Sens DCT Series Operating manual
DCT SERIES
CASE SIZE 2A
FILTERED BATTERY CHARGER
12V/100A
24V/75-100A
32V/50-100A
48V/50-75A
120V/25-35A
240V/12A
OPERATION & MAINTENANCE
GUIDE
SENS part number: 101137-2
Document revision: B
DCN number: 105286
Date: 1/17/2007
1840 Industrial Circle
Longmont, CO 80501
Fax: (303) 678-7504
Tel: (303) 678-7500
Web: www.sens-usa.com
Installation or service questions? Call SENS at 1-800-742-2326 (303-678-7500) between 8 a.m.
and 5 p.m. (Mountain Time) Monday through Friday, or visit our website.
Copyright © Stored Energy Systems LLC 2006

DCT Series Charger Manual
2
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
This manual contains important safety and operating instructions for Stored Energy Systems (SENS)
model DCT.
Before using the battery charger, read all instructions and cautionary markings on the battery charger,
battery and equipment connected to the battery system.
WARNING:
Please read
these safety
warnings and
heed them.
Failure to do so
could result in
either severe
personal injury
or equipment
damage.
This equipment uses and generates potentially lethal voltages. The equipment should only be installed and
maintained by trained persons. Do not attempt to install or operate this equipment unless you are certain
you are adequately trained.
To reduce the risk of injury, charge only properly sized lead-acid or nickel cadmium batteries. Other types
of batteries or under-sized batteries may burst, causing personal injury and damage.
“GROUND INSTRUCTIONS – This battery charger should be connected to a grounded, metal
permanent wiring system; or an equipment – grounding conductor should be run with circuit conductors
and connected to equipment – grounding terminal or lead on battery charger. Connections to battery
charger should comply with all local codes and ordinances.
• Do not install or operate charger if it has been dropped or otherwise damaged. Return it to the factory for
repair.
• Install the charger in accordance with all local codes.
• Do not expose charger to rain or snow.
• Do not disassemble charger. Return to factory when service or repair is required. Incorrect assembly
may result in a risk of electric shock or fire.
• To reduce risk of electric shock, de-energize and disconnect the AC input and the battery from the
charger before attempting maintenance or cleaning.
• Use of an accessory not recommended or sold by SENS may result in a risk of fire, electric shock or
personal injury.
• During normal operation, batteries may produce explosive hydrogen gas. Never smoke, use an open
flame, or create sparks near the battery or charger.
• Remove jewelry, watches, rings, etc. before installing battery or charger.
Maintenance
Instructions User maintenance is limited to charger adjustment. All on-site servicing should be performed by qualified
service personnel. If qualified personnel are not available, return the charger to the factory for repair, or
contact the factory to arrange for field service.
When returning a unit to the factory for repair, ship it in the original factory packaging if possible. If the
original carton is not available, pack in a carton with at least two inches of approved packaging material on
all sides of the charger to help prevent shipping damage.

