ADL300 CiA® 417- Description of functions and parameter list Page 3 of 46
Table of contents
1. Introduction ............................................................................................................................................................... 4
2. REFERENCE STANDARDS....................................................................................................................................... 5
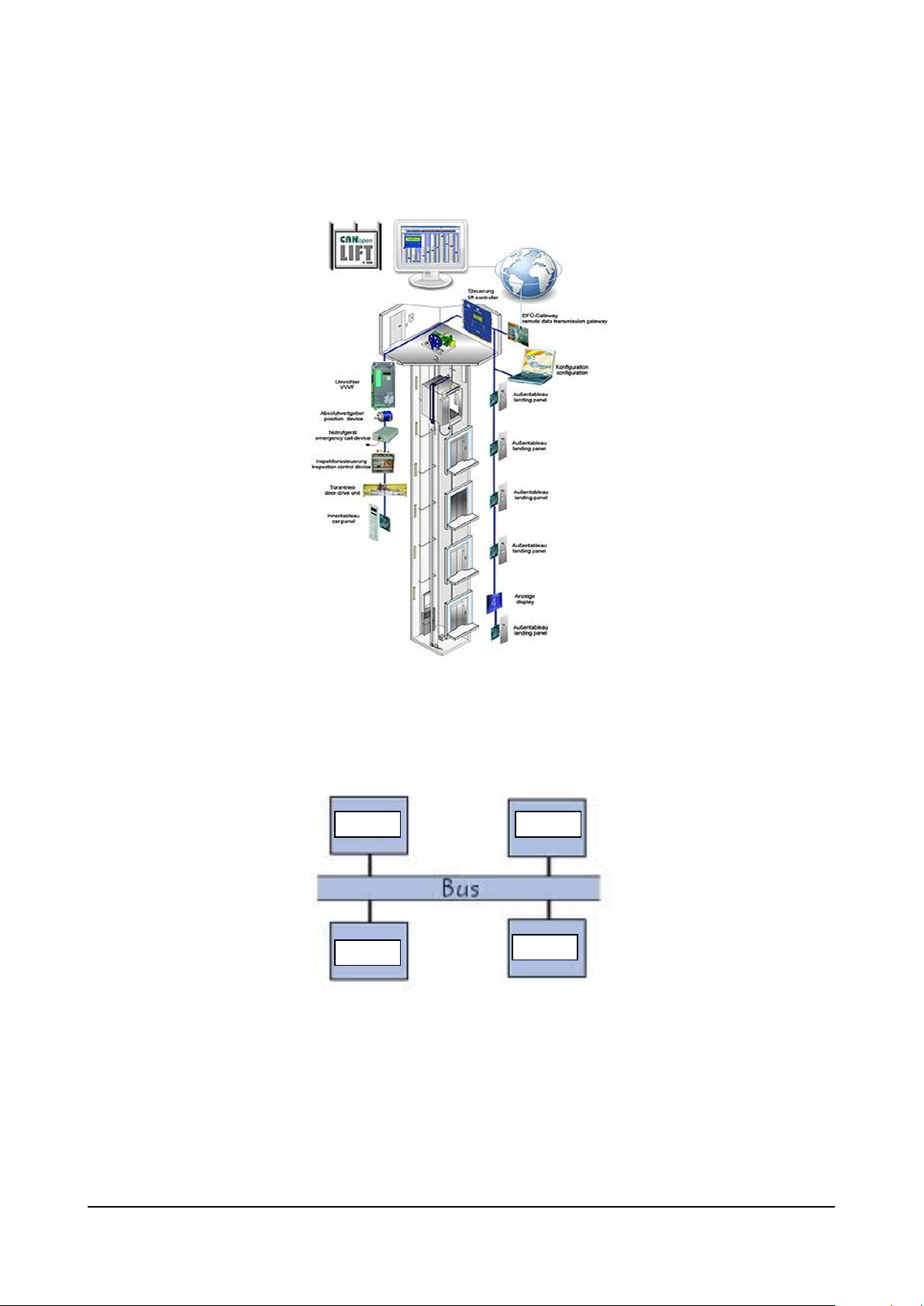
3. A STANDARD COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL ....................................................................................................... 6
4. SHARING THE DRIVE MENU .................................................................................................................................... 8
5. FUNCTIONAL LOGIC................................................................................................................................................. 9
6. Control mode........................................................................................................................................................... 10
6.1 Speed Control ................................................................................................................................................... 10
6.2 Position Control ................................................................................................................................................. 11
