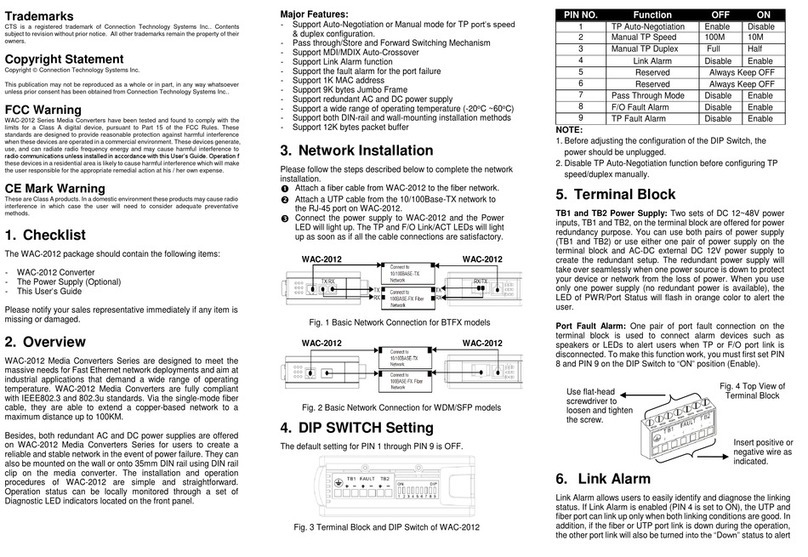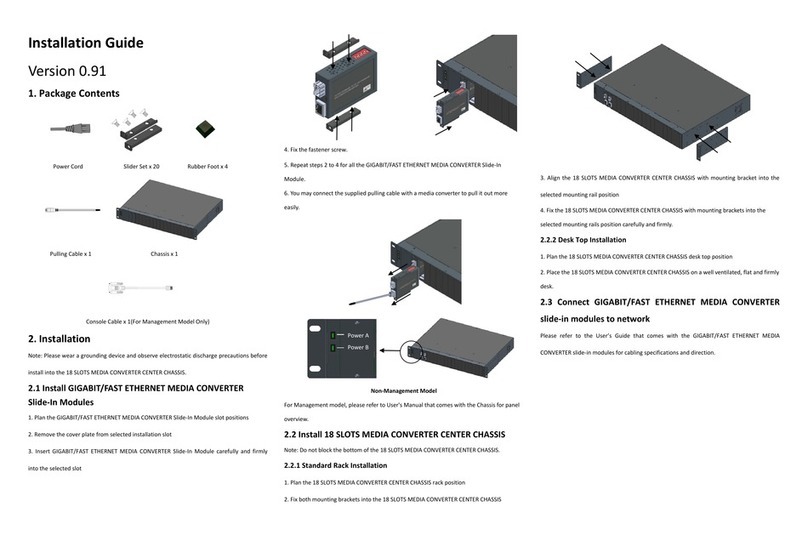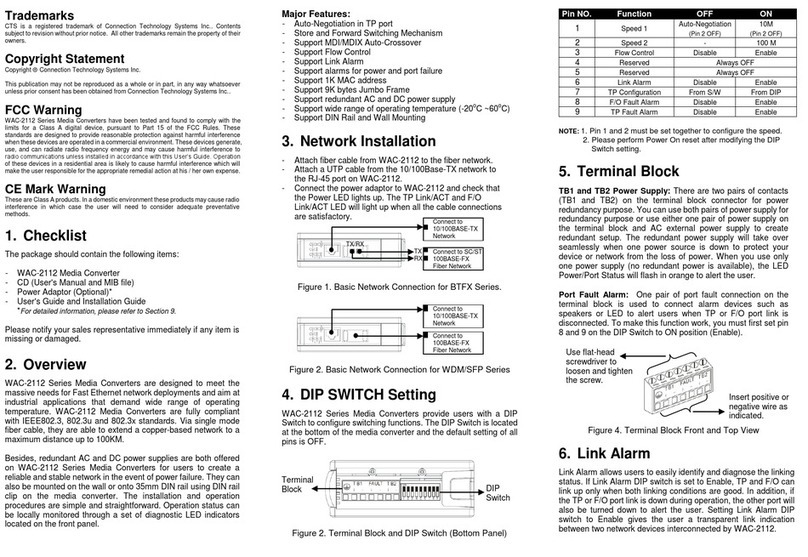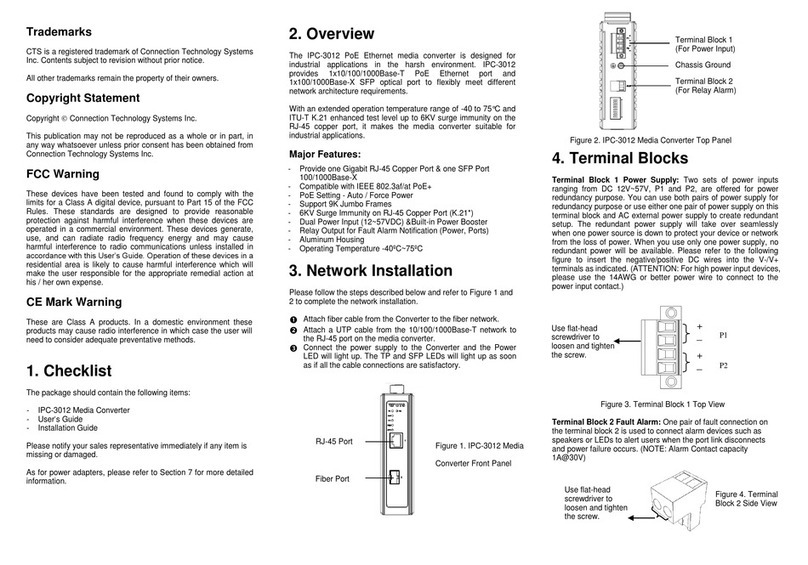