set it aside until Step 6. Add
1 mL of ISA to the flask and invert repeatedly to mix.
4. Use lab pH paper to check the pH of the standard. The
value must be between 4.0 and 4.5; if it is not, add ISA in
1 mL increments and continue mixing until the value is
within this range.
5. Fill your flask to the 100 mL mark with the low standard
solution that you removed in Step 3. (If you do not have
enough solution to reach the 100 mL mark, simply add all
of the removed solution.) Invert repeatedly to mix, then
pour the entire solution into a 150 mL beaker.
6. Rinse the electrode with DI water, blot dry, and place it into
the beaker. Start data collection and wait for a stable
reading. (This may take several minutes.)
7. Once the reading stabilizes, record the potential reading in
mV and the known concentration of the low standard
solution.
8. Remove the electrode from the beaker. Rinse the electrode
with DI water and blot dry.
9. Remove approximately 10 mL of your high concentration
standard from its volumetric flask and set aside until the
next step. Add 1 mL of ISA to the flask and invert to mix.
10. Repeat Step 4 for the high standard solution, then fill the
flask to the 100 mL mark with the high standard solution
removed in the previous step. Invert to mix, then pour the
solution into a new 150 mL beaker.
11. Once the reading stabilizes, record the potential reading
and the known concentration of the high standard solution.
12. Remove the electrode from the beaker, rinse with DI water,
and blot dry.
13. Using semilogarithmic graph paper, prepare a calibration
curve by plotting the recorded millivolt values on the linear
axis and the known concentration values of the standard
solutions.
Measuring with direct concentration reading
After completing Calibrating with direct concentration
reading, measure the sample concentration with these steps:
1. Remove 10 mL of your sample solution from the 100 mL
volumetric flask and set it aside for Step 3. Add 1 mL of ISA
and invert to mix.
2. Use lab pH paper to check the pH of the sample. The value
must be between 4.0 and 4.5; if it is not, add ISA in 1 mL
increments and continue mixing until the value is within this
range.
3. Fill the flask to the 100 mL line with the remaining solution
removed in Step 1. Invert repeatedly to mix, then pour the
solution into a 150 mL beaker for testing.
4. Rinse the electrode with DI water, blot dry, and place it into
the beaker.
5. In the program the sensor is connected to, create a Digits
display measuring the concentration of carbon dioxide from
the ISE Probe.
6. Begin data collection. Once the reading stabilizes, record
the concentration value.
7. Repeat Steps 1 through 6 for any additional samples.
Carbon Dioxide ISE Probe | PS-3517
4