Siemens SG-3118 Owner's manual
Other Siemens Industrial Electrical manuals
Siemens
Siemens SIRIUS 3RA132.-8XB30 User manual

Siemens
Siemens SIRIUS 8WD44 User manual
Siemens
Siemens 3KF1-B Series User manual
Siemens
Siemens 8UC6 Series User manual

Siemens
Siemens SIMOTION D45 Series User manual

Siemens
Siemens 38-3AH3-GTD User manual
Siemens
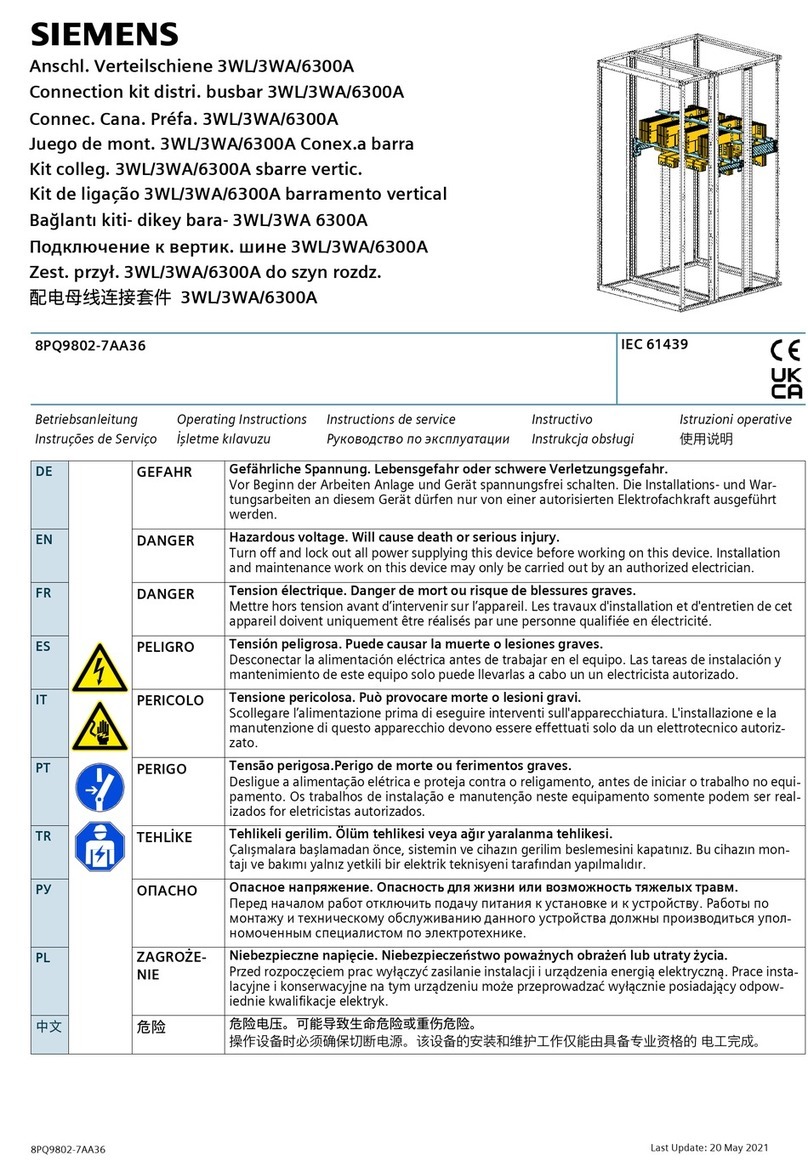
Siemens 6300A User manual
Siemens
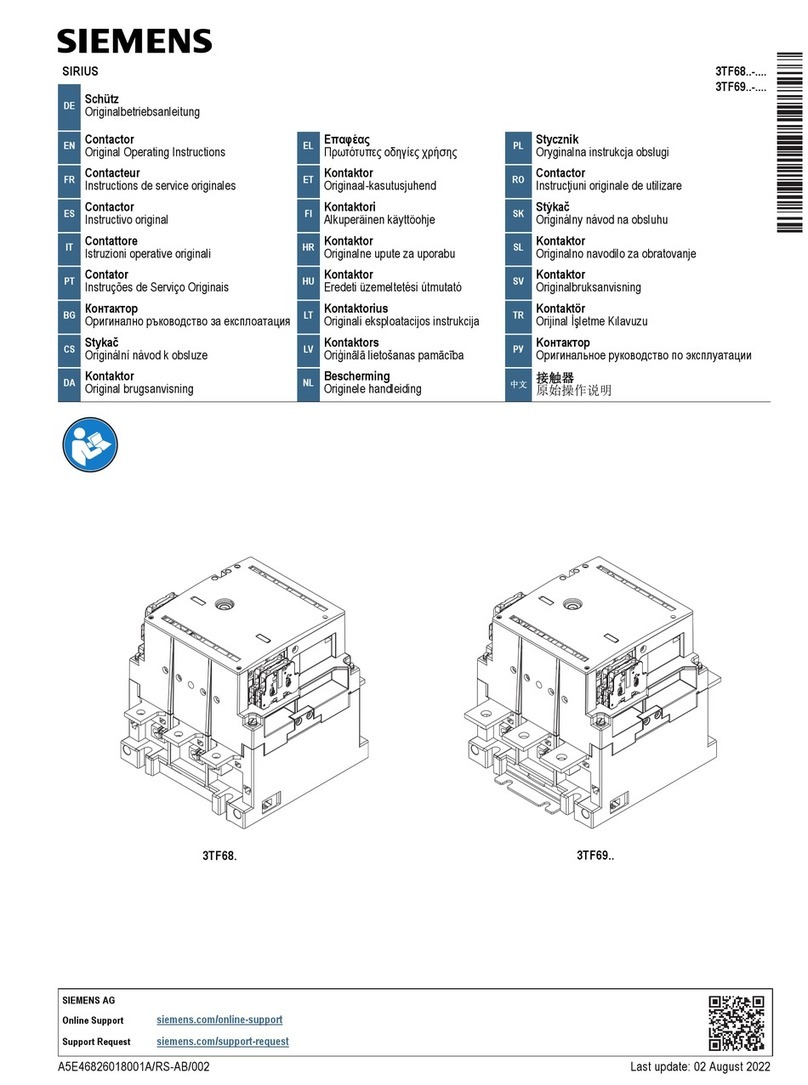
Siemens SIRIUS 3TF68 Series User manual
Siemens
Siemens SIVACON 8PS BD2 Series User manual