DCT Series Charger Manual
3
1
Overview
This manual covers installation, operation and troubleshooting of SENS model DCT filtered battery
charger in case size 2A.
1.1 READ THIS FIRST
Please follow the installation and use instructions. They are vital to the satisfactory operation of the
charger. If you have any doubts about adjusting, maintaining or servicing the equipment, contact SENS’
service department.
Changing factory-set potentiometers voids the warranty. Contact the factory if you believe the settings on
your charger are incorrect.
Before determining the charger is not working correctly, check the following:
1. Is AC power available to the charger?
2. Are any circuit breakers tripped or fuses blown?
3. Is the charger connected to a battery of the correct voltage?
4. Was the charger damaged in transit or installation?
5. If you determine that the charger is not working because it is not putting out any current, check the
battery’s state of charge. If the battery is fully charged it is normal for the charger to indicate zero
current flow.
6. The charger may have shut down due to excessive output voltage. To ensure that the high volt
shutdown has been reset, turn off both the AC input breaker and DC output breaker for five minutes.
This is more than sufficient time for the DC voltage to decay and reset the shutdown.
7. If the battery is being over- or undercharged, check whether the output voltage settings have been
tampered with. The pots should be covered with either white adhesive paper dots or a hard colored
varnish.
1.2 Description and Application
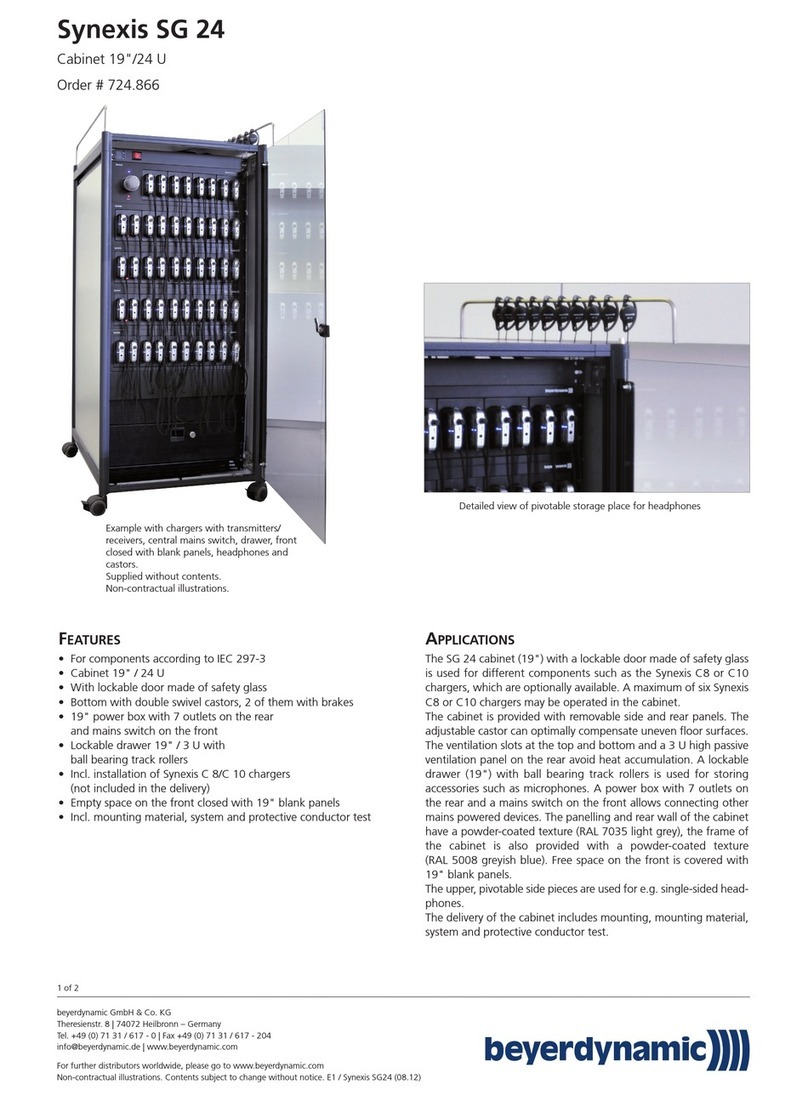
The DCT is a fully automatic battery charger and DC current source offering the following features:
• Constant voltage output
• Electronic current limiting
• Filtered output. Output ripple on battery rated in AH four times amp rating of charger for 12, 24, 48 volt
units is 30 mV rms. 120 volt units: 150 mV rms; 240 volt units: 300 mV rms.
• Temperature compensation to maximize battery performance and life
• Optional remote temperature compensation
• Circuit breakers for AC input and DC output
The chargers are designed to power equipment requiring a low ripple DC source and to simultaneously
recharge and maintain lead-acid or nickel-cadmium batteries.
1.3 Upon Delivery
Inspect the charger for damage caused during transit, and report damage to the carrier immediately. Then
contact SENS to determine how to best repair/replace the damaged unit.
2
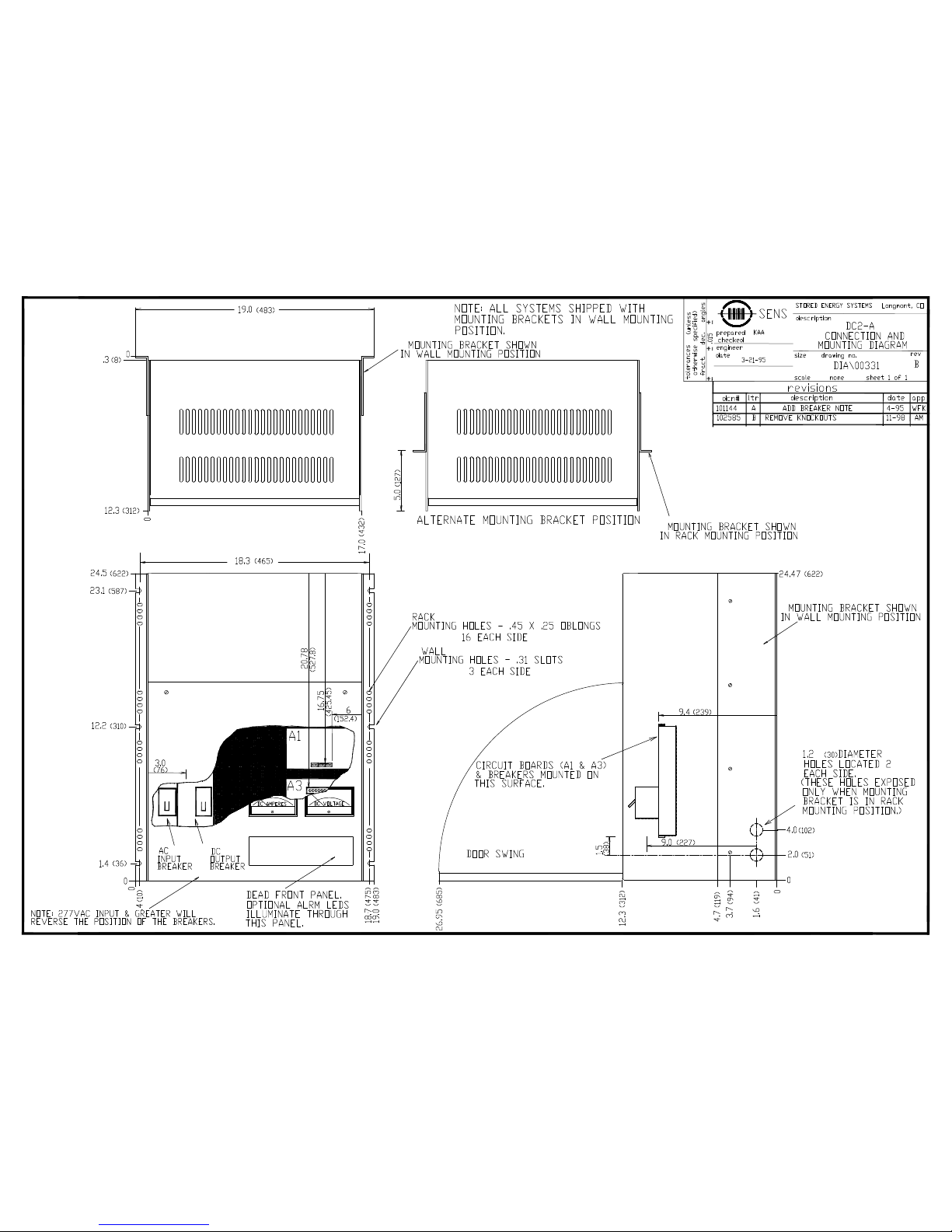
Installation
2.1 Mechanical Installation
Caution: Heed the following warning to prevent damaging the lower cover of the charger.

DCT Series Charger Manual
4
FIGURE 2.1
Lifting Instructions
WHEN INSTALLING
DO NOT LIFT UNIT
FROM MIDDLE OF
LOWER COVER - THE
COVER WILL BEND.
USE A SPREADER
PLATE EQUIVALENT TO
1" THICK PLYWOOD
ACROSS THE BOTTOM
OF THE UNIT WHEN
LIFTING
The charger can be mounted either on a wall or in a standard 19” relay rack. Locate the charger in a
dry place as close to the battery and load as possible to minimize voltage drop.
WARNING: These chargers are not approved for operation in areas with explosive atmospheres!
Wall Mounting
Mount the system to a robust wall using 1/4” bolts with flat washers behind the mounting holes, if
necessary, to level the charger on an uneven wall. The charger should be located as close to the
battery and load as possible to reduce voltage drop in the charging leads. Refer to the mechanical
drawings at the end of this document for case and mounting dimensions.
Relay Rack Mounting
The charger is shipped on its back with the mounting flanges in the wall-mount position. Place the
charger in a vertical position, then unbolt and reverse the mounting flanges. CAUTION: When
changing the angles from wall mount (the standard shipping configuration) to rack mount, you
MUST either stand the charger up vertically, or otherwise remove the charger’s weight from the
rack angles when removing the rack angle bolts. If you do not, the bolts in heavy chargers may strip
on their way out.
Protect the charger from construction grit, metal chips, paint or other debris. Clean away debris after
installation and before turning on the charger.
2.2 Electrical - Power Wiring
WARNING: Heat sinks and many other metallic components inside the charger are LIVE with
either line or output voltage. These voltages can be lethal. Do not touch any exposed metal surfaces
inside the enclosure while the charger is operating.
Remove the two 1/4-turn fasteners securing the charger's top front panel and open the front panel.
Make AC and DC connections direct to the AC and DC circuit breakers in accordance with either
diagram 2.2a or 2.2b.
Caution: Small sense leads are connected to the output side of the DC breaker. These must remain
connected to the output side of the breaker after installation of the DC cabling, or the charger will not
function properly.

