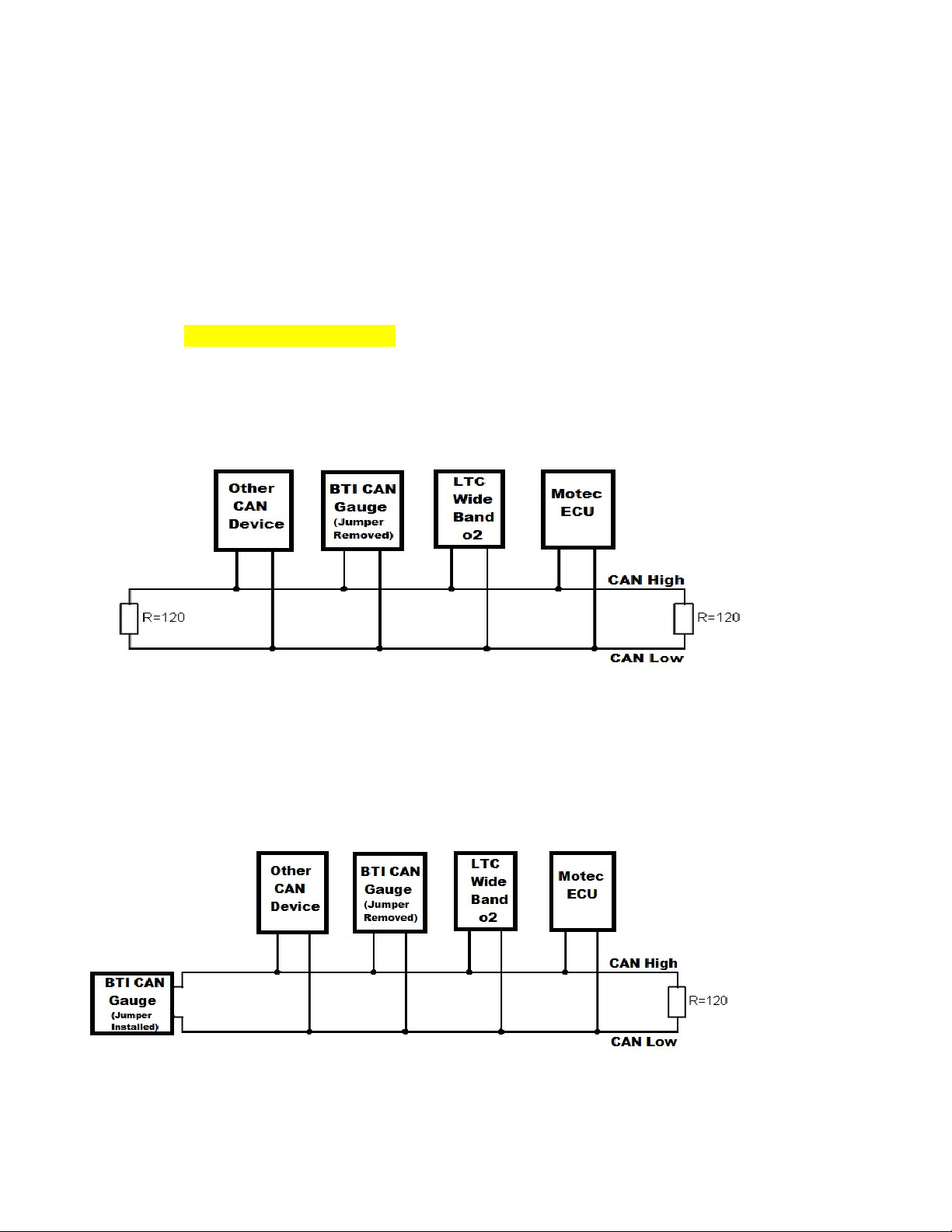
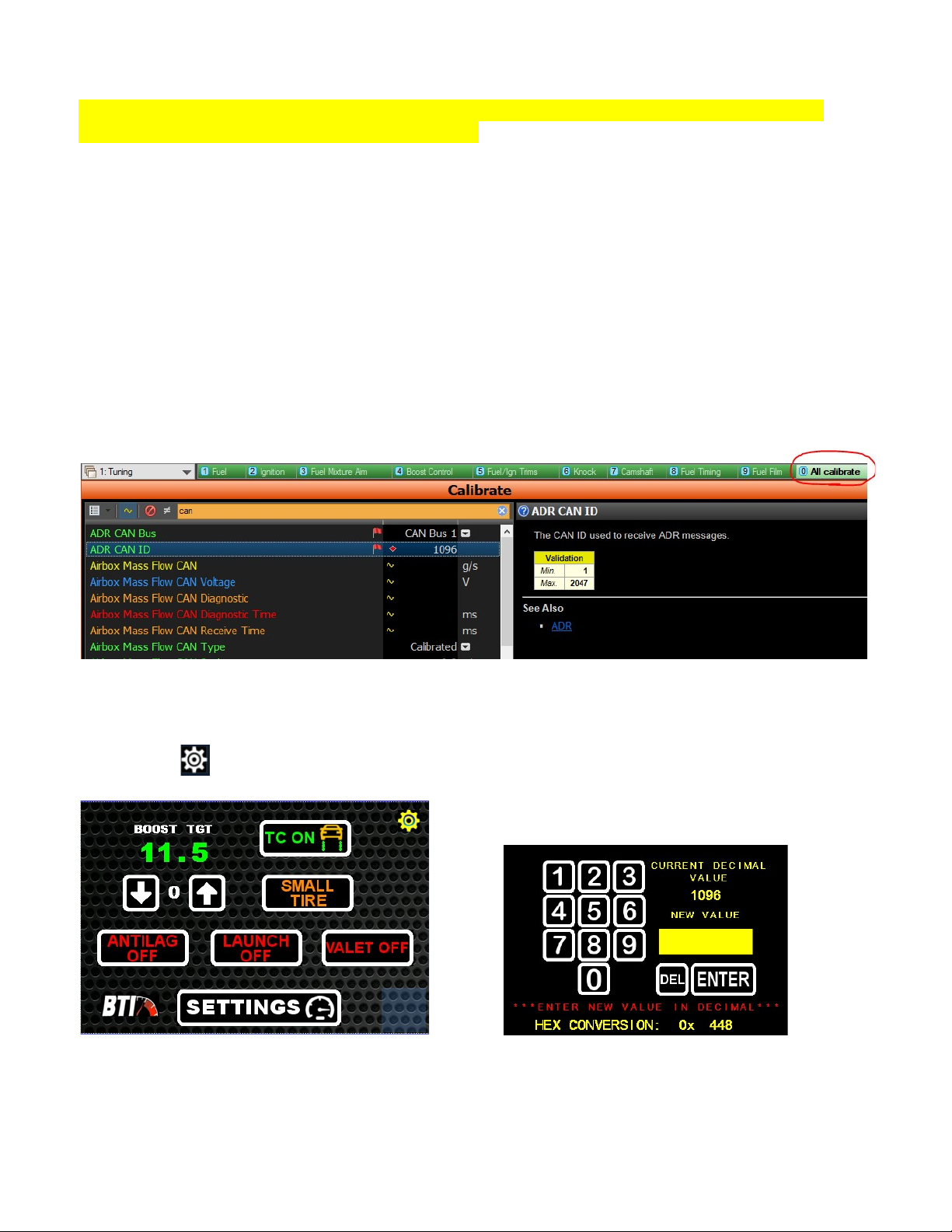
Parameter scale: Use this screen to set the maximum
range for boost pressure and various temperature slide
bars and graphs.
Example: You will be running a 30 psi boost target. The
max boost pressure could be 35 psi to give the slide bars
and graphs the best resolution. The same goes for
temperatures. These values should be entered with
respect to which units are selected: SI or SAE. If SI units
are selected, Boost Pressure should be entered in kPa
and temps should be entered in Celsius. If SAE units are
selected, Boost Pressure should be entered in psi and temps in Fahrenheit.
Shift Light Configuration:
Touch the gear that you wish to change the shift light
RPM on. That gear number will appear above the up and
down arrows for verification. Use the up and down arrows
to adjust the shift light RPM set-point of said gear. Press
the back arrow button at the bottom right hand corner to
save the settings. The shift light should flash once the
settings are saved.
Base Fuel Pressure configuration:
In order to calculate the base fuel pressure, the engine
should be idling. Press the CALCULATE button and the
base pressure will be calculated and displayed. This is
used on the fuel screen in order to graph the fuel
pressure vs. boost pressure for simple regulator function
verification.