Siemens
Siemens Simatic S7-1500 User manual

Siemens
Siemens 3TF68 Q Series User manual

Siemens
Siemens 3VA1 Series User manual

Siemens
Siemens 3VA9117-0HB 0 Series User manual

Siemens
Siemens IP Viewer N151 Service manual

Siemens
Siemens SIVACON 8PS User manual

Siemens
Siemens SINAMICS G120P User manual

Siemens
Siemens SWT-3000 Technical Document

Siemens
Siemens 3VA9157-0PK11 User manual
Siemens
Siemens SIRIUS S00 User manual
Siemens
Siemens 8MF1000-2HA User manual
Popular Industrial Electrical manuals by other brands

Rexroth Indramat
Rexroth Indramat DURADRIVE SYSTEM200 Project planning manual

Abtech
Abtech HVJB Series Installation, operation & maintenance instructions
Murata
Murata GRM0335C1H8R1DA01 Series Reference sheet

SAF-HOLLAND
SAF-HOLLAND CBX 5415.5 Installation and operation manual

Eaton
Eaton Ulusoy HMH24-04 user manual
Murata
Murata GJM0335C1E4R4BB01 Series Reference sheet

Newlong
Newlong NP-7H NSTRUCTION MANUAL/PARTS LIST

Stahl
Stahl 8575/12 operating instructions
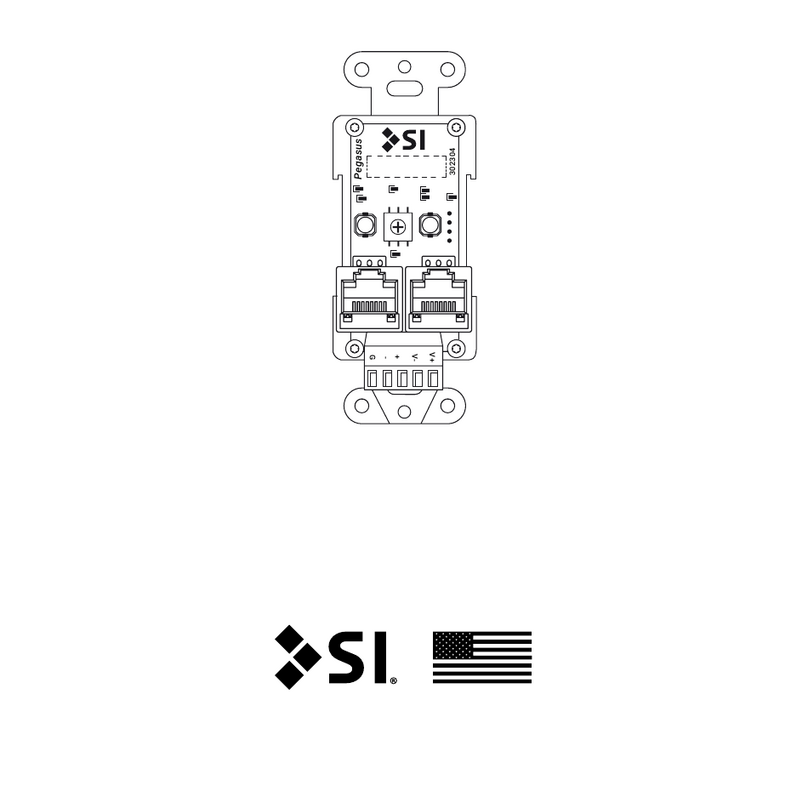
SI
SI Pegasus installation instructions
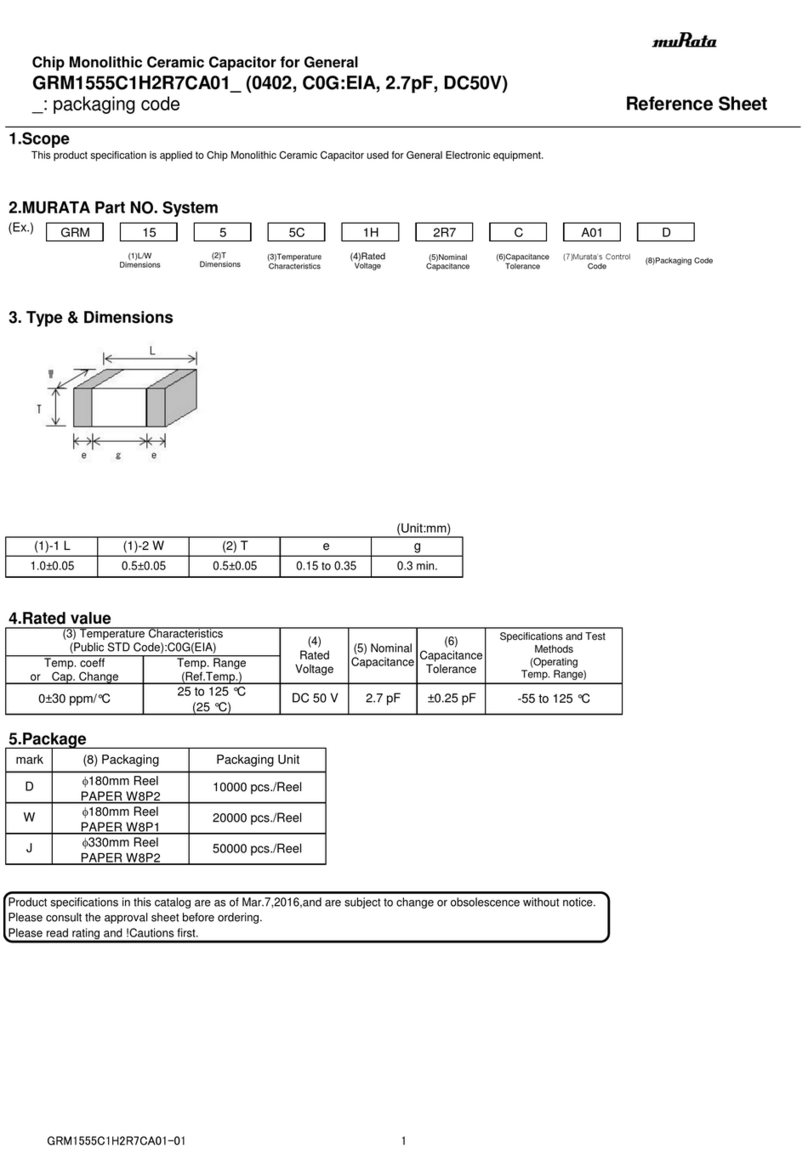
Murata
Murata GRM1555C1H2R7CA01 Seies Reference sheet
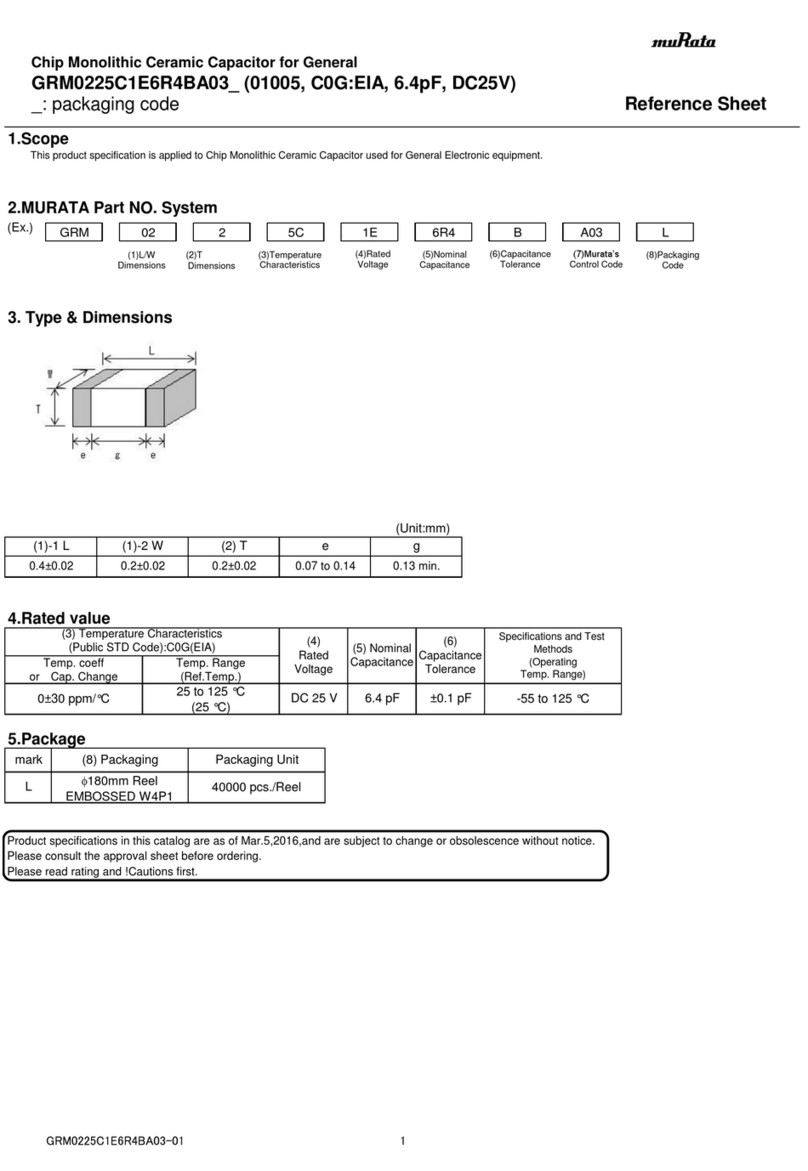
Murata
Murata GRM0225C1E6R4BA03 Series Reference sheet