DCT Series Charger Manual
5
FIGURE 2.2a
Power Connections - 240 Volts AC Input or Lower
AC INPUT DC OUTPUT 240 VAC OR LESS
MAKE INPUT & OUTPUT
CONNECTIONS DIRECT
TO CIRCUIT BREAKERS
AS SHOWN.
LN
or
L
-+
FIGURE 2.2b
Power Connections - 277, 380, 415 or 480 VAC
277, 380, 415 OR 480 VAC
MAKE INPUT & OUTPUT
CONNECTIONS DIRECT
TO CIRCUIT BREAKERS
AS SHOWN.
AC INPUT
LN
or
L
DC OUTPUT
-+
Connections should be made by a qualified installer in accordance with national and local electrical
codes. The installer should determine the gauge of wire to be used based on the length of cable runs
and the ampere requirements of the charger.
Refer to Table 2.2 for ratings of the charger’s AC breaker. Chargers supplied with field-selectable
input voltage are identified with an “A” as the first digit of the part number suffix. In these units the
AC breaker is sized for 115-volt operation. When the field setting is made for 115-volt operation,
size the AC feed to provide a maximum of 20% less than the breaker ratings listed in Table 2.2.
(The charger’s maximum power consumption is less than 20% below the breaker rating). When set
for 230-volt operation the current consumption will be half of the 115 volt figure.
Chargers with 480-volt input require half the current of 230 VAC units.
Use the charger’s rated DC amperes to determine DC cable gauge.
WARNING: The battery charger should be connected to a grounded permanent wiring system.
A ground stud or terminal is provided for this purpose.
DCT Series Charger Manual
6
TABLE 2.2
AC Input Circuit Breaker Ratings
Charger output Breaker Breaker
115 V 230 V
V A V A V A V A amps amps
24 75 40 same
24 100 50 same
48 75 50
240 6 20 same
120 25 240 12 60 same
120 35 45
Caution: Do NOT connect the battery backwards; charger damage may result.
The voltmeter will show battery voltage as soon as the DC connection is completed. Check the
voltmeter as soon as the DC connection has been made. If the meter reads zero or is deflecting
below zero, reverse the polarity of the battery connections.
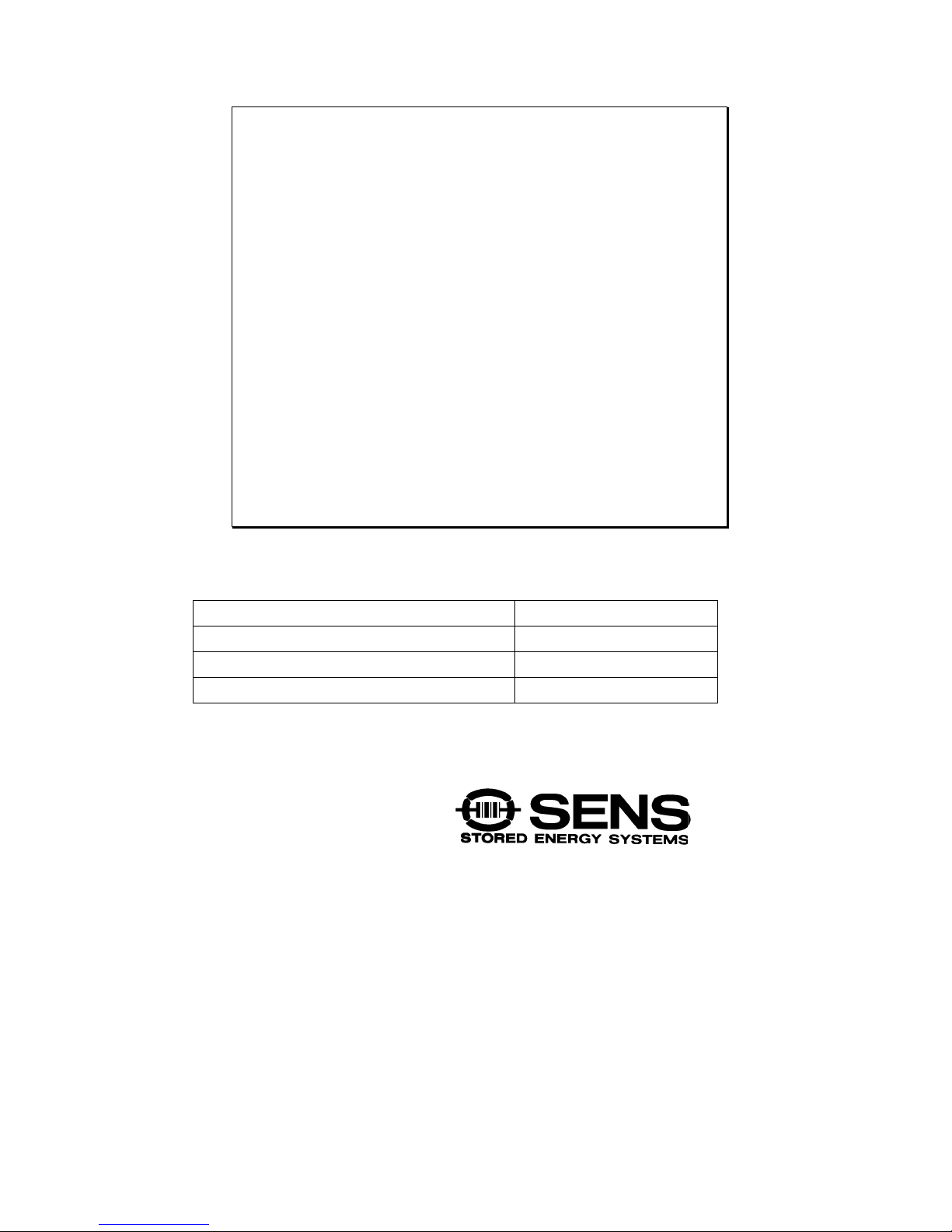
2.3 115/230 Volt Strapping
Chargers equipped with field-selectable, dual-voltage input are factory-set at 230 volts. If your input
supply is 115 volts, change the voltage selection terminal block to the configuration shown below.
The input voltage selection block is located inside the charger front door.
Figure 2.3
115/230 Volt Strapping Configurations
230 volt configuration 115 volt configuration
230 V Configuration
If 115 VAC is accidentally applied, the charger output voltage may sag, even though the “AC On”
and Float LEDs are lit. “Low DC” and “Charge Fail” may be dimly lit. Please strap accordingly for
the proper input voltage.
115 V Configuration
If 230 VAC is accidentally applied, the charger will enter a high voltage shutdown (HVSD)
condition, turning off the control board and the charger. No output voltage or current will be present.
Please strap accordingly for the proper input voltage.
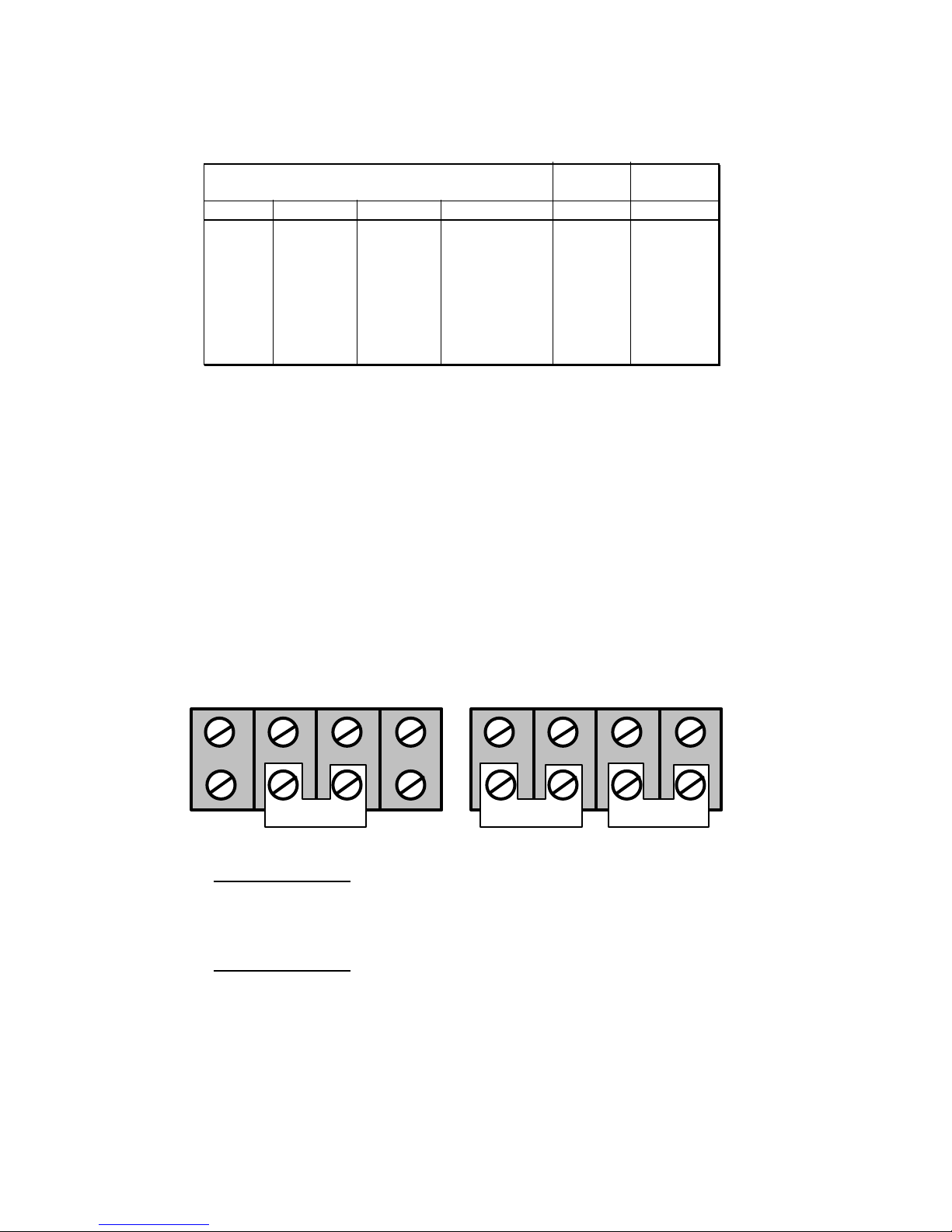
2.4 Alarm Connections
DCT chargers are supplied with one of three following alarms configurations:
DCT Series Charger Manual
7
TABLE 2.4
Charger Part Number Suffix and Alarms Configuration
-4042, -6042,
-7042, -8042
Alarms “0”
-4642, -6642,
-7642, -8642
Alarms “6”
Charger alarm system code
Indication
None Float or boost mode LED
None AC fail LED & Form C contact
None Charger fail LED & Form C contact
None Low battery voltage LED & Form C contact
None High battery voltage LED & Form C contact
None Ground fault + LED
None Ground fault - LED
None Ground fault + or - Form C contact
None Summary of above Form C contact
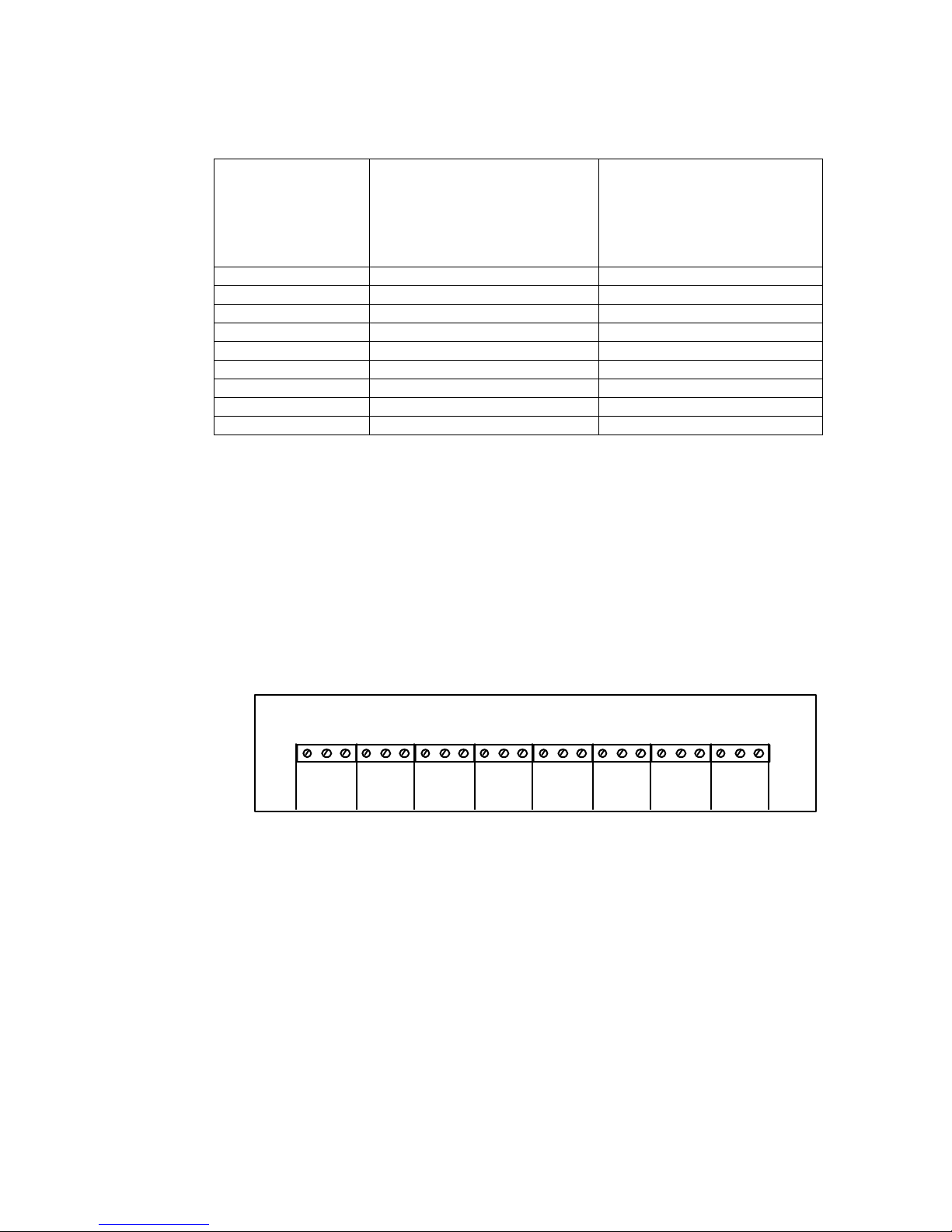
Connect to the charger’s Form C contacts according to Figure 2.4.
1. Make connections to the system's Form C alarm contacts as shown.
2. Run alarm wiring out of the charger separately from the AC supply wiring.
3. Use 16 to 22-gauge wire.
NOTE: Do not exceed the relay maximum current rating of 1A @ 117 VAC or 2A @ 26 VDC.
The remote alarm connection board is located on the circuit breaker pan, adjacent to the control
board. See Figure 2.4.
FIGURE 2.4
Remote Contact Terminal Block
FAIL
OK
COM
GROUND
FAULT
AC
FAIL
CHARGE
FAIL
LOW DC
VOLTS
HIGH DC
VOLTS
LOW DC
DISC.
OPTIONSUMMARY
FAIL
OK
COM
FAIL
OK
COM
FAIL
OK
COM
FAIL
OK
COM
FAIL
OK
COM
FAIL
OK
COM
FAIL
OK
COM
2.5 Temperature Compensation
DCT chargers include battery temperature compensation (TC). TC is required by all batteries for
maximum performance and life. The TC feature automatically reduces the charger’s output voltage
at high temperatures and vice-versa.
The factory configuration is for charger local sensing of battery temperature (i.e. at the cooling air
intake of the charger). The charger also includes, as standard, the provision for extension of a
temperature sensor to a remote location. At installations where the battery is located in a different
room, or is otherwise subject to ambient temperatures different from the charger, it is necessary to
sense temperature at the battery. If this is the case, the optional SENS remote temperature sensor
(RTS) should be obtained from the factory. When the optional remote sensor is attached correctly
to the charger control board the charger automatically selects the remote sensor over the local
sensor. If the remote sensor becomes damaged or disconnected, temperature sensing automatically
reverts to local.