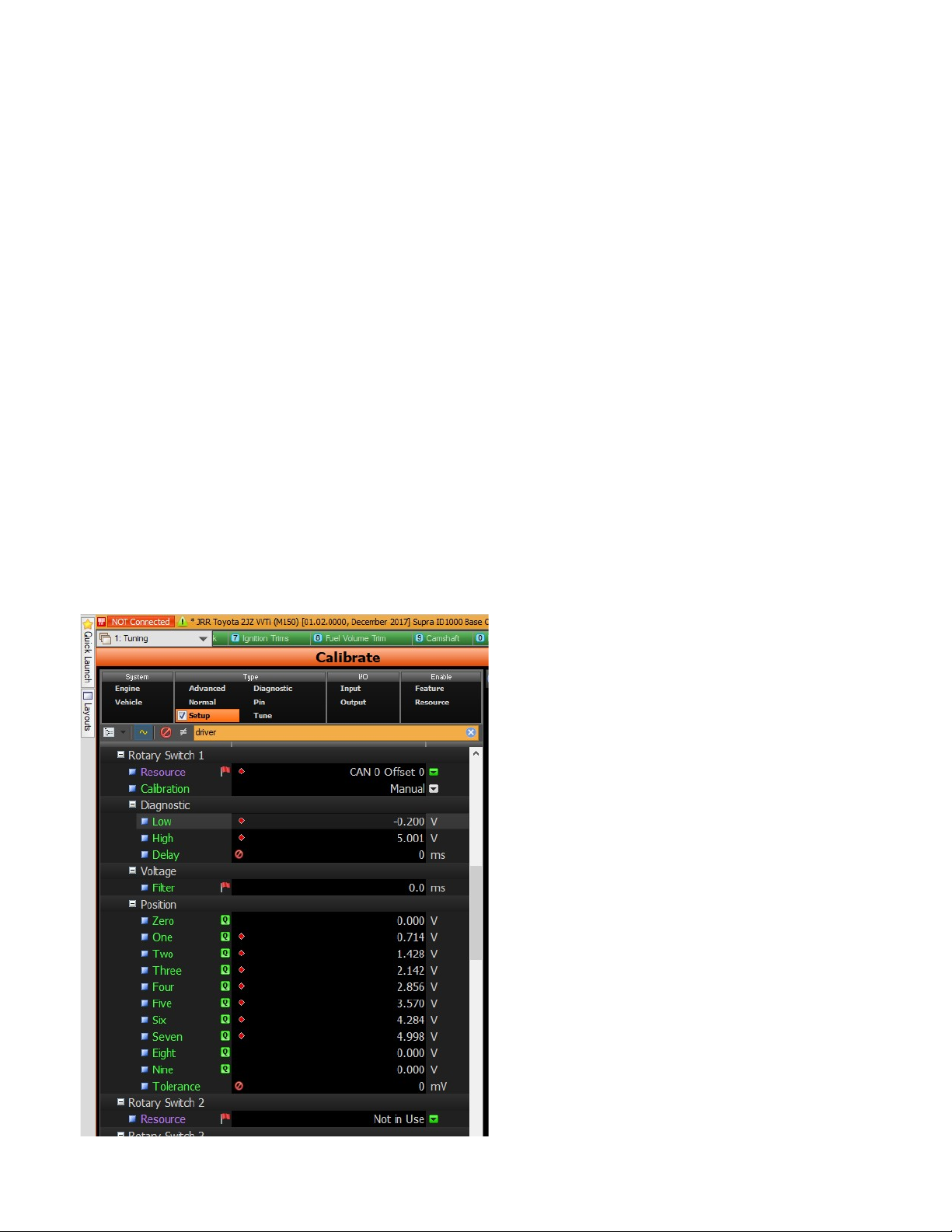
TRAC and BOOST PWM Steps:
Use these two buttons to configure how many steps are to
be programmed in the Infinity Tuner software for Boost
and Slip. Typically the scale is from 0-5 volts and the max
amount of steps allowed is 7 which give you 8 settings (0-
7). Example: a value of 7 here would make each step
would have a value of .71 volts. A value of 1 here would
give the step a value of 5 volts. It is imperative to view
each step in the M1 Tuner software when configuring this
as there could be a potential difference with regard to