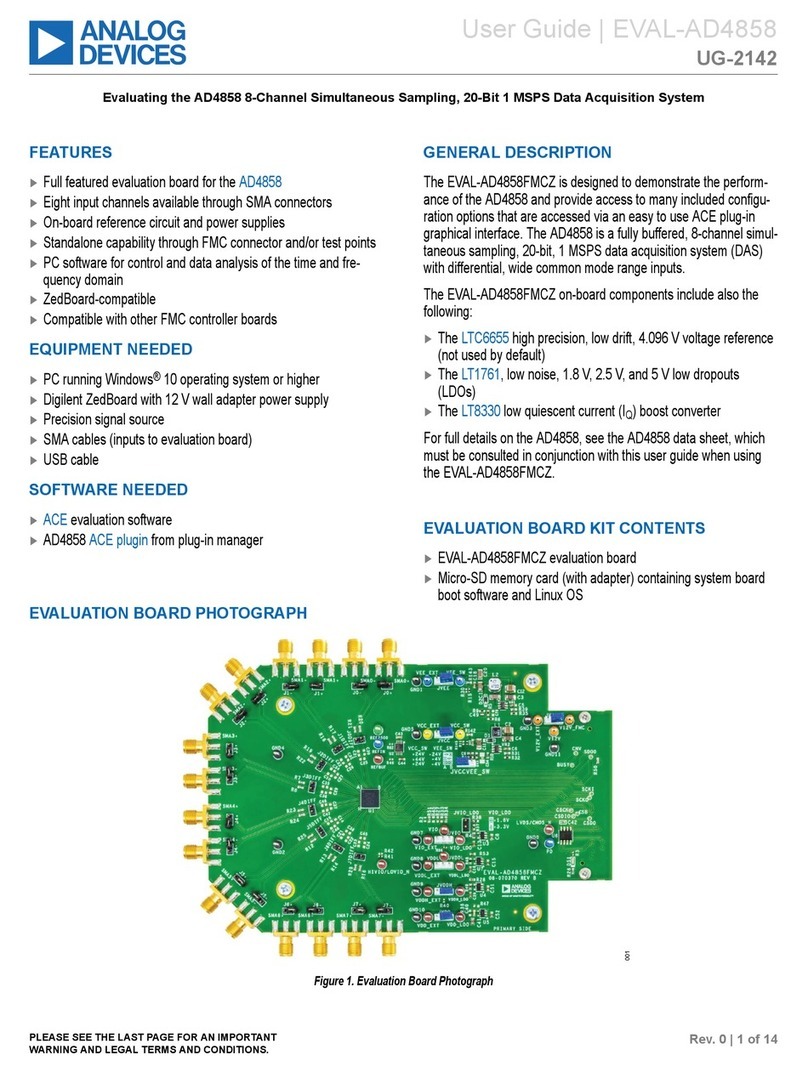
Evaluation Board User Guide UG-203
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 8
EVALUATION BOARD HARDWARE
The following instructions are for setting up the physical
connections to the AD9550 evaluation board.
SETTING UP THE POWER CONNECTIONS
Set up the power connections as follows:
1. The AD9550 evaluation board is powered via the TB1
connector located in the top center of the evaluation board.
Connect Pin 1 and Pin 5 to ground. Connect Pin 2, Pin 3,
Pin 4, and Pin 6 to a 3.3 V power supply.
2. Pin 2, Pin 3, Pin 4, and Pin 6 may be tied together as well
as Pin 1 and Pin 5, for ease of use.
SETTING UP THE SIGNAL CONNECTIONS
After setting up the power connections, use the following
procedure to set up the signal connections:
1. Connect a 3.3 V CMOS signal, with the intended input
frequency, to the reference input (SMA Connector J1,
labeled REFA). By default, the reference input of this
evaluation board is dc-coupled.
2. The AD9550 does not support a differential input or a
secondary input (REFB).
3. Connect a measurement device (such as oscilloscope,
spectrum analyzer, or frequency counter) to any of the
SMA Connectors J3 through J6. By default, the output
signals of the AD9550 evaluation board are ac-coupled
with a 100 Ω differential termination.
PROGRAMMING THE AD9550 GUIDELINES
The AD9550 is programmed via pin programming, that is,
setting the logic levels on the frequency select pins of the device,
which is accomplished by using the DIP switches located on
four switch groupings, S1 through S4, located at the bottom
right of the AD9550 evaluation board. Within the frequency
select pins are three subsets of pins, A[3:0], Y[5:0], and
OM[2:0], which together determine the AD9550 operation. The
A[3:0] pins define the expected reference input frequency, the
Y[5:0] pins define the output frequency, and the OM[2:0] pins
define the output drivers. Once the user-defined pin
combinations are implemented via the DIP switches and the
expected reference input frequency is preset, the RESET pin
should be toggled low to high to reset the AD9550, load the part
settings defined by the frequency select pins, and assert an
autocalibration on the VCO. Note that some A[3:0] and Y[5:0]
pin combinations are not compatible or may require the
changing of external loop filter components on the evaluation
board (described in further detail in the Loop Filter section). To
avoid this, verify the chosen frequency select pin combinations
with Table 4.
DIP SWITCH PIN CONTROL DESCRIPTIONS
A[3:0] Pins
These pins define a four-digit binary value, which is decoded to
a set of predetermined input frequencies, described in Table 2.
These pins are located on Switch Group S3.
Y[5:0] Pins
These pins define a six-digit binary value, which is decoded to a
set of predetermined output frequencies, described in Table 3.
These pins are located across Switch Group S1 and Switch
Group S2. Note that the A[3:0] and Y[5:0] pin combination
determines the charge pump current and feedback divider of
the PLL (see Table 4).
OM[2:0] Pins
These pins define a three-digit binary value, which is decoded
to a set of predetermined output driver modes for the two
output clocks, described in Table 1. These pins are located on
Switch Group S4.
Table 1. Logic Family Assignment via the OM[2:0] Pins
OM[2:0]
Logic Family
OUT1 OUT2
000 LVPECL LVPECL
001 LVPECL LVDS
010 LVDS LVPECL
011 LVPECL CMOS
100 LVDS LVDS
101 LVDS CMOS
110 CMOS LVDS
111 CMOS CMOS
RESETB Pin
This pin performs a hard reset of the AD9550. It also asserts
an autocalibration of the VCO, though this calibration is
only effective if the frequency select pins are set to a valid
combination and a valid reference input frequency, as
determined by the A[3:0] pins, at the time that RESETB is
brought high.
REFB_SEL Pin
The AD9550 supports only one reference input and; therefore,
this pin is tied to a logic low state.