DCT Series Charger Manual
8
The two leads of the optional RTS are connected to a port on the control board as follows: Connect
the yellow lead of the sensor to J7 “YEL” and the violet lead to J7 “VIO”. If the sensor is
connected properly “RTS OFF” will not illuminate when the charger is in operation. If “RTS OFF”
stays lit, check that RTS leads are not reversed, and check that the remote sensor is not damaged.
Any excess length of the RTS leads should be cut off rather than coiled, to ensure the shortest
possible length. The RTS leads should be routed separately and away from all other AC power, DC
power, and alarm wires and cables to prevent noise coupling that may cause abnormal operation of
the charger.
NOTE: “RTS OFF” on the control board will remain lit whenever the remote temperature sensor is
either not used or if the remote sensor is disabled. This is normal when RTS is not used.
3
Operation
3.1 Start-up, Shut-down
Start with both input and output breakers OFF.
First, check that the connected battery voltage is correct (e.g. 120 volts for a 120-volt charger). It is
OK if the battery voltage is different from the nominal value by a few percent. If the battery
voltage is more than 10% different from the rated voltage of the charger, recheck your connections
BEFORE turning on either breaker.
Then close the AC input breaker. Check that the charger voltage comes up to approximately 15%
above nominal. (Some voltage overshoot on initial startup is normal).
Next, close the DC output breaker. The charger will immediately begin to supply current, if
required by the battery or load.
In chargers with alarms code “6”, the front panel AC FAIL and CHARGE FAIL lights will
extinguish, and it should be replaced by the green AC ON light.
The charger will automatically supply power to the load and maintain the battery without further
attention. If the charger does not start as described, or appears to have failed, check the following:
• Verify that AC mains power is available
• Verify that no external circuit breakers are tripped
• Verify that contractor-installed AC, DC and alarm connections are correct
• Disconnect AC and DC power sources. Open the charger. Verify that no components (e.g. main
DC output fuse, if fitted) or harness connections are blown, loose or damaged.
If all of the above appear to be in order, contact SENS at the toll-free service number on the front of
this document for troubleshooting assistance.
At power down or disconnection of charger from battery. The DC output breaker must not be
operated from the closed to open position when AC power is present. Always open AC breaker
before opening the DC output breaker.
3.2 FLOAT/BOOST MODES
Two modes of voltage control are provided in all DCT chargers as follows:
FLOAT
The float mode is the battery “maintenance” voltage. It is the normally fully charged voltage of the
battery. This is the normal charging position for all batteries and the recommended charging
position at all times for Valve Regulated Lead Acid (VRLA) batteries.
DCT Series Charger Manual
9
BOOST
This voltage is slightly higher than the float setting. Boost slightly overcharges the battery in order
to ensure that all the cells of a battery are fully charged to the same voltage. Continued operation in
boost is not recommended because the high charging voltage will cause battery electrolyte to boil
away quickly. This is a particular problem with VRLA batteries where there is no way to replenish
lost electrolyte.
3.3 FLOAT/BOOST CONTROL
DCT chargers are equipped with one of the four following float/boost voltage control systems,
depending on the configuration ordered:
FLOAT/BOOST front panel rotary switch
The charger will operate indefinitely in the mode that is selected. The AUTO position may be
shown on the front panel. If the AUTO position is locked out, the AUTOBOOST feature is not
supplied.
AUTO/FLOAT/BOOST front panel rotary switch
When the selector switch is in the FLOAT or BOOST mode, the charger will operate indefinitely in
the mode that is selected.
The AUTO mode selects automatic equalization of the battery. The charger determines when the
battery is in need of fast charging, and it operates in the fast charge boost mode only until the
battery is fully charged. The charger determines state of charge by measuring the amount of current
drawn from the output terminals. When the selector switch is in the AUTO position the charger
will start in the BOOST mode and stay there until current demanded drops below about 50% of the
charger’s rated current. When current demand increases to about 70% of the charger’s rated output,
the charger will resume operation in the BOOST mode.
Please see the Appendix for a diagram of how the AUTOBOOST system works. The AUTO
setting eliminates the need to periodically equalize the cells of a battery as the charger does this
automatically. The AUTO position should not be selected when the continuous load on the charger
is greater than about 50% of the charger’s maximum rated current.
Manually initiated boost timer (either 0-24 hours or 0-72 hours)
When the timer is turned clockwise the charger will be in BOOST mode, where it will remain until
the timer returns to 0 hours. At the end of the selected time the charger will return to FLOAT
mode.
Manually initiated boost timer, plus AUTO/FLOAT/BOOST rotary switch
Selection of the AUTO position allows the charger to operate in the AUTOBOOST mode.
Selection of the FLOAT mode forces the charger to remain in the FLOAT mode unless the boost
timer is activated by turning past zero. If the boost timer is activated, the charger will revert to
FLOAT mode after the time selected on the timer expires.
Selection of the BOOST mode forces the charger into boost charge, where it will remain until
BOOST is deselected manually.
3.4 Alarm Indications
NOTE: Chargers are equipped with a “dead-front” panel. Alarm LEDs are behind the dead-front
panel and will be visible when they illuminate due to an alarm condition, or when the TEST button
is pressed. See Figure 3.4 for the location of LED indicators. Chargers with no alarms (alarms
code “0”) have no LEDs or test button.