Cooper Power Systems
Cooper Power Systems VXE15 Installation and operation instructions
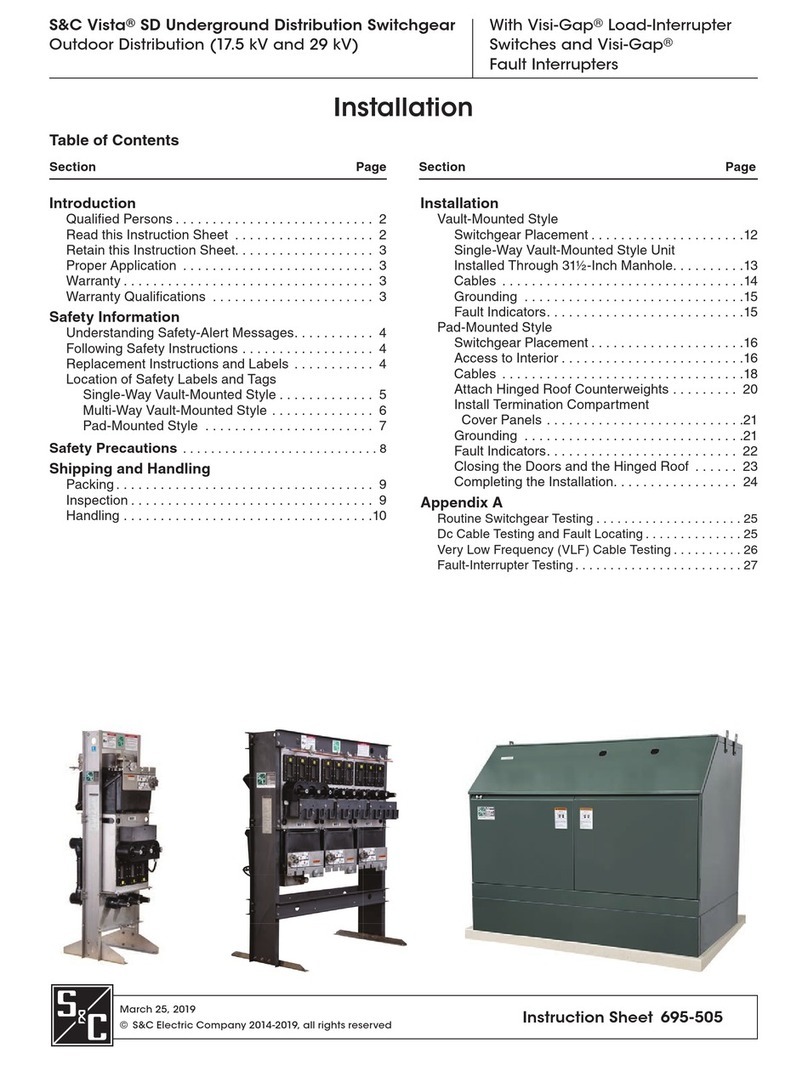
S&C
S&C Vista SD manual