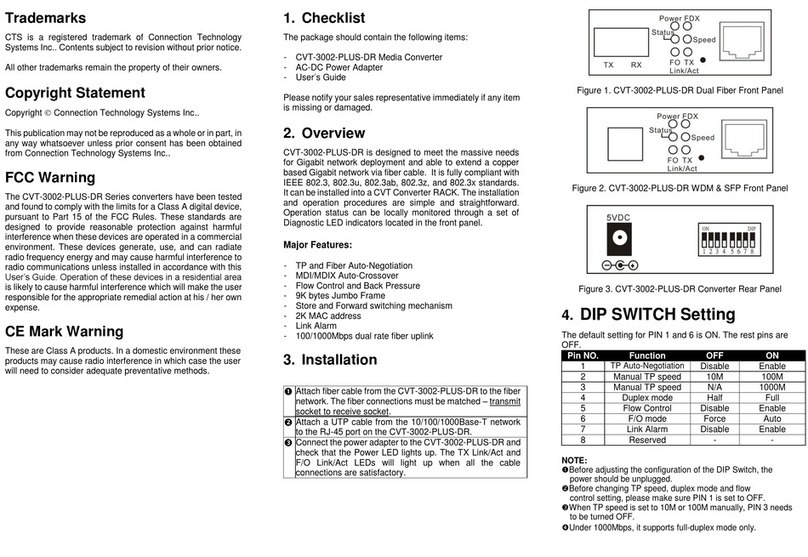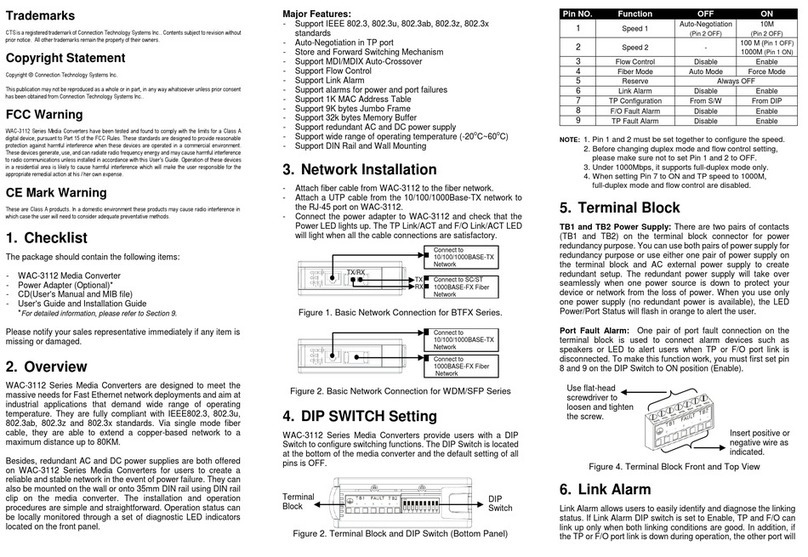
(Version 1.0)
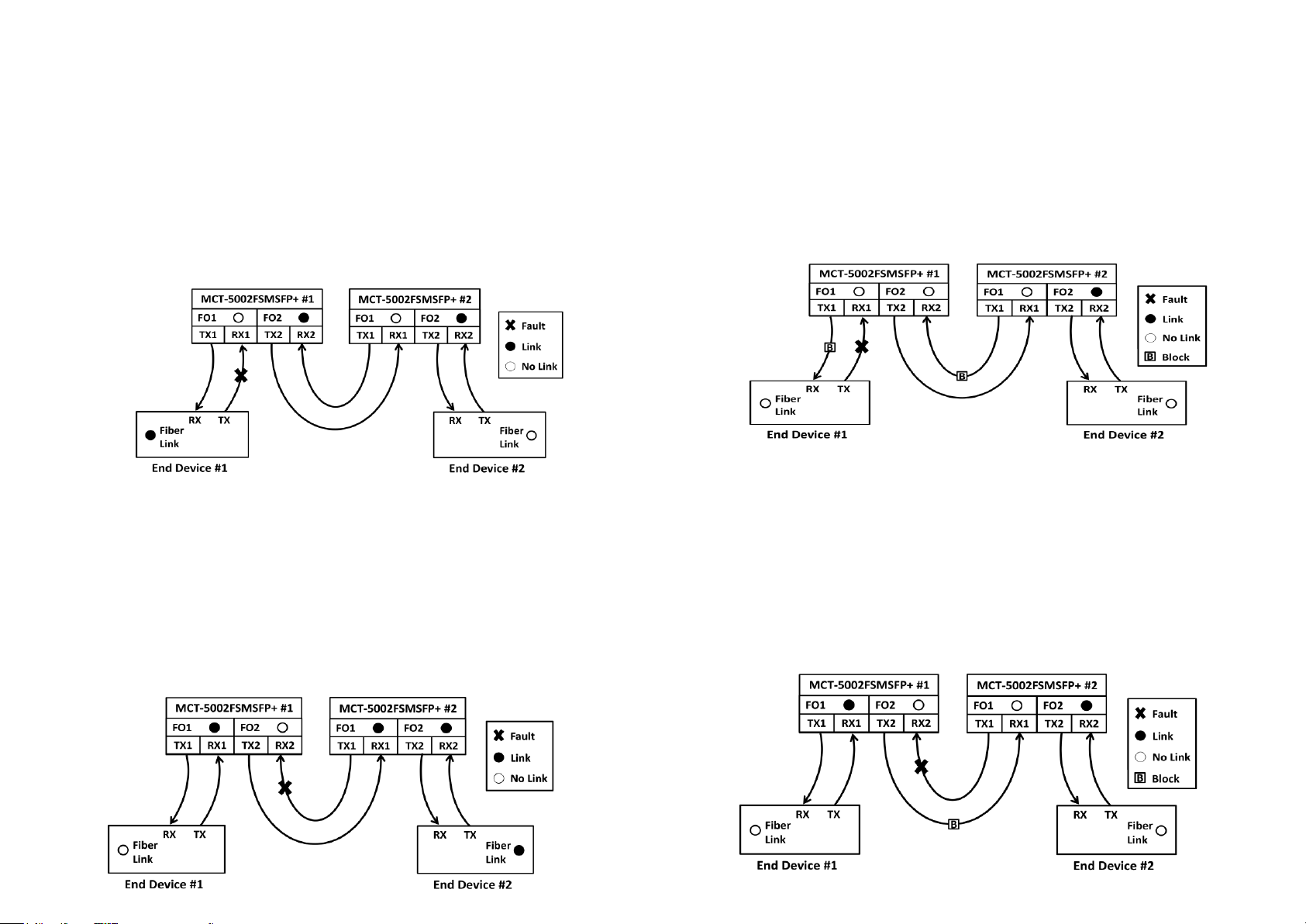
Scenario 2-1: When two sets of MCT-5002FSMSFP+ that link together connect
to one end device separately, and the link fault occurs on MCT-5002FSMSFP+
#1’s RX1 with “Disabled”Signal Loss Alarm.