DCT Series Charger Manual
10
FIGURE 3.4
LED Indicators on Charger Front Panel
LOW DC
AC FAIL + GROUND
- GROUND
LAMP TEST
FLOAT
BOOST
AC ON CHGR FAIL
HIGH DC
SHUTDOWN
AC ON
Indicates that AC power is being supplied to the charger.
BOOST
The charger is operating in the BOOST mode.
FLOAT
The charger is operating in the FLOAT mode.
AC FAIL
Indicates that AC power is not available to the charger. Input AC is failed, or AC breaker is
tripped.
CHGR FAIL
Indicates that the charger is failing to produce the output current required by the battery and load.
When the battery and load demand no current, the failure alarm will not activate.
In the event that the CHARGE FAIL and AC ON lights are illuminated simultaneously, then the
charger has failed. The probable causes of an alarm, in descending order of likelihood, are:
a) A failure of AC power
b) A tripped AC breaker
c) The charger has malfunctioned
LOW DC
Indicates that DC voltage has dropped to approximately 8.5% below nominal battery voltage (e.g.
21 volts for a 24-volt system). Probable causes:
a) The AC power has failed, and the battery has become discharged
b) The charger has malfunctioned and the battery has become discharged
c) The battery is defective
There is a time delay in the low voltage alarm which prevents the alarm from activating until
approximately 30 seconds after the low voltage condition starts.
HIGH DC
Indicates that the charger’s output has exceeded a pre-set threshold level (approximately 20% above
nominal battery voltage - e.g. 29 volts for a 24-volt system). If this alarm stays activated for any
period of time, the charger should be shut down and serviced. The charger may have
malfunctioned, or the alarm card may be misadjusted. The alarm activates immediately upon high
voltage condition, but stays activated for approximately 30 seconds after the condition disappears.

