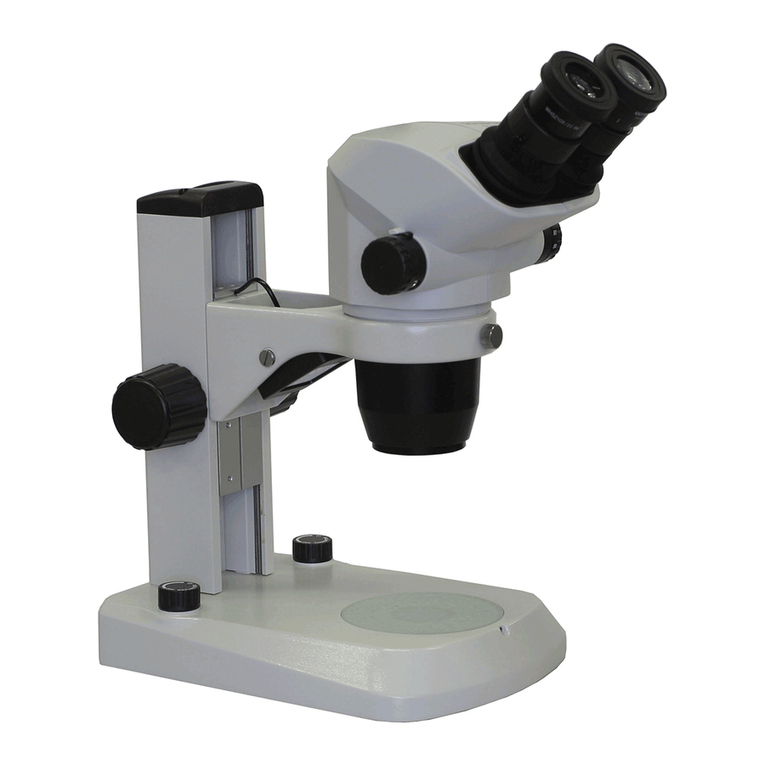
Zeiss EM 10 A User manual
Other Zeiss Microscope manuals

Zeiss
Zeiss VISU 200 User manual

Zeiss
Zeiss LSM 710 User manual

Zeiss
Zeiss ?IGMA VP-FE-SEM User manual

Zeiss
Zeiss IV FL User manual

Zeiss
Zeiss AxioImager A1 Assembly instructions

Zeiss
Zeiss AxioObserver D1 User manual
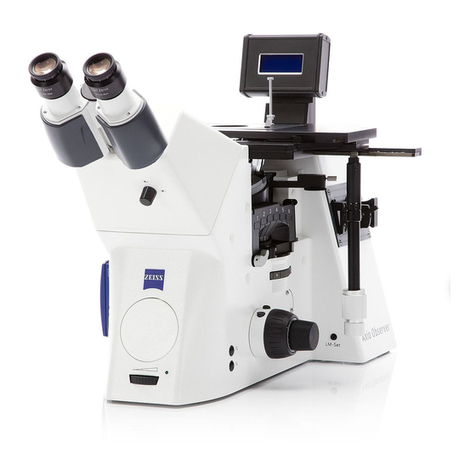
Zeiss
Zeiss Axio Observer Series User manual

Zeiss
Zeiss OPMI VISU 160 User manual

Zeiss
Zeiss Stemi 305 User manual

Zeiss
Zeiss LSM 800 User manual

Zeiss
Zeiss Crossbeam 350 User manual

Zeiss
Zeiss Transillumination top 450 mot. User manual
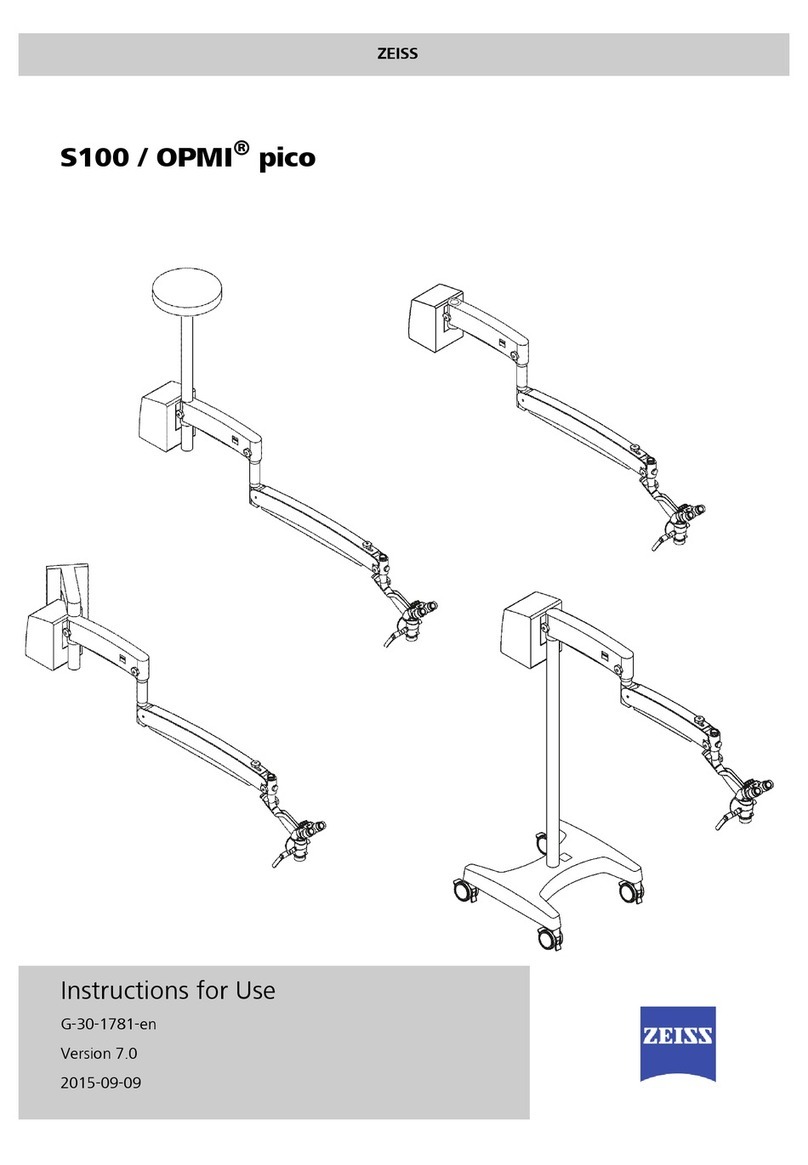
Zeiss
Zeiss S100/OPMI pico User manual

Zeiss
Zeiss LSM 900 User manual

Zeiss
Zeiss Smartzoom 5 User manual

Zeiss
Zeiss Smartzoom 5 User manual

Zeiss
Zeiss SIGMA Series User manual

Zeiss
Zeiss OPMI PROergo S7 User manual

Zeiss
Zeiss Axio Imager User manual

Zeiss
Zeiss Axio Scope.A1 User manual