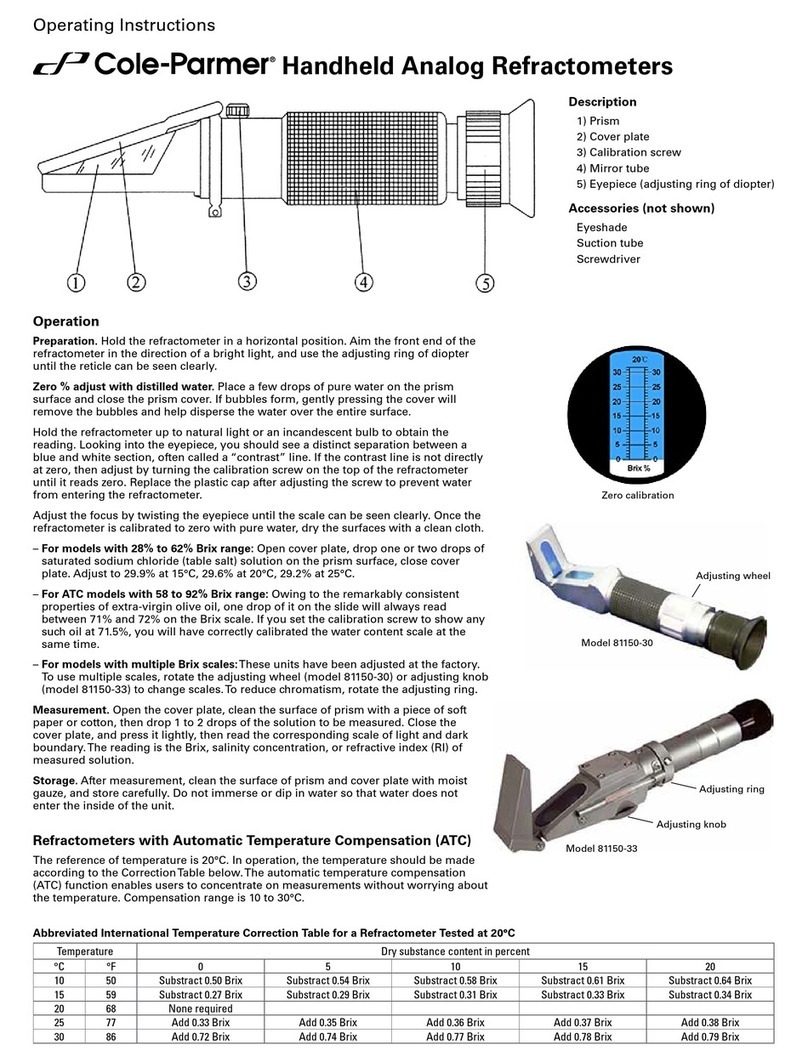
6
9.1.3 Setting the Measurement Time Interval .................................................................... 37
9.1.4 Setting Lag Time..................................................................................................... 37
9.1.5 Selecting Absorbance or % Transmittance................................................................. 37
9.1.6 End Point Concentration .......................................................................................... 37
9.2 Calibration.................................................................................................................... 38
9.3 Sample Measurement.................................................................................................... 38
9.4 Data Analysis................................................................................................................ 40
Section 10 - Multi-Wavelength.......................................................................
41
10.1 Method Set up.............................................................................................................. 41
10.1.1 Selecting a Wavelength ........................................................................................... 41
10.1.2 Equation Parameters ............................................................................................... 42
10.1.2.1 Entering a Factor............................................................................................... 43
10.1.2.2 Selecting Concentration Units............................................................................. 43
10.1.3 Selecting Absorbance or % Transmittance................................................................. 43
10.2 Calibration.................................................................................................................... 44
10.3 Sample Measurement.................................................................................................... 44
Section 11 - Saving, Loading, Deleting and Printing......................................
45
11.1 Saving Methods ............................................................................................................ 45
11.1.1 Saving Methods to Internal Memory ......................................................................... 45
11.1.2 Saving Methods to CPLive........................................................................................ 45
11.1.3 Saving Methods to USB Memory Stick....................................................................... 45
11.2 Loading Methods .......................................................................................................... 45
11.2.1 Loading Methods from Internal Memory.................................................................... 45
11.2.2 Loading Methods from USB Memory Stick ................................................................. 45
11.3 Deleting Methods.......................................................................................................... 45
11.4 Saving Results .............................................................................................................. 46
11.4.1 Saving Results to Internal Memory ........................................................................... 46
11.4.2 Saving Results to CPLive.......................................................................................... 46
11.4.3 Saving Results to USB Memory Stick......................................................................... 46
11.5 Loading Results ............................................................................................................ 46
11.5.1 Loading Results from Internal Memory ..................................................................... 46
11.5.2 Loading Results from USB Memory Stick................................................................... 46
11.6 Deleting Results............................................................................................................ 46
11.7 Printing ........................................................................................................................ 46
Section 12 - Accessories and Spare Parts ......................................................
47
12.1 Optional Accessories ..................................................................................................... 47