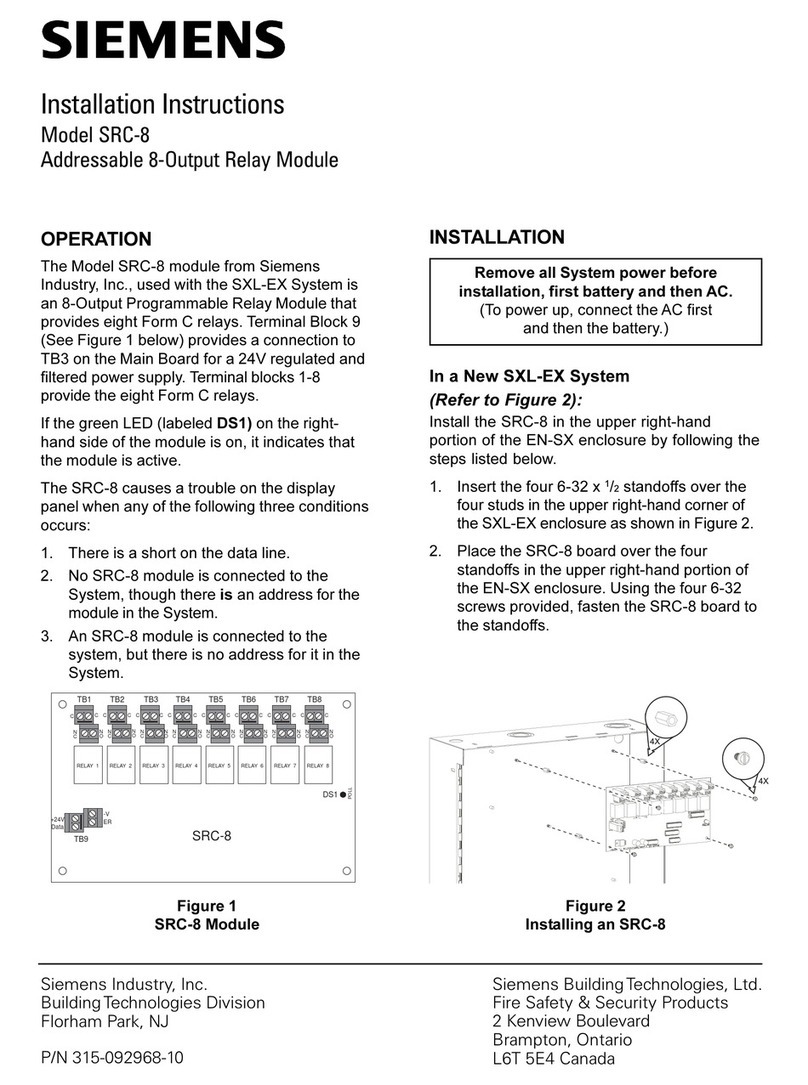
7SG163 Ohmega 300 Series SingleDEF
©2010 Siemens Protection Devices Ltd Chapter 12 Page 4 of 5
2.1 DEF Schemes
There are two active schemes for the relay.
2.1.1 DEF Direct Trip
In the DEF Direct Trip mode, the relay will trip on detecting an earth fault in the set direction. The DEF element is
time graded, and may be set to standard IEC or ANSI Curves or as a DTL element.
2.1.2 DEF POR
The other DEF scheme is DEF POR (permissive overreach). This is designed to be used in conjunction with a
signalling channel, to form a directional comparison scheme. When the DEF element operates it sends a
permissive signal, using the output contact assigned as Signal Send 2, to the remote end. In order to trip
instantaneously on DEF the relay must detect an earth fault on the forward direction and have received a signal to
Status Input Signal Receive 2 from the remote end. Obviously if the relays at both ends of the line detect a fault in
the forward direction, the fault must be within the line section, and tripping should be carried out instananeously.
In case the signalling channel fails, if the DEF element operates, and no signal is received from the remote end,
the relay will carry out a time delayed DEF back-up trip.
Additional logic is included within the DEF Scheme to ensure correct operation of the relay.
2.1.2.1 Current Reversal Guard
A current reversal guard is included to prevent incorrect tripping on parallel feeders.
Consider a fault at Point F on the parallel line system shown below:
Both Relay A and Relay B will detect earth fault current in the forward direction. Both DEF elements will operate,
permissive signals will be sent by both relays, and when these signals are received, Relays A and B will carry out
a DEF Aided Trip, isolating the fault.
Observing the direction of current flow, Relay C will also detect earth fault current in the forward direction , and
send a permissive signal to the remote end (Relay D). Relay D will detect earth fault current in the reverse
direction, and will not operate when the permissive signal is received from Relay C.
Now consider a situation, where the circuit breaker controlled by Relay B operates slightly before the circuit
breaker at A.
The direction of current seen by relays C and D will change, so Relay C will detect earth fault current in the
reverse direction, and relay D will detect earth fault current in the forward direction.
Under these circumstances, there is a “race condition” between the drop off of the Signal Send 2 output from
relay C and the operation of the forward DEF element at relay D.
If the DEF element at D operates before the Signal Send 2 from Relay C drops off, Relay D may mal-trip.
Thus, if the Circuit Breaker is closed, the relay does not detect fault current in the forward direction, a residual
voltage is present on the system,and a permissive signal has been received from the remote end, the Current
Reversal Guard logic is started. If the relay then detects a forward DEF it will enforce a time delay (the DEF
Current Reversal Reset) on the DEF Aided Trip to allow the remote end Signal Send 2 element to drop off, and
ensure stability of the protection.
2.1.2.2 CB Echo
The DEF POR scheme relies upon relays at both ends of the line detecting the fault. With the circuit breaker at
one end of the line open, the DEF element at one end cannot operate. Thus no permissive signal can be sent, so
the fault would be cleared after a time delay as a back-up trip for an in-zone fault.
Thus, if the local Circuit Breaker is open AND a permissive signal is received from the remote end, the relay will
send (or “echo”) a permissive signal back to the remote end. The duration of this permissive signal is set as the
POR CB Echo Pulse Width
Relay
D
Relay
C
S/Stn 1 S/Stn 2
Relay
B
Relay
A
F