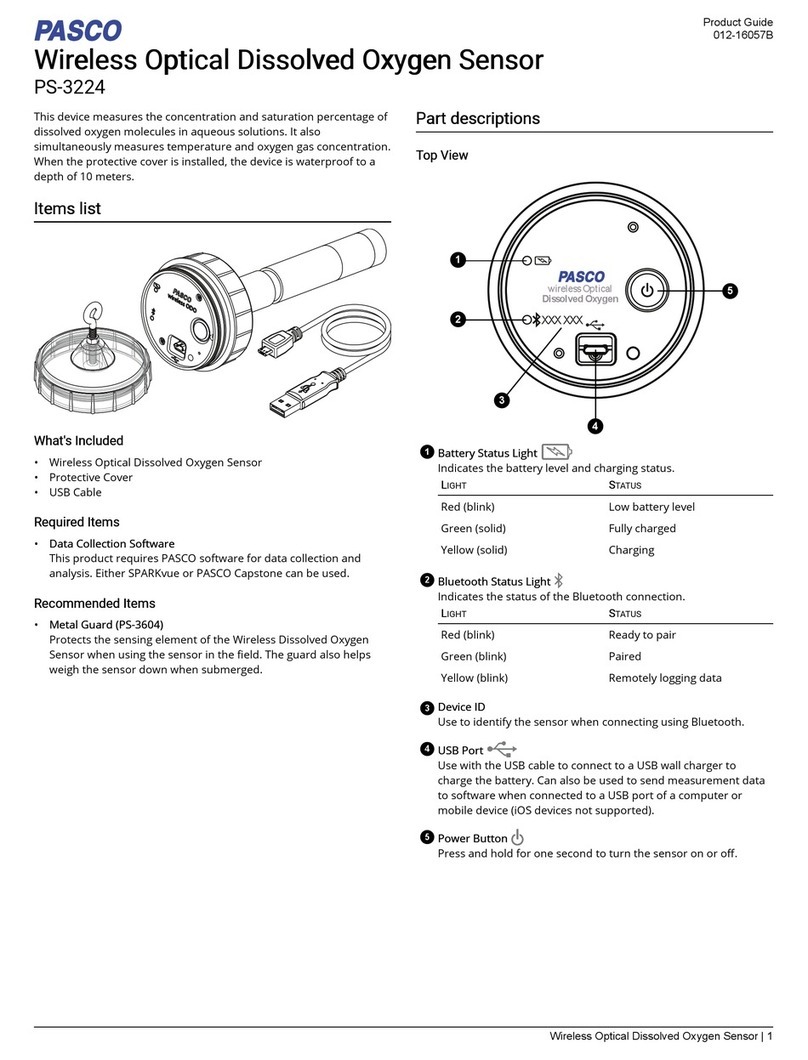
To protect the Motion Sensor from being hit by an object, use a device such as the SE-7256
Motion Sensor Guard (g) or ME-9806 bracket with a rubber band (h). The Motion Sensor can
“see through” a wire screen or rubber band placed close to the transducer.
Troubleshooting: If the Motion Sensor fails to perform satisfactorily, try these steps:
•Ensure that the target object is no closer than 15 cm.
•Switch the range switch to the other setting.
•Adjust the aim left, right, up, or down. In some cases the Motion Sensor works best
when it is aimed slightly to the side or above the target in order to exclude interfering
objects.
•Improve the target by adding a larger or harder surface to refect ultrasound. A small
object can be a better refector than large object if it has a harder surface.
•Remove interfering objects near the target object or sensor.
•Increase or decrease the sample rate.
Theory ofOperation:
The Motion Sensor uses an electrostatic transducer as both a speaker and a microphone.
When triggered by the interface, the transducer transmits a burst of 16 ultrasonic pluses
with a frequency of about 49 kHz. This burst of pulses can be heard as a single click. The
ultrasonic pulses refect oan object and return to the sensor. The target indicator on the
sensor fashes when transducer detects an echo.
Sound intensity decreases with distance; to compensate, the sensor increases the gain of the
receiver amplier as it waits for the echo. The increased gain allows the sensor to detect an
object up to 8 m away. The lower gain at the beginning of the cycle reduces the circuit's
sensitivity to echoes from false targets.
The interface measures the time between trigger rising edge and the echo rising edge. The
data acquisition software uses this time and the speed of sound to calculate the distance to
the object. To determine velocity, the software uses consecutive position measurements to
calculate the rate of change of position. Similarly, it determines acceleration using
consecutive velocity measurements.
Minimum Range: 15 cm
Maximum Range: 8 m
Transducer Rotation: 360°
Range Settings:
•Short Range: for distance measurement up to 2 m with improved rejection offalse target
signals and air-track noise
•Long Range: for distance measurement up to 8 m
Mounting Options:
•On rod up to 12.7 mm diameter
•Directly to PASCO dynamics tracks
•On table top
Connector: Dual stereo phone plug for ScienceWorkshop-compatible interfaces
Verify the Sensor's Performance and connection to DAQ (data acquisition) software:
1. Connect the Acceleration Sensor to the computer interface with the interface cable
(see Figure 1a) and set up Capstone. Open a Digital Display and select position from
the pop-up menu. Set the range switch on the sensor to long (stick gure icon).
2. Create a digital display of the position reading and begin recording data in continuous
mode
3. wave a hand around and watch the echo indicator and the digital display to get a feel
for the cone of reliable detection
4. take picture of group members miming the extent of the cone
5. change range to short (cart)
6. Wave around again to get a feel for the cone of detection
7. take picture of group members miming the extent of the cone