7. SUPPORTED ARCHITECTURES ............................................................................................................................ 12
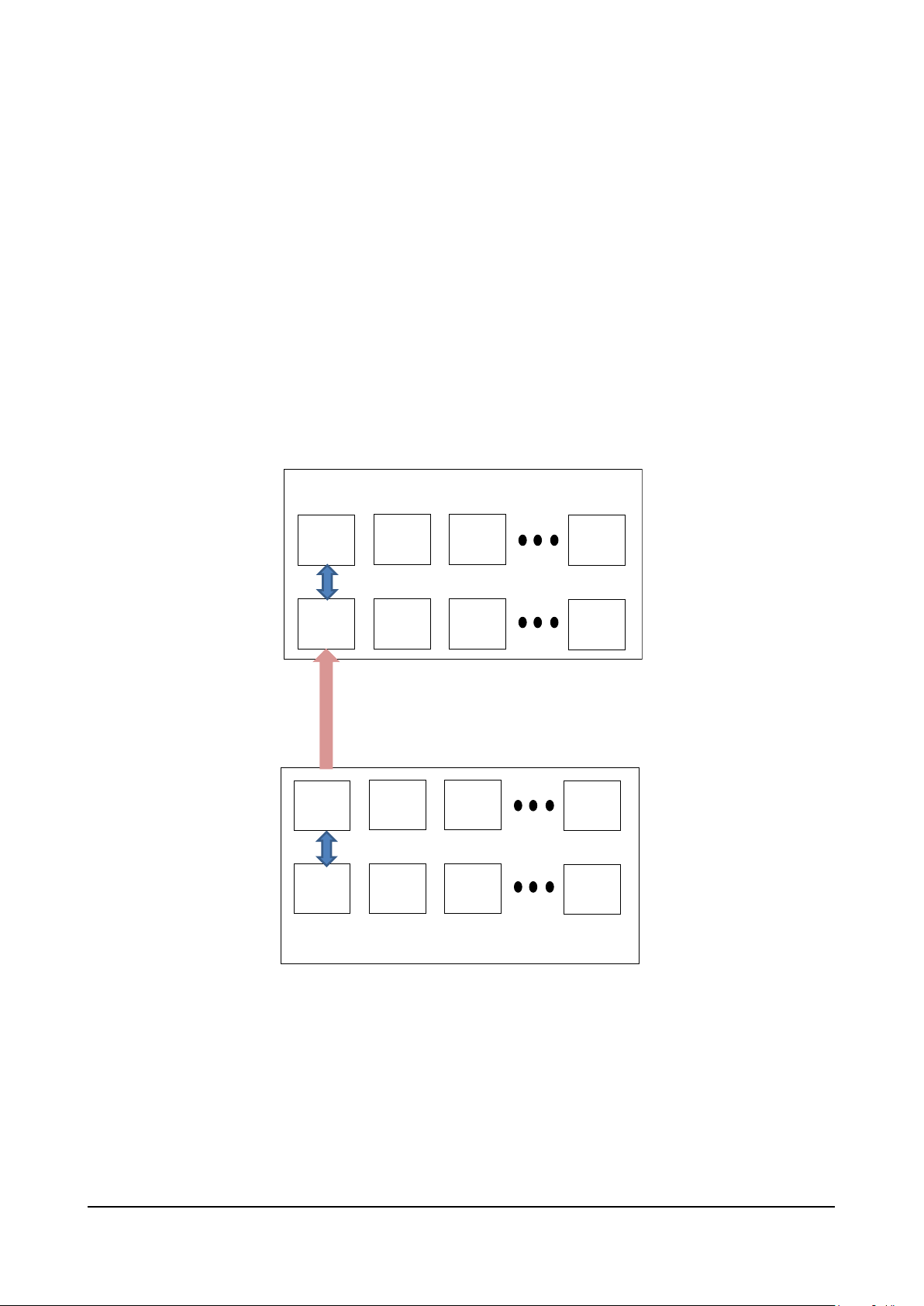
8. APPLICATION OBJECTS AND PROCESS DATA OBJECTS MANAGED............................................................. 13
8.1 Process Data Object ......................................................................................................................................... 13
8.2 Application Object ............................................................................................................................................. 13
9. STATE MACHINE..................................................................................................................................................... 14
10. DRIVE CONNECTION .............................................................................................................................................. 15
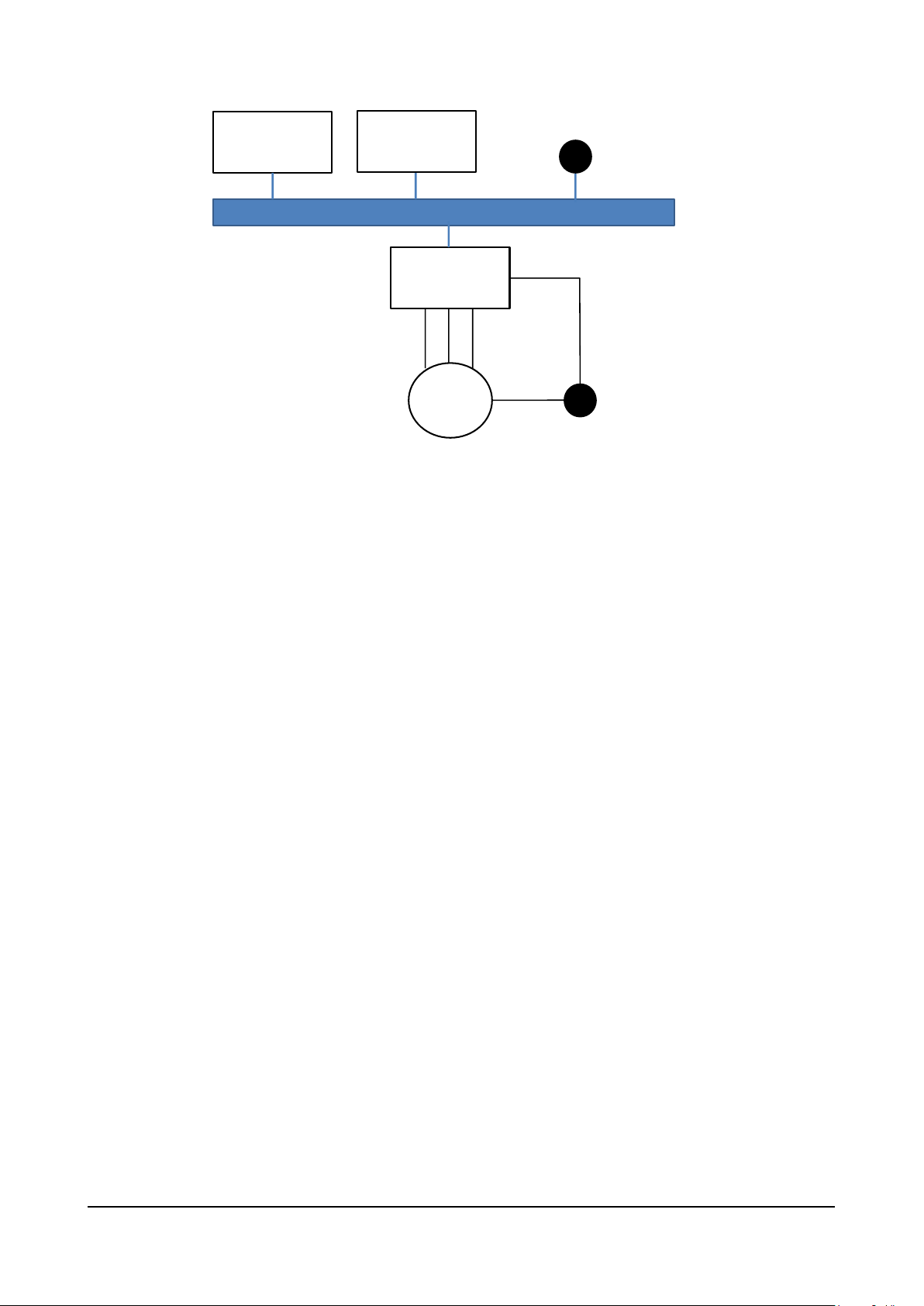
10.1 Interface with Master CAN................................................................................................................................. 15
10.2 Wiring ................................................................................................................................................................ 16
10.3 Bus connection.................................................................................................................................................. 16
10.4 Bit Rates Supported .......................................................................................................................................... 17
10.5 Node IDs ........................................................................................................................................................... 17
11. INSTALLING THE APPLICATION ........................................................................................................................... 18
11.1 General ............................................................................................................................................................. 18
11.2 Requirements.................................................................................................................................................... 18
11.3 Preliminary operations....................................................................................................................................... 18
12. COMMISSIONING FROM ALPHANUMERIC KEYPAD ........................................................................................... 19
13. DESCRIPTION OF PARAMETERS.......................................................................................................................... 22
13.1 Legend .............................................................................................................................................................. 22