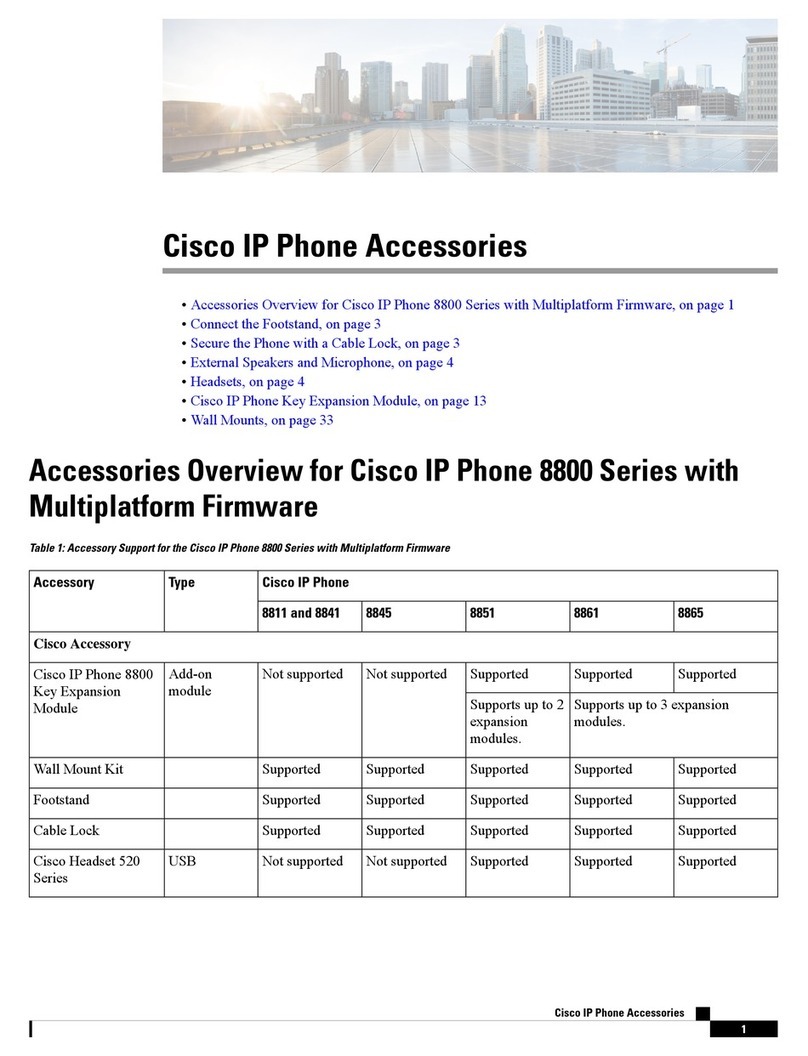
1-3
Cisco ATA 187 Analog Telephone Adaptor Administration Guide for SIP (Version 1.0)
OL-21862-01
Chapter 1 Cisco ATA 187 Analog Telephone Adaptor Overview
Session Initiation Protocol Overview
•Determines the media capabilities of the target endpoint. Using the Session Description Protocol
(SDP), SIP determines the lowest level of common services between endpoints. Conferences are
established using only the media capabilities that are supported by all endpoints.
•Establishes a session between the originating and target endpoint. If the call can be completed, SIP
establishes a session between the endpoints. SIP also supports mid-call changes, such as adding
another endpoint to the conference or changing the media characteristic or codec.
•Handles the transfer and termination of calls. SIP supports the transfer of calls from one endpoint
to another. During a call transfer, SIP establishes a session between the transferee and a new
endpoint (specified by the transferring party) and terminates the session between the transferee and
the transferring party. At the end of a call, SIP terminates the sessions between all parties.
Conferences can consist of two or more users and can be established using multicast or multiple
unicast sessions.
Components of SIP
SIP is a peer-to-peer protocol. The peers in a session are called User Agents (UAs). A user agent can
function in one of these roles:
•User agent client (UAC)—A client application that initiates the SIP request.
•User agent server (UAS)—A server application that contacts the user when a SIP request is received
and returns a response on behalf of the user.
Typically, a SIP endpoint is capable of functioning as both a UAC and a UAS, but functions only as one
or the other per transaction. Whether the endpoint functions as a UAC or a UAS depends on the UA that
initiated the request.
From an architectural standpoint, the physical components of a SIP network can also be grouped into
two categories—Clients and servers. Figure 1-3 illustrates the architecture of a SIP network.
Note SIP servers can interact with other application services, such as Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
(LDAP) servers, a database application, or an extensible markup language (XML) application. These
application services provide back-end services such as directory, authentication, and billable services.