In case there is a fault taken place on the fiber cable (See Fig. 2-1), the port link of FO1 on
MCT-5002FSMSFP+ #1 will be down due to the failure of receiving the optical signal. End
Device #2 will also become link-down because it cannot receive the optical signal transmitted
from FO1 fiber port of MCT-5002FSMSFP+ #1.
End Device #1 will link up due to the reason that it can continuously receive the optical signal
transmitted from FO2 fiber port of MCT-5002FSMSFP+ #2 through FO2 fiber port of
MCT-5002FSMSFP+ #1. Thus, the network administrator may be unaware of the link fault.
Actually, the total network cannot work normally.
Scenario 3-1: When two sets of MCT-5002FSMSFP+ that link together connect
to one end device separately, and the link fault occurs on MCT-5002FSMSFP+
#1’s RX2 with “Disabled”Signal Loss Alarm.
In case there is a fault taken place on the fiber cable (See Fig. 3-1), the port link of FO2on
MCT-5002FSMSFP+ #1 will be down due to the failure of receiving the optical signal. End
Device #1 will also become link-down because it cannot receive the optical signal transmitted
from FO2 fiber port of MCT-5002FSMSFP+ #1.
End Device #2 will link up due to the reason that it can continuously receive the optical signal
transmitted from FO1 fiber port of MCT-5002FSMSFP+ #1 through FO1 fiber port of
MCT-5002FSMSFP+ #2. Thus, the network administrator may be unaware of the link fault.
Actually, the total network cannot work normally.
Scenario 2-2: When two sets of MCT-5002FSMSFP+ that link together connect
to one end device separately, and the link Fault occurs on MCT-5002FSMSFP+
#1’s RX1 with “Enabled” Signal Loss Alarm.
In case there is a fault taken place on the fiber cable (See Fig. 2-2), the port link of FO1 on
MCT-5002FSMSFP+ #1 will be down due to the failure of receiving the optical signal. End
Device #2 will also become link-down because it cannot receive the optical signal transmitted
from FO1 fiber port of MCT-5002FSMSFP+ #1, and the optical signal transmitted to End
Device#1 from FO2 fiber port of MCT-5002FSMSFP+ #2 through FO2 fiber port of
MCT-5002FSMSFP+ #1 will be blocked as well. Thus, end devices at both sides will link down
to alert the network administrator to do the network troubleshooting immediately.
Scenario 3-2: When two sets of MCT-5002FSMSFP+ that link together connect
to one end device separately, and the link fault occurs on MCT-5002FSMSFP+
#1’s RX2 with “Enabled”Signal Loss Alarm.
In case there is a fault taken place on the fiber cable (See Fig. 3-2), the port link of FO2on
MCT-5002FSMSFP+ #1 will be down due to the failure of receiving the optical signal. End
Device #1 will also become link-down because it cannot receive the optical signal transmitted
from FO2 fiber port of MCT-5002FSMSFP+ #1, and the optical signal transmitted to End
Device#2 from FO1fiber port of MCT-5002FSMSFP+ #1 through FO1fiber port of
MCT-5002FSMSFP+ #2 will be blocked as well. Thus, end devices at both sides will link down
to alert the network administrator to do the network troubleshooting immediately.