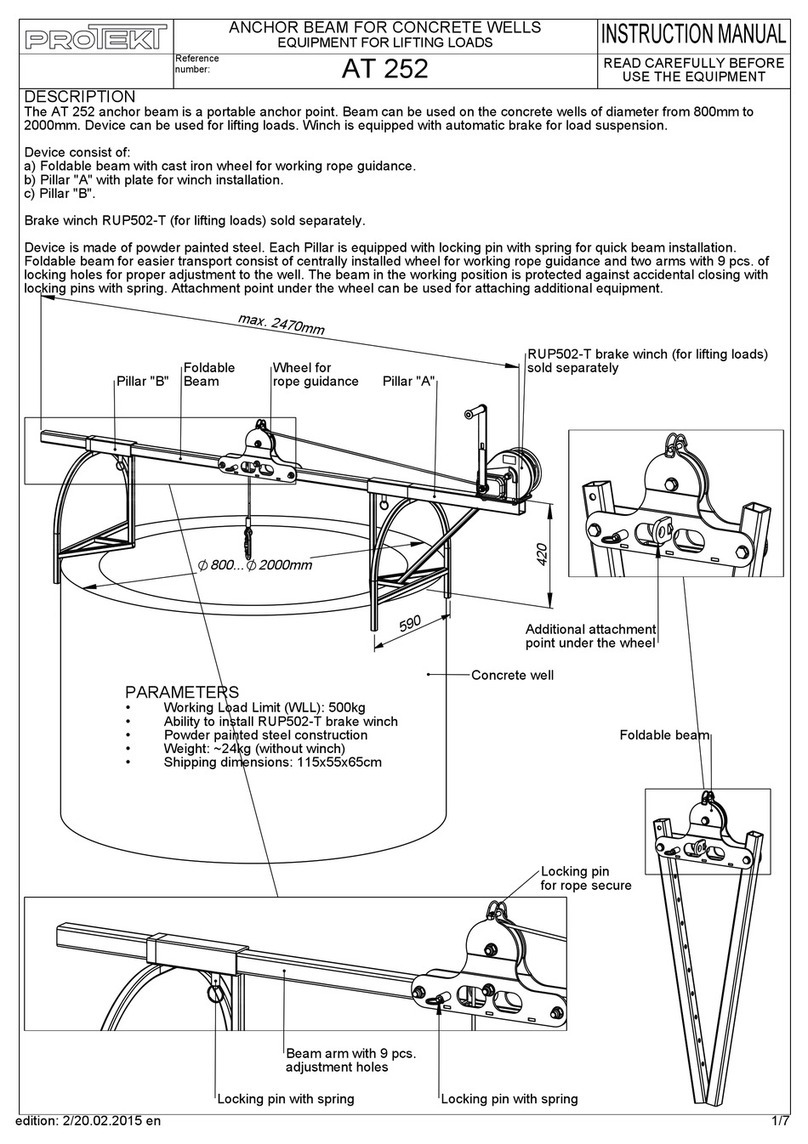
3
Sehr geehrter Kunde,
vielen Dank, dass Sie sich für ein ALFRA-Produkt entschieden haben. Lesen Sie diese Bedienungsanleitung vor der
ersten Verwendung Ihres neuen Gerätes aufmerksam durch und heben Sie sie zusammen mit der beigelegten
Product Control Card auf, um bei Bedarf darin nachschlagen zu können.
Sicherheitshinweise
Beim Transport von Lasten entstehen durch unsachgemäße Handhabung und/oder schlechte Wartung der Hebe-
zeuge Gefahren, die zu schweren Unfällen mit tödlichen Verletzungen führen können. Lesen Sie diese
Bedienungsanleitung sehr genau und befolgen Sie alle aufgeführten Sicherheitshinweise. Wenden Sie sich bei
Fragen an den Hersteller.
•den Lasthebemagneten vollständig aktivieren
•den Lasthebemagneten auf metallischen, ferromagnetischen Materialien aktivieren
•Lasten senkrecht heben
•die gesamte Magnetfläche beim Heben nutzen
•auf planen Oberflächen heben
•die magnetische Haltekraft prüfen, indem die Last um etwa 10 cm angehoben wird
•die Magnetfläche reinigen und von Schmutz, Spänen und Schweißkörnern befreien
•den Lasthebemagneten sanft absetzen, um die Magnethaftfläche nicht zu beschädigen
•den Gefahrenbereich beim Heben der Last überprüfen
•den gesamten Lasthebemagneten und insb. die Magnetfläche auf Beschädigung prüfen
•die passenden Hebezeuge verwenden
•die Anweisungen dieser Bedienungsanleitung befolgen
•neue Nutzer in den sicheren Gebrauch von Lasthebemagneten einweisen
•die lokalen, landesspezifischen Richtlinien befolgen
•in einer trockenen Umgebung lagern und verwenden
Niemals…
•runde oder gewölbte Objekte heben
•eine seitliche Belastung der Ringschraube zulassen
•über der angegebenen Maximallast heben
•Lasten über Personen hinweg transportieren
•mehrere Werkstücke gleichzeitig anheben
•den Lasthebemagneten deaktivieren, bevor die Last sicher abgesetzt ist
•Lasten zum Schwingen bringen oder abrupt anhalten
•Lasten außerhalb der empfohlenen Größen heben
•Lasten mit Hohlräumen, Ausschnitten oder Bohrungen heben
•ungleichmäßige Lasten heben
•Veränderungen am Lasthebemagneten vornehmen oder Hinweisschilder entfernen
•den Lasthebemagneten bei Beschädigung oder bei fehlenden Teilen verwenden
•die Magnetunterseite starken Stößen oder Schlägen aussetzen
•unter der gehobenen Last aufhalten
•Lasten anheben, so lange sich Personen im Gefahrenbereich aufhalten
•die gehobene Last unbeaufsichtigt lassen
•den Lasthebemagneten ohne fachgerechte Einweisung verwenden
•benutzen, sofern diese Bedienungsanleitung nicht vollständig gelesen und verstanden wurde
•den Lasthebemagneten zum Unterstützen, Heben oder Transportieren von Personen nutzen
•den Lasthebemagneten bei Temperaturen über 60°C (140°F) betreiben
•mit ätzenden Stoffen in Verbindung bringen
Personen mit Herzschrittmacher oder anderen medizinischen Apparaten dürfen den
Lasthebemagneten nur nach vorheriger Zustimmung eines Arztes benutzen!