DCT Series Charger Manual
11
HIGH DC SHTDN
Indicates that the charger has been shut down by the high output voltage shutdown circuit.
Probable causes of a high DC shutdown are as follows:
a) The float or boost voltages have been increased above the pre-set shutdown voltage.
b) The high voltage shutdown set point has been changed from the factory setting.
c) The charger has malfunctioned and is not regulating properly.
There is a delay of approximately five seconds after the onset of the high voltage condition until the
unit shuts down. When a high volt shutdown occurs, the red HVS LED on the control board will
illuminate, along with the SHUTDOWN LED on the front panel.
If the high DC shutdown activates, the charger will stay off until the battery voltage drops to
approximately nominal, at which point the circuit will reset and the charger will start. Manual reset
of the shutdown is accomplished as follows:
1) Turn off the AC input breaker. (Note that while the SHUTDOWN LED will extinguish, the
charger is still locked out. This is because the shutdown LED is driven by the control board's
power supply, which is derived from the AC supply, rather than from the battery).
2) Turn off the DC output breaker.
3) Wait for about one minute for capacitor voltage to decay through the capacitor bleeder resistor.
4) Turn on the DC output breaker.
5) Turn on the AC input breaker. If the charger is still in high DC shutdown, repeat steps 1 through
3, waiting longer before turning DC and AC breakers back on.
The control board includes two sets of Form C contacts for high volt shutdown indication. Either
one of these can be used for remote indication of high voltage shutdown.
GROUND (optional)
This is a ground fault alarm. If either the charger’s positive or negative is connected to ground,
even through a high resistance path, this alarm will activate. LEDs indicate either positive or
negative grounding. The Form C contact only indicates that a fault has occurred.
Some applications require that ground be referenced to either the positive or negative output. In
this case, the activated ground fault alarm will be a nuisance. The alarm can be safely disabled by
placing the ground fault jumper, located on the alarm board (mounted on the charger’s front door),
in the “disabled” position. When pins 1 and 2 of J5 are connected together the ground fault alarm is
disabled. When pins 2 and 3 are connected the ground fault alarm is enabled.
4
Adjustments
4.1 Output Voltage Adjustment
WARNING: Working inside the charger exposes you to dangerous AC and DC voltages. Do not
touch circuit breakers, filter capacitors, heat sinks or any other exposed metal surfaces.
NOTE: Do not tamper with factory adjustments unless sure adjustment is necessary.
Temperature-compensated control circuitry automatically adjusts the output voltage, depending on
temperature. Adjust the output only under these circumstances:
a) To correct a previous unauthorized adjustment
b) To adjust the charger for a different type of battery (e.g. from lead-acid to nickel-cadmium)
c) If your battery is consistently being over-charged or under-charged
NOTE: Unless authorized by SENS, any charger adjustment, including output voltage adjustment,
voids the warranty.
Procedure
1. Use a precision external voltmeter connected directly to the charger output terminals.
2. Set the charger’s front panel FLOAT/BOOST control to FLOAT.
3. Open the charger’s front panel and locate the control card. It contains two potentiometers labeled
“FLOAT” (R14) and “BOOST” (R15), both located near the center of the board.

DCT Series Charger Manual
12
4. Adjust the FLOAT pot until the desired voltage is achieved.
Adjustment of the BOOST voltage is similar to adjustment of FLOAT, except that you adjust the
BOOST pot instead of the FLOAT pot. Be sure that the charger front panel mode switch is in
BOOST when you make adjustments.
Please note that the BOOST adjustment controls the level above FLOAT voltage, not the absolute
voltage. Therefore, whenever the FLOAT voltage is changed, the BOOST voltage also changes.
4.2 Factory-Set Output and Alarm Voltages
NOTE: Output voltages are temperature compensated (vary with temperature). The factory
settings below are at 20 degrees C. The compensation is -0.18% per degree C. The alarm voltage
settings are NOT temperature compensated.
Chargers set for sealed maintenance-free lead-acid battery
12 Volt 24 Volt 32 Volt 48 Volt 120 Volt 240 Volt
Float voltage 13.62 27.24 36.32 54.48 136.20 272.40
Boost voltage 13.80 27.60 36.80 55.20 138.00 276.00
Low DC alarm 11.00 22.00 29.33 44.00 110.00 220.00
High DC alarm 14.61 29.22 38.96 58.44 146.10 292.21
High DC shutdown 15.19 30.39 40.52 60.78 151.95 303.89
Chargers set for flooded lead-acid battery
12 Volt 24 Volt 32 Volt 48 Volt 120 Volt 240 Volt
Float voltage 13.32 26.64 35.52 53.28 133.20 266.40
Boost voltage 14.00 28.00 37.28 55.92 139.80 279.60
Low DC alarm 11.00 22.00 29.33 44.00 110.00 220.00
High DC alarm 14.82 29.64 39.47 59.20 148.01 296.02
High DC shutdown 15.41 30.83 41.05 61.57 153.93 307.86
Chargers set for nickel cadmium battery. Multiply volts per cell times number of cells for actual voltage.
Per Cell
Float voltage 1.43
Boost voltage 1.52
Low DC alarm 1.19
High DC alarm 1.61
High DC shutdown 1.67
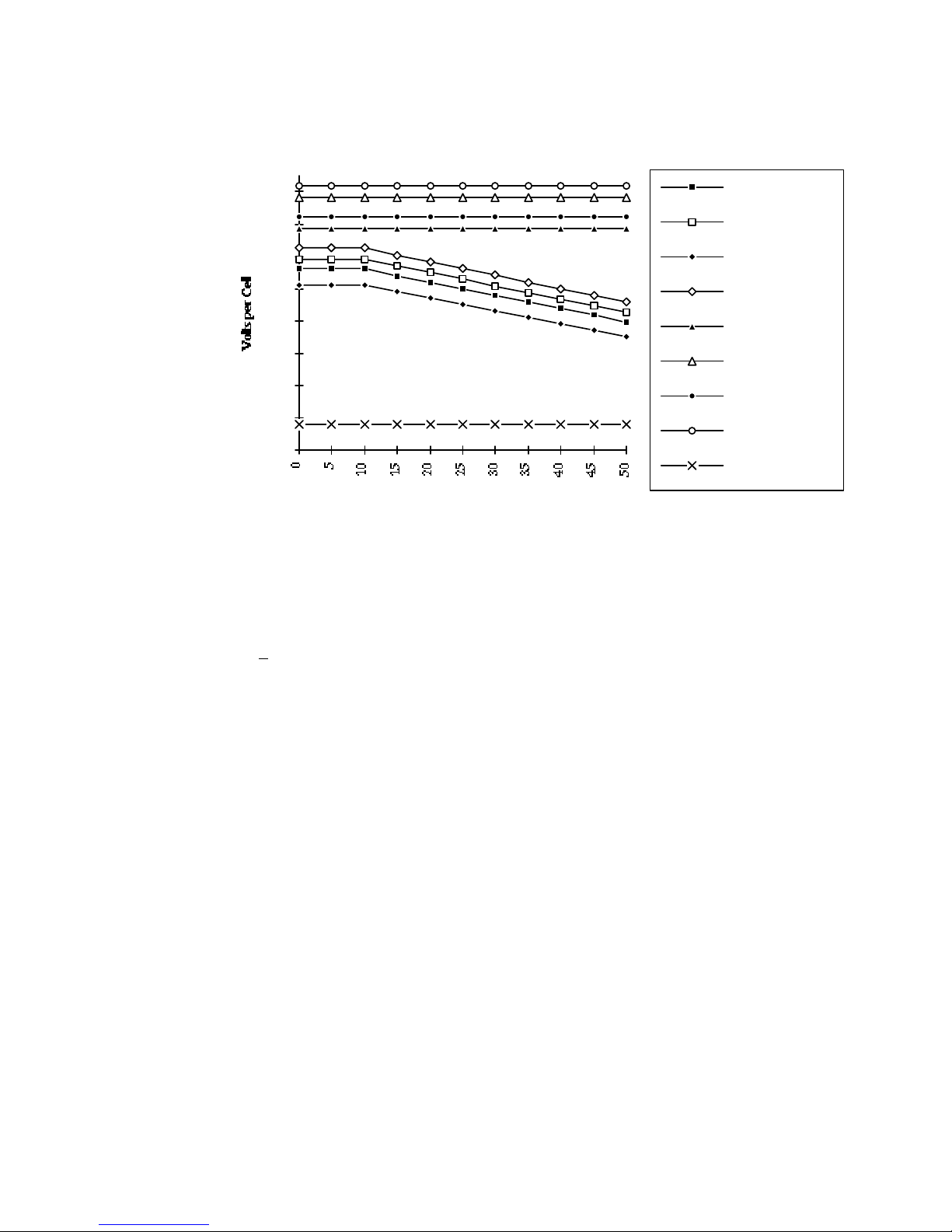
Chart 4.2 shows the relationship between charger output voltage, alarms and high voltage shutdown
Note: The output voltage is temperature compensated down to 10 degrees C, below which the
compensation ends.
To determine the charger’s voltage at temperatures other than 20 degrees C., multiply the number of
degrees Celsius difference between your ambient and 20 degrees times .0018. Multiply that product
times the factory voltage setting (e.g. 27.24), and add it to the factory setting.
Example 1: Float voltage at 10 degrees C of a 24 volt charger set for 27.24 volts at 20 degrees C:
20-10 (.0018) (27.24) + 27.24 = 27.73 volts
Example 2: Float voltage at 50 degrees C of a 24 volt charger set for 27.24 volts at 20 degrees C:
20-50 (.0018) (27.24) + 27.24 = 25.77 volts
DCT Series Charger Manual
13
CHART 4.2
Graph of Factory-Set Output, Alarm and Shutdown Voltages
Degrees C
1.75
1.85
1.95
2.05
2.15
2.25
2.35
2.45
2.55 VRLA Float
VRLA Boost
Flooded Float
Flooded Boost
HV Alm VRLA
HV Shtdn VRLA
HV Alm Flooded
HV Shtdn Flooded
Low DC Alarm
4.3 Forced Load Sharing
Chargers can be set up for forced load sharing when used in parallel with units of the same current
rating. Forced load sharing causes the chargers to share the load from light loading to full load,
except when either charger is in BOOST mode (whether activated manually or via the
AUTOBOOST system) or if either charger is operating in current limit. Chargers will share the load
within + 10% of each other.
To set up, ensure that the DC output leads from each charger are identical in length and wire gauge.
Install a Load Share Cable (supplied by SENS or assembled by user) between terminals on both
control boards where labeled “PAR”.
To assemble a Load Share Cable:
1. Cut desired length of signal wire (18 or 22 AWG).
2. Connect a 10KΏ, 2 Watts or more, resistor inline with signal wire. Connect resistor to wire
using a Butt Connector or twist wires together and cover with Heat – shrink.
DCT Series Charger Manual
14
5
Trouble-
shooting
5.1 Troubleshooting Table
If there is a problem and you suspect the charger is at fault, turn off the AC mains supply before
proceeding. Ensure that the following are correct: AC input wiring, battery and/or load connections
and PC card connectors. Ensure no foreign objects are in the charger.
Symptom
Possible Cause
Test
Corrective Action
No output /
fail alarm
Control board failure Replace with known good
board
Replace board
DC fuse blown Check fuse for continuity Replace if open
High DC shutdown Check HVS LED on control
board
If lit, see "High Output
Voltage" symptom below
Power rectifier
circuit failure
Test all power diodes with
meter; test SCRs
Replace all shorted, open, or
bad parts
AC failure Check input supply Restore AC input supply
Shutdown due to
excessive output
voltage
Check whether HVS LED on
control board is lit
Shut off AC and DC breakers
for at least 2 minutes, then
restore
AC breaker
trips
repeatedly
Power diode, SCR,
or freewheeling
diode short
Check all power devices for
shorts
Replace shorted device(s)
DC brkr trips
repeatedly
Control board failure Replace with known good
board
Replace board, send bad
board to SENS for repair
Freewheeling diode
short
Check diode for short Replace diode
Low output
volts / alarm
Control board failure Replace with known good
board
Replace board
Misadjusted float
voltage
Adjust pot to see if output
voltage is affected
Adjust float pot to correct
output voltage
Overloaded charger Turn off DC breaker, check
voltage on INSIDE breaker
terminals
Check load for problems, and
check battery condition
Bad filter capacitor Disconnect capacitors one at a
time and check for change in
output voltage
Replace capacitor that
corrected output voltage
when removed
Line voltage less
than charger's
operating range
Measure AC line voltage Use larger gauge AC wires or
contact utility company
High output
volts /alarm
Control board failure Replace with known good
board
Replace board
Misadjusted float
voltage pot on
control board
Adjust pot and see if output
voltage is affected
Adjust float pot to correct
output voltage
High ripple
voltage
Control board failure Replace with known good
board
Replace board
Power diode / SCR
failure
Test power diodes; perform
SCR test on SCRs
Replace all open or bad parts
AC line voltage too
high
Check for AC line voltage
over charger's specified
operating range
Contact utility company
Bad filter capacitor Disconnect capacitors one at a
time and check for change in
output voltage
Replace capacitor that
corrected output voltage
when removed
Improperly
functioning
indicators
Alarm, display, or
control board failure
Replace each board in turn
with a known good board
Replace failed board(s)

