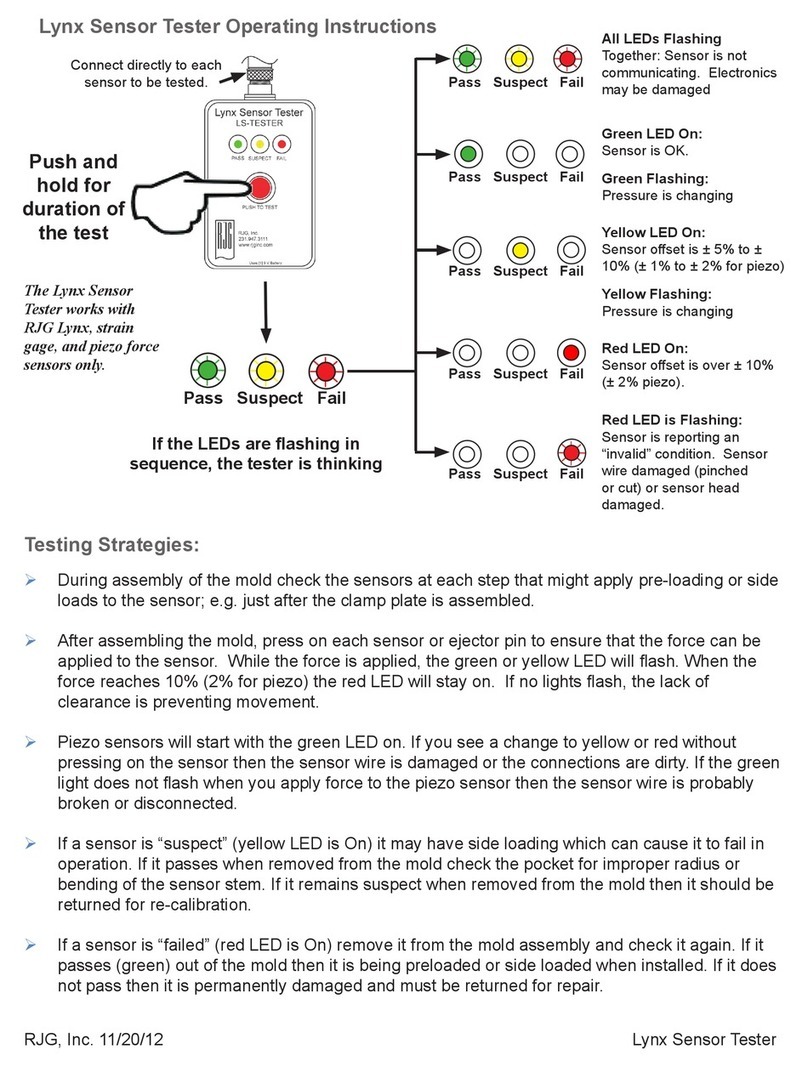
2-1
SECTION 2: CONTROLS AND INDICATORS
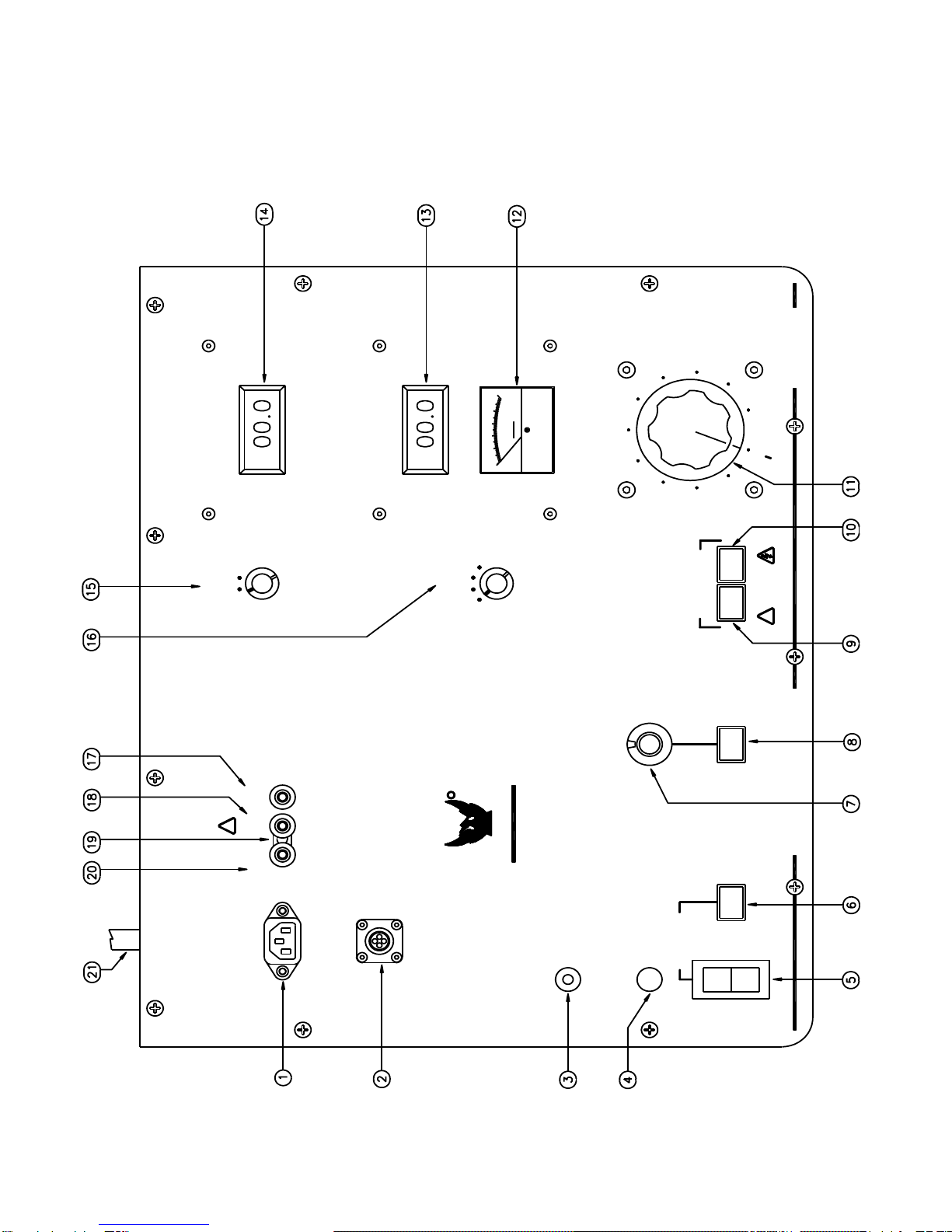
CONTROL PANEL
(Refer to Figure 2-1).
1. AC POWER INPUT. Plug into a suitable grounded receptacle. See specifications tag on unit for voltage
and current requirements.
2. EXTERNAL INTERLOCK. If desired, remove jumper from connector and replace with contact(s) that must
be maintained closed during testing. Some examples include footswitch, deadman switch, gate interlock,
panic button, etc.
3. THERMAL OVERLOAD. Circuit breaker protects primary of high voltage transformer. If circuit breaker
trips, turn High Voltage off and return Voltage Control knob to zero before resetting.
4. F1. Control Power Fuse.
5. MAIN POWER CIRCUIT BREAKER. Press Ito connect power, Press Oto disconnect power.
6. MAIN POWER INDICATOR. Lights to indicate that power is available for testing.
7. Current Trip Adjust. Dial adjusts from 1 to 11 corresponding to approximately 10% to 110% of selected
output current range. Current Trip/Reset lamp illuminates and high voltage turns off when output current
exceeds setting, causing circuit to trip. Circuit also acts as short circuit and overload protection on high
voltage output. To reactivate high voltage, Voltage Control must be returned to zero, and Reset switch
must be pressed to clear Current Trip circuit.
8. Reset. Reset lamp illuminates to show that current trip circuit has tripped. High voltage circuits are
deactivated. Momentary Reset switch must be pressed to extinguish Reset lamp to allow high voltage to
be reapplied after returning Voltage Control to zero.
9. High Voltage On. Press to turn on high voltage.
Conditions required before high voltage will activate are:
Voltage control at Zero Start
External Interlock loop closed.
Current Trip circuit Reset.
10. High Voltage Off. Press to turn off high voltage output. Under normal circumstances the voltage control
should be returned to zero, and the high voltage allowed to decay near zero before switching High Voltage
OFF.
CAUTION: Capacitive loads may retain voltage for a short time after high voltage is turned off
while the internal circuitry bleeds their charge to ground. High Voltage Off lamp must be illuminated
before High Voltage ON can be activated. Conditions required for illumination are:
External Interlock loop must be closed.
Overcurrent Trip/Reset circuit must not be tripped. (Push Reset if circuit is tripped)