4 Supporting Functional Safety Systems
By using the TPS6594-Q1 and LP8764-Q1 solution to power the DRA821 processor, the system can leverage
the following PMIC functional safety features:
• Independent Power Control of MCU and Main Rails
• Independent Monitoring and Reset for MCU and Main Rails
• Input Supply Monitoring
• Output Voltage and Current Monitoring
• Question & Answer Watchdog
• Fault Reporting Interrupts
• Enable Drive Pin that provides an independent path to disable system actuators
• Error Pin Monitoring
• Internal Diagnostics including voltage monitoring, temperature monitoring, and Built-In Self-Test
Refer to the Safety Manuals of the TPS6594-Q1 and LP8764-Q1 devices for full descriptions and analysis of
the PMIC functional safety features. These functional safety features can assist in achieving up to ASIL-D rating
for a system. Additionally, these features help in achieving the functional safety assumptions utilized by the
processor to achieve up to ASIL-D rating. See the DRA821 Safety Manual for Jacinto™ 7 Processors for a
complete list of functional safety system assumptions.
4.1 Achieving ASIL-B System Requirements
To achieve a system functional safety level of ASIL-B, the following PDN features are available:
• PMIC over voltage and under voltage monitoring on the power resource voltage outputs
• PMIC over-voltage monitoring and protection on the input to the PMIC (VCCA)
• Watchdog monitoring of safety processor
• MCU error monitoring
• MCU reset
• I2C communication
• Error indicator, EN_DRV, for driving external circuitry (optional)
• Read-back of EN_DRV pin
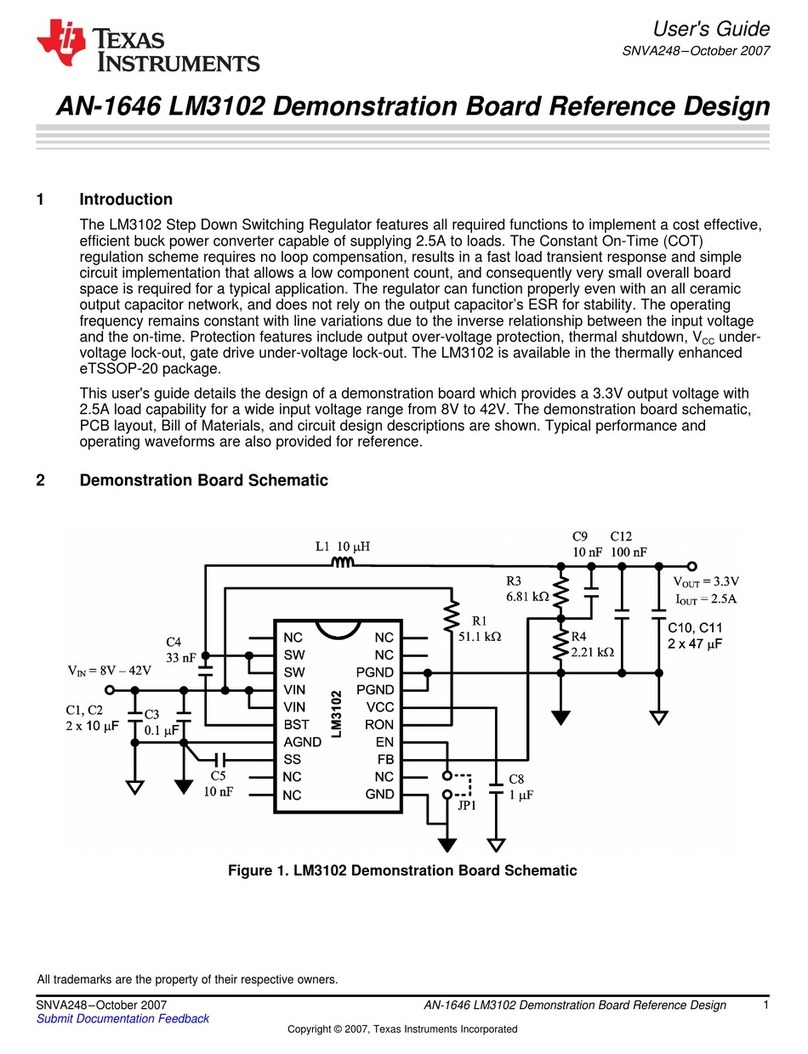
The PDN has an in-line, external power FET between the input supply and PMICs. This FET can quickly isolate
the PMICs when an over-voltage event greater than 6 V is detected on the input supply to protect the system
from being damaged, as shown in Figure 3-1. Note that any power rail connected after the FET can be protected
from an over voltage event. Any power connected upstream from the FET is not protected from over voltage
events. In Figure 3-1 the load switches that supply power to the MCU and Main I/O domains and the discrete
buck supplying the DDR are all connected after the FET to extend the over voltage protection to these processor
domains and discrete power resources.
The PMIC internal over voltage and under voltage monitoring and their respective monitoring threshold levels
can be enabled through I2C after startup. To monitor the load switch voltage that supplies the MCU I/O of the
processor, it is recommended to use the processor POK monitor built into the VDDSHV0_MCU voltage domain.
The PMIC Internal Q&A Watchdog is enabled by default on the TPS6594-Q1 device. Once the device is in
ACTIVE state, the trigger or Q&A watchdog settings can be configured through the secondary I2C in the device.
The steps for configuring the watchdog settings can be found in the TPS6594-Q1 data sheet. Setting the
DISABLE_WDOG signal high on TPS6594-Q1 GPIO_8 disables the watchdog timer if this feature needs to be
suspended or is not required in the system.
GPIO_7 of the TPS6594-Q1 PMIC is configured as the MCU error signal monitoring, and must be enabled
though the ESM_MCU_EN register bit. MCU reset is supported through the connection between the primary
PMIC nRSTOUT pin and the MCU_PORz of the processor. Lastly, there are 2 I2C ports between the TPS6594-
Q1 and the processor. The first is used for all non-watchdog communication, such as voltage level control, and
the second allows the watchdog monitoring to be on an independent communication channel.
There is an option to use the EN_DRV of theTPS6594-Q1 PMIC to indicate an error has been detected and the
system is entering SAFE state. This signal can be utilized if the system has some additional external circuitry
that needs to be driven by an error event. In this PDN, the EN_DRV is not utilized, but available if needed.
www.ti.com Supporting Functional Safety Systems
SLVUBY7A – OCTOBER 2020 – REVISED OCTOBER 2022
Submit Document Feedback
Powering DRA821 with TPS6594-Q1 and LP8764-Q1 9
Copyright © 2022 Texas Instruments Incorporated