Murata
Murata GRM0335C2A7R3CA01 Series Reference sheet
Murata
Murata GRM32ER60G227ME05 Series Reference sheet
Rockwell Automation
Rockwell Automation Allen-Bradley MP-Series installation instructions

Phasemation
Phasemation DG-100 owner's manual
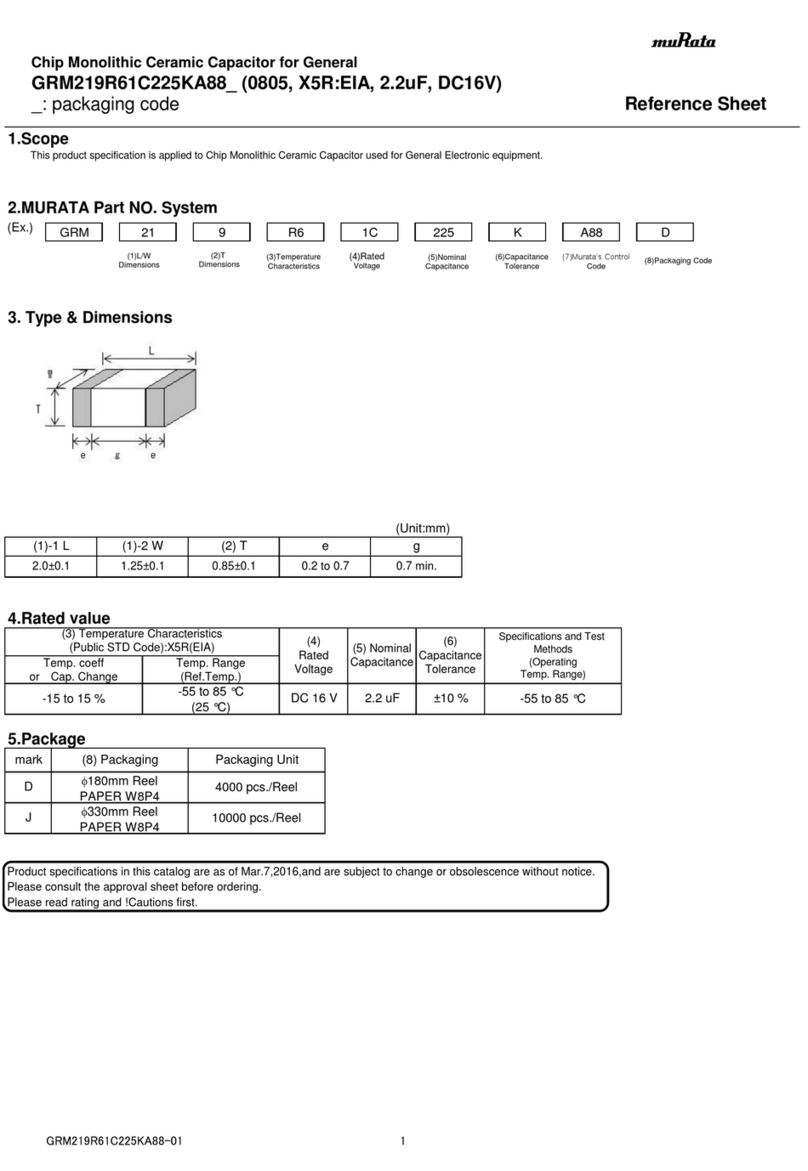
Murata
Murata GRM219R61C225KA88 Series Reference sheet