DCT Series Charger Manual
15
5.2 Component Diagnostic Tests
Test #1: With transformer leads disconnected, energize the transformer with the normal AC supply
voltage. Measure entire secondary voltage. It should be 1.5 to 2 times the nominal battery voltage.
Test #2: With one or both leads disconnected from the inductor, measure the resistance across the
inductor terminals. If the resistance is near a short circuit condition, the inductor is OK.
Test #3: Using a digital multimeter set to the diode testing function, measure the junction voltage
across the diode. A reading of between 0.4 volt and 0.8 volt in the forward polarity direction and
infinity in the reverse polarity direction indicate a good diode.
Test #4: Refer to Figure 5.2. Disconnect all the leads to the SCR and its heat sink. Connect a
voltmeter across the 1KΩresistor to measure the voltage drop. With the battery connected as shown,
Vdrop should read approximately 2.3V (Vsource-0.7V). Remove the voltage source to the gate, but
keep it connected to the 1KΩresistor and cathode. Vdrop should equal zero. Reconnect the gate and
reverse the batteries polarity. Vdrop should read zero volts. Readings other than these indicate a
defective SCR.
Test #5: Due to the modest cost of the control circuit, we recommend that the entire unit be replaced
rather than attempting to repair it. If the troubleshooting guide has not revealed any defective
components (tests #1-4), the control circuit should be replaced as a unit.
Test #6: Remove all wires from the current shunt. Place a milliohmmeter across the two terminals.
The following formula should be used to determine the correct resistance:
Resistance in ohms should equal 0.5/Output current rating of the charger, except in 35 amp units
when resistance should equal 0.1 ohms.
If the resistance is more than 20% too low, the current shunt should be replaced.
FIGURE 5.2
SCR test setup
25 ž
approx. 3 volt source(2 "D"
batteries in series)
Cathode Gate
SCR
Anode
-
+
+
-
Vdrop 1 Kž

DCT Series Charger Manual
16
Appendix Diagram of Automatic Boost Operation (Optional Feature)
Boost voltage
Float voltage
Point at which charger changes
from current limit to voltage limit
Point at which AUTOBOOST
returns charger to float voltage
100% charger
output current
50% to 75% of
charger current limit
Amps
Volts
Charger output current
Battery voltage
NOTE:
Zero current flow
0Time
When the charger switches from BOOST to FLOAT mode,
no current will flow into the battery for a while due to the battery's
high state of charge. This is completely normal, and indicates
that the charger is working properly.

CFOK CFOK
HIGH VOLT
SHUTDOWN
HIGH VOLT
SHUTDOWN
KA
PAR
PARRALLEL
TEMPERATURE
SENSING
REMOTE
FOR COMPLETE
SEE BODY OF
OF ALARM
EXPLANATION
USER GUIDE
CONNECTIONS.
FUNCTION &
MAXIMUM WIRE
SIZE-#14.
ALARM
CONNECTIONS:
FAIL
CHARGE
FAIL
FAIL
LOW DC
VOLTS GROUND
FAIL
FAIL
FAULTFAIL
AC
COM
OK
OK
OK
COM
COM
OK
LOW DC
FAIL
FAIL
DISC.
SUMMARY OPTION
COM
FAIL
HIGH DC
VOLTS
FAIL
COM
OK
COM
OK
COM
OK
COM
OK
A3
BATTERY AND LOAD ALARM
CONNECTIONS
OUTPUT
INPUT DC
AC
1. INPUT VOLTAGES OF 277VAC
2. A3 OPTIONAL ONLY IF UNIT IS
EQUIPPED WITH ALARMS.
POSITION OF BREAKERS.
& GREATER WILL REVERSE THE
MAKE INPUT & OUTPUT CONNECTIONS
MAXIMUM WIRE SIZE: AC-#8, DC-#2
DIRECT TO CIRCUIT BREAKERS
GRND
FOR
NOTES:
#10
STUD
AM11-96CORRECT INPUT & OUTPUT
ltrdcn# NRC101751 description
revisions date app
A1
N/A
B
none
scale
DIA\00335
1 OF 1
sheet
4-25-95
release date
TITLE
SIZE
Longmont, CO
STORED ENERGY SYSTEMS
DCT 1 & 2A CASE
SENS
rev
FSCM NO.
CONNECTION DIAGRAM
DWG NO.
otherwise specified)
fract.
tolerances
DESIGN ACTIVITY
CUSTOMER
angles
(unless
.015
dec.
DATE
DRAWN
CONTRACT NO.
KAA
DESIGN
CHECKED
Table of contents
Other Sens Batteries Charger manuals

Sens
Sens EnerGenius NRG24-20 User manual

Sens
Sens EnerGenius IQ2 User manual

Sens
Sens EnerGenius NRG24-10 User manual

Sens
Sens EnerGenius DC COMPACT User manual

Sens
Sens MicroGenius S2 User manual
Sens
Sens MicroGenius 2 User manual

Sens
Sens MicroGenius 2 User manual

Sens
Sens TD Series Operating manual

Sens
Sens MicroGenius User manual
Sens
Sens F3 SERIES Manual

Sens
Sens EnerGenius NRG12-20 User manual
Sens
Sens MicroGenius S4 User manual

Sens
Sens NRG12-10 User manual
Sens
Sens MicroGenius S2 User manual

Sens
Sens EnerGenius DC Wallbox User manual

Sens
Sens F3 SERIES Manual

Sens
Sens FC Operating manual

Sens
Sens Q012-012 User manual

Sens
Sens EnerGenius NRG22